Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.16 Friction- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.16 Friction- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.16 Friction- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.16 know that friction is a force that opposes motion
Friction as a Force That Opposes Motion
Friction is a force that acts between two surfaces that are in contact. It always acts in a direction that opposes motion or attempts to prevent motion from starting.
Friction is present whenever two surfaces touch and one surface moves, or tries to move, over the other.
What Is Friction?
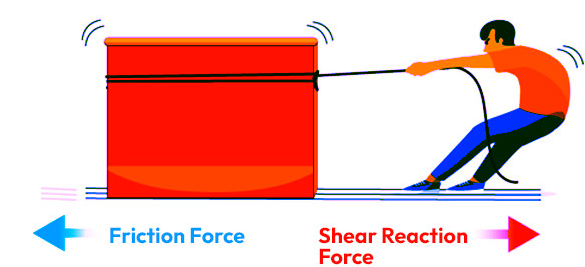
- Friction is a contact force.
- It acts parallel to the surfaces in contact.
- It always acts opposite to the direction of motion.
Direction of Friction
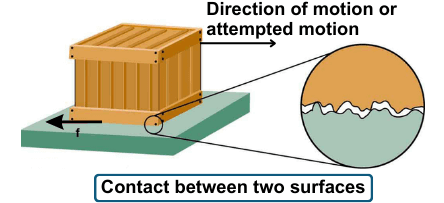
- If an object is moving, friction acts to slow it down.
- If an object is stationary, friction acts to prevent it from moving.
- Friction never acts in the same direction as motion.
Frictional Force Formula
The size of the frictional force depends on how rough the surfaces are and how hard they are pressed together.
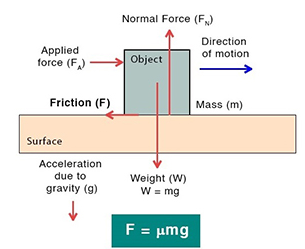
\( \mathrm{F = \mu R} \)
- \( \mathrm{F} \) = frictional force (N)
- \( \mathrm{\mu} \) = coefficient of friction (no units)
- \( \mathrm{R} \) = normal contact force (N)
A rougher surface has a larger value of \( \mathrm{\mu} \), producing more friction.
Factors Affecting Friction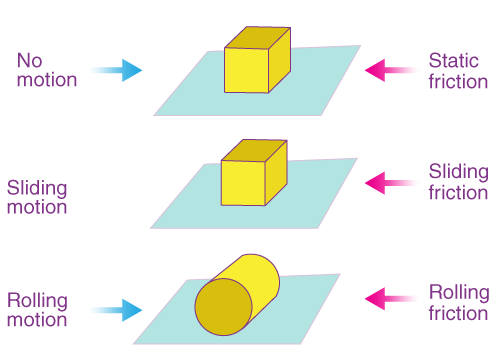
- Roughness of the surfaces in contact.
- Size of the normal contact force.
Key Idea
- Friction always opposes motion.
- It can slow down or prevent motion.
- Its size depends on surface roughness and contact force.
Important Points to Remember
- Friction is measured in newtons (N).
- It acts only when surfaces are in contact.
- Reducing friction makes movement easier.
Example
A box is pulled along a rough floor. The normal contact force on the box is \( \mathrm{20\ N} \). The coefficient of friction between the box and the floor is \( \mathrm{0.4} \). Calculate the frictional force acting on the box.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use: \( \mathrm{F = \mu R} \)
\( \mathrm{F = 0.4 \times 20} \)
\( \mathrm{F = 8\ N} \)
The frictional force acting on the box is \( \mathrm{8\ N} \), opposite to the direction of motion.
Example
A car moves along a road at constant speed. State the direction of the frictional force acting on the car.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The frictional force acts opposite to the direction of motion.
It acts backwards relative to the car’s movement.
