Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.29P Newton’s Third Law- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -Link- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -Link- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.29P demonstrate an understanding of Newton’s third law
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Newton’s Third Law of Motion describes how forces act between interacting objects. It explains that forces always occur in pairs.![]()
This law is essential for understanding motion in situations such as walking, swimming, collisions, and rocket propulsion.
Statement of Newton’s Third Law
Newton’s third law states that:
When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object simultaneously exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object.
Action–Reaction Force Pair
- Forces always come in pairs.
- The two forces are equal in magnitude.
- The two forces act in opposite directions.
- The forces act on different objects.
These pairs of forces are called action–reaction pairs.
Key Relationship
For an action–reaction pair:
\( \mathrm{F_{A\ on\ B} = -F_{B\ on\ A}} \)
This shows that the forces are equal in size but opposite in direction.
Why Objects Still Move
Although the forces are equal and opposite, they do not cancel out because:
- They act on different objects.
- Each object responds according to its own mass.
This explains why motion occurs even though forces appear balanced.
Common Examples of Newton’s Third Law
- Walking: foot pushes backward on the ground; ground pushes forward on the foot.
- Swimming: swimmer pushes water backward; water pushes swimmer forward.
- Rocket motion: gases are pushed downward; rocket is pushed upward.
- Collisions: objects exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
Key Idea
- Forces always occur in pairs.
- The forces are equal and opposite.
- The forces act on different objects.
Important Points to Remember
- Action and reaction forces never act on the same object.
- Newton’s third law pairs do not cancel each other.
- This law applies whether objects are moving or stationary.
Example
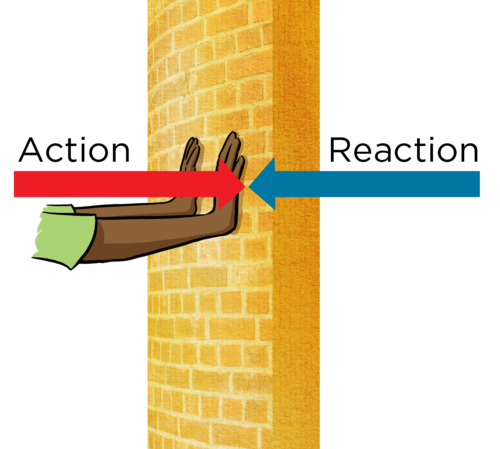
A person pushes against a wall. Identify the action–reaction force pair.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The person exerts a force on the wall.
The wall exerts an equal and opposite force on the person.
Example
A rocket expels gas downward at high speed. Explain how Newton’s third law causes the rocket to move upward.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The rocket pushes the gas downward.
The gas exerts an equal and opposite force on the rocket.
This force pushes the rocket upward.
