Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.31P Centre of Gravity- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.31P Centre of Gravity- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.31P Centre of Gravity- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.31P know that the weight of a body acts through its centre of gravity
Centre of Gravity
The centre of gravity of a body is the point through which the entire weight of the body appears to act.
For an object in a uniform gravitational field, the centre of gravity is the same as the centre of mass.
Weight and Centre of Gravity
The weight of a body always acts vertically downward through its centre of gravity.
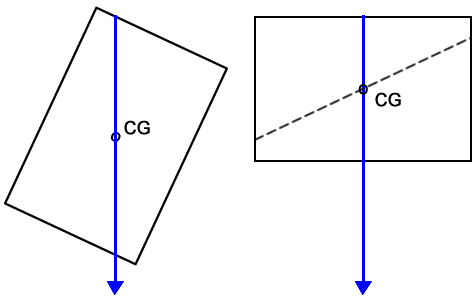
- Weight acts as a single force.
- The line of action passes through the centre of gravity.
- This applies whether the object is moving or stationary.
Key Formula
The weight of a body is given by: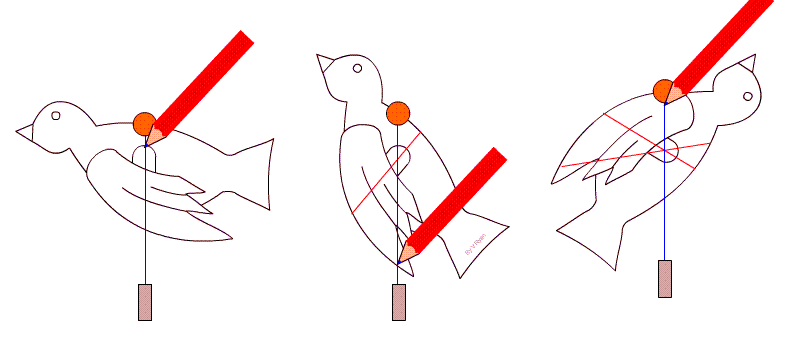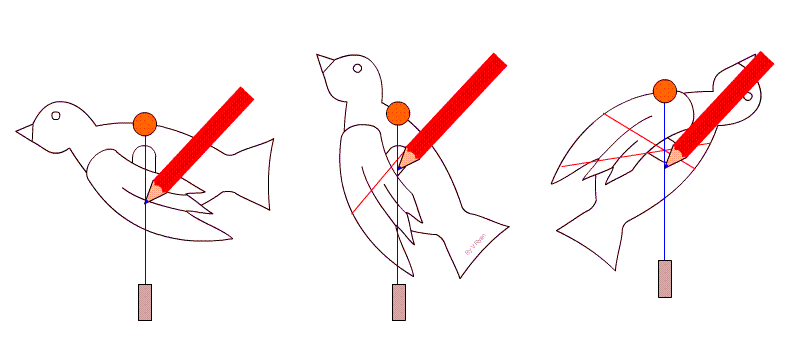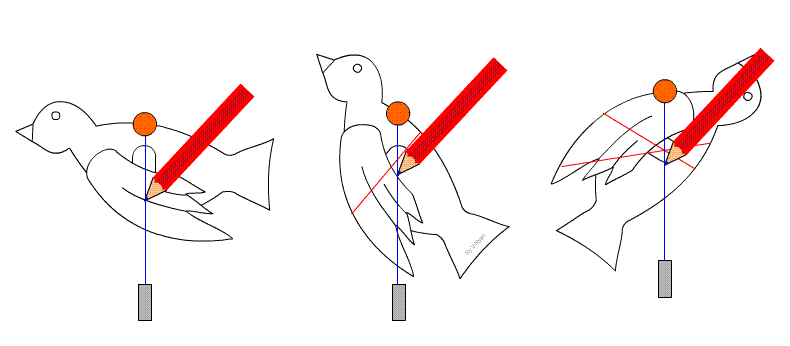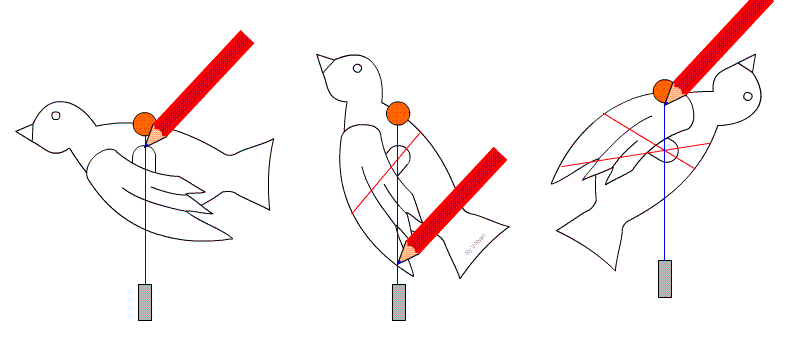
\( \mathrm{W = mg} \)
- \( \mathrm{W} \) = weight (N)
- \( \mathrm{m} \) = mass (kg)
- \( \mathrm{g} \) = gravitational field strength (N/kg)
The force \( \mathrm{W} \) acts through the centre of gravity.
Centre of Gravity in Different Objects
![]()
- For a regular, uniform object, the centre of gravity is at its geometric centre.
- For an irregular object, the centre of gravity may be outside the object.
- For objects with uneven mass distribution, the centre of gravity shifts toward the heavier part.
Centre of Gravity and Stability
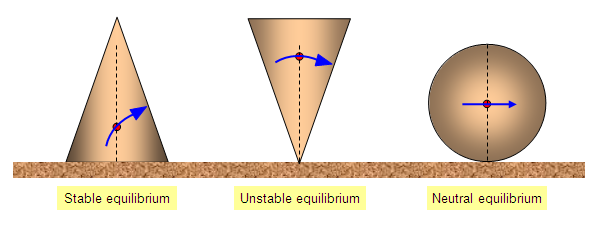
- An object is stable when the line of action of its weight passes through its base.
- If the line of action falls outside the base, the object topples.
- Lower centre of gravity increases stability.
Finding the Centre of Gravity
For a flat object:
- Suspend the object from one point.

- Draw a vertical line downwards.
- Repeat from another point.
- The intersection gives the centre of gravity.
Key Idea
- Weight acts through the centre of gravity.
- The centre of gravity determines balance and stability.
- Its position depends on shape and mass distribution.
Important Points to Remember
- Weight always acts vertically downward.
- Centre of gravity is not always inside the object.
- Stability depends on the position of the centre of gravity.
Example
A uniform rectangular block is balanced on a flat surface. Where does its weight act?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The weight acts vertically downward through the centre of gravity.
For a uniform block, this is at the geometric centre.
Example
A body has a mass of \( \mathrm{5\ kg} \). Calculate its weight and state where this force acts.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use: \( \mathrm{W = mg} \)
\( \mathrm{W = 5 \times 9.8 = 49\ N} \)
The force of \( \mathrm{49\ N} \) acts through the centre of gravity.
