Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.4 Speed, Distance and Time Relationship- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.4 Speed, Distance and Time Relationship- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -1.4 Speed, Distance and Time Relationship- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
1.4 know and use the relationship between average speed, distance moved and time taken:
average speed = distance moved / time taken
Average Speed, Distance and Time
Average speed describes how fast an object moves over a period of time. It takes into account the total distance travelled and the total time taken, regardless of whether the object’s speed changes during the motion.
Average speed is widely used in physics to describe journeys where the motion is not uniform, such as vehicles moving through traffic or athletes changing pace during a race.
Key Relationship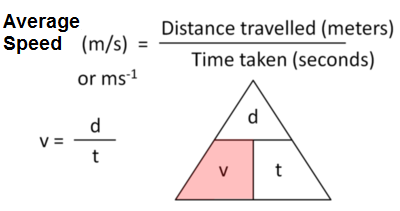
The relationship between average speed, distance moved, and time taken is:
\( \mathrm{average\ speed = \dfrac{distance\ moved}{time\ taken}} \)
This equation shows that an object will have a higher average speed if it travels a greater distance in a shorter time.
Units Used
- Distance is measured in metres (m).
- Time is measured in seconds (s).
- Average speed is measured in metres per second (m/s).
Rearranging the Equation

The equation for average speed can be rearranged depending on which quantity is required:
- Distance moved: \( \mathrm{distance = average\ speed \times time} \)
- Time taken: \( \mathrm{time = \dfrac{distance}{average\ speed}} \)
Important Points to Remember
- Average speed uses total distance, not displacement.
- The object does not need to move at a constant speed.
- Stopping during a journey increases the time taken and reduces the average speed.
- Always convert values to SI units before calculating.
Link to Graphs
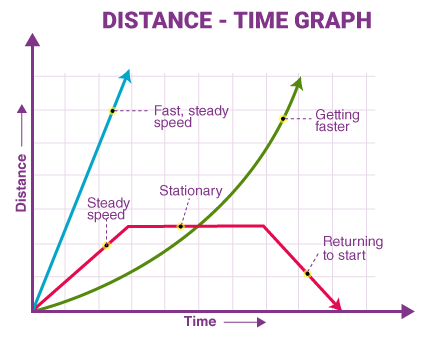
On a distance–time graph, the gradient represents speed. A steeper gradient means a higher speed, while a horizontal line means the object is at rest.
Example
A cyclist travels a distance of \( \mathrm{600\ m} \) in \( \mathrm{120\ s} \). Calculate the average speed of the cyclist.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use: \( \mathrm{average\ speed = \dfrac{distance}{time}} \)
\( \mathrm{average\ speed = \dfrac{600}{120}} \)
\( \mathrm{average\ speed = 5\ m/s} \)
Example
A car travels at an average speed of \( \mathrm{18\ m/s} \) for \( \mathrm{50\ s} \). Calculate the distance travelled by the car.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use: \( \mathrm{distance = average\ speed \times time} \)
\( \mathrm{distance = 18 \times 50} \)
\( \mathrm{distance = 900\ m} \)
