Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.2 Domestic Electrical Safety- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.2 Domestic Electrical Safety- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.2 Domestic Electrical Safety- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Electrical Safety in Domestic Appliances
Domestic electrical appliances are designed with safety features that protect both the user and the device. These features reduce the risk of electric shock, overheating, and fire.
Main Electrical Safety Features
- Insulation
- Double insulation
- Earthing
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
1. Insulation
Insulation is a layer of non-conducting material (such as plastic or rubber) that surrounds electrical wires.
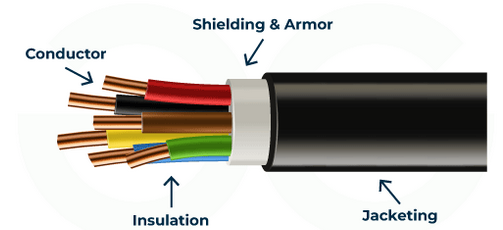
- Prevents contact with live wires.
- Reduces the risk of electric shock.
- Stops current leaking to the surroundings.
Example: Plastic coating around the live and neutral wires.
2. Double Insulation
Double insulated appliances have two layers of insulation and do not require an earth wire.
- Outer case is made of plastic.
- Even if one layer fails, the second layer provides protection.
- Often marked with the double-square symbol.
Examples include hairdryers, electric drills, and phone chargers.
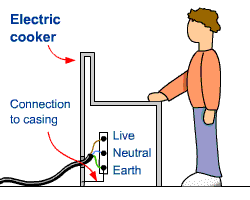
3. Earthing
Earthing connects the metal casing of an appliance directly to the ground.
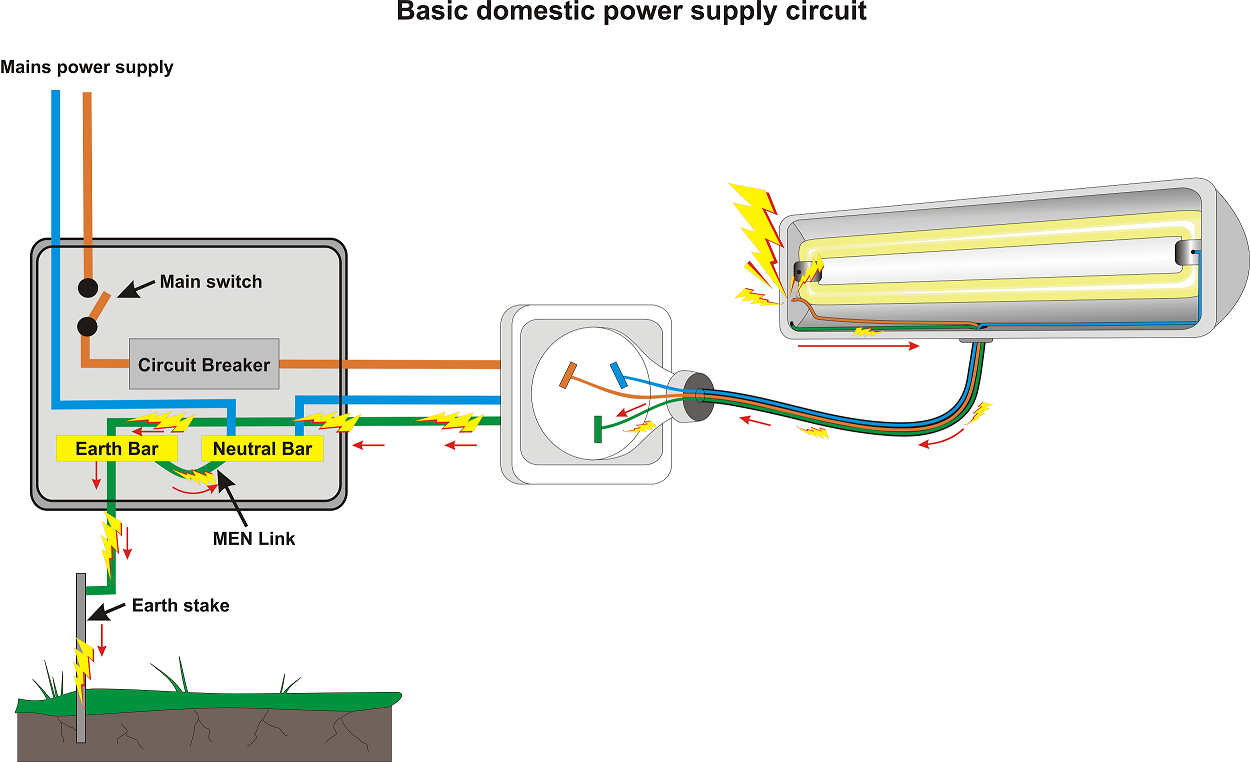
- Provides a low-resistance path for current.
- Prevents the metal case from becoming live.
- Causes a large current to flow if a fault occurs.
If a live wire touches the metal case, current flows safely to Earth instead of through the user.
4. Fuses
A fuse is a thin wire that melts when the current is too large.
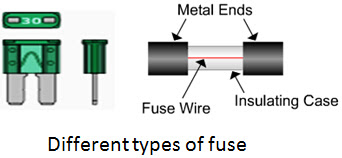
- Connected in the live wire.
- Breaks the circuit if current exceeds a safe value.
- Protects appliances from overheating and fire.
Choosing a Fuse Rating
The operating current of an appliance is calculated using:
\( \mathrm{P = VI} \)
\( \mathrm{I = \dfrac{P}{V}} \)
5. Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers automatically switch off the circuit when a fault is detected.
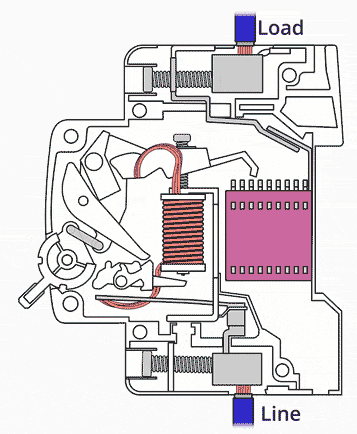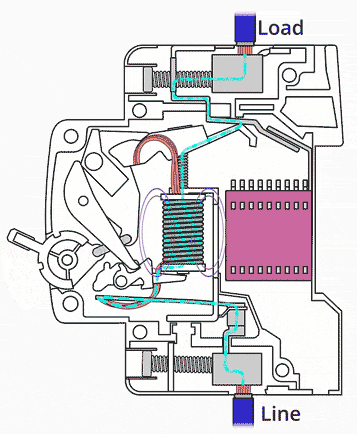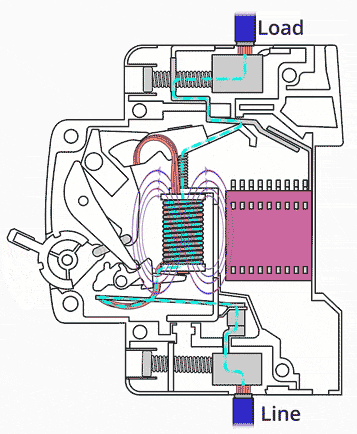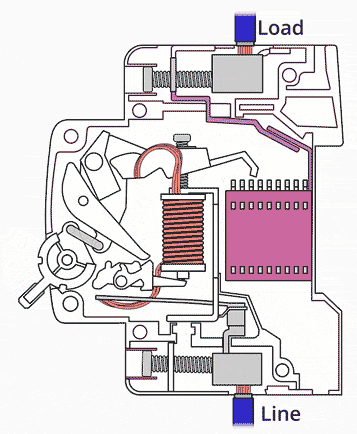
- React faster than fuses.
- Can be reset after tripping.
- Protect against short circuits and overloads.
They are commonly used in modern consumer units.
How These Features Protect Users
- Insulation prevents contact with live parts.
- Double insulation removes the need for earthing.
- Earthing directs fault current safely to the ground.
- Fuses and circuit breakers stop excessive currents.
Key Idea
- Electrical safety reduces shock and fire risk.
- Different features work together.
- Faults must be removed quickly and safely.
Important Points to Remember
- Metal-cased appliances must be earthed.
- Double insulated appliances do not need an earth wire.
- Fuses protect appliances, not people directly.
Example
Explain how earthing protects a user if a live wire touches the metal case of a washing machine.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The earth wire provides a low-resistance path to the ground.
A large current flows, causing the fuse to melt or the circuit breaker to trip.
The metal case does not remain live, preventing electric shock.
Example
An electric kettle has a power rating of \( \mathrm{2200\ W} \) and operates at \( \mathrm{230\ V} \). Calculate the current and state a suitable fuse rating.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use: \( \mathrm{I = \dfrac{P}{V}} \)
\( \mathrm{I = \dfrac{2200}{230}} \)
\( \mathrm{I \approx 9.6\ A} \)
A suitable fuse rating is \( \mathrm{13\ A} \).
