Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.24P Positive and Negative Charge- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.24P Positive and Negative Charge- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.24P Positive and Negative Charge- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.24P explain how positive and negative electrostatic charges are produced on materials by the loss and gain of electrons
Production of Positive and Negative Electrostatic Charges
Electrostatic charges are produced when electrons are transferred between materials. This usually happens when materials are rubbed together, but can also occur by contact or induction.
Only electrons move during charging. Protons remain fixed inside atoms.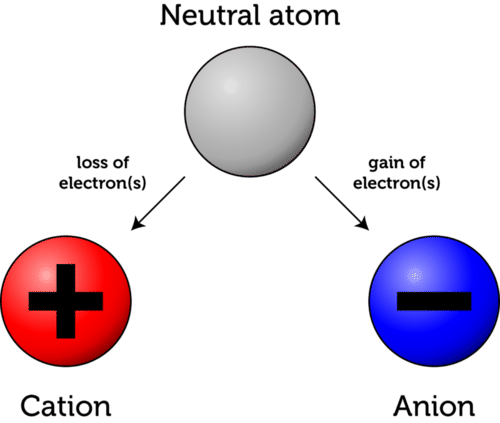
Key Idea
- Electrons have a negative charge.
- Protons have a positive charge and do not move.
- Charging occurs due to loss or gain of electrons.
How Negative Charge Is Produced
A material becomes negatively charged when it gains electrons.
- Electrons are transferred onto the material.
- There are more electrons than protons.
- The overall charge becomes negative.
Example: A plastic rod rubbed with wool gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
How Positive Charge Is Produced
A material becomes positively charged when it loses electrons.
- Electrons are transferred away from the material.
- There are fewer electrons than protons.
- The overall charge becomes positive.
Example: The wool that loses electrons becomes positively charged.
Charging by Friction
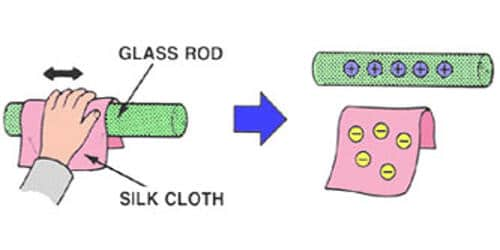
- Two insulating materials are rubbed together.
- Electrons move from one material to the other.
- Both objects become charged.
- The charges are equal in size and opposite in sign.
This follows the principle of conservation of charge.
Why Only Electrons Move
- Electrons are much smaller and lighter than protons.
- Protons are fixed in the atomic nucleus.
- Electrons can be transferred between atoms.
Link to Charge Formula
Electric charge is measured in coulombs:
\( \mathrm{Q = I \times t} \)
- In electrostatics, charge builds up without a continuous current.
- Charge is transferred, not created.
Key Idea
- Gaining electrons → negative charge.
- Losing electrons → positive charge.
- Total charge is conserved.
Important Points to Remember
- Objects do not gain or lose protons.
- Electrons move between materials.
- Static charges remain on insulators.
Example
A balloon is rubbed on dry hair. Explain why the balloon becomes negatively charged.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Electrons are transferred from the hair to the balloon.
The balloon gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
Example
Explain why an object that loses electrons becomes positively charged.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Losing electrons leaves more protons than electrons.
This gives the object an overall positive charge.
