Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.25P Forces Between Electric Charges- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.25P Forces Between Electric Charges- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.25P Forces Between Electric Charges- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.25P know that there are forces of attraction between unlike charges and forces of repulsion between like charges
Forces Between Electrostatic Charges
Electrically charged objects exert electrostatic forces on each other. These forces act at a distance and can cause objects to attract or repel without touching.
Basic Rules of Electrostatic Forces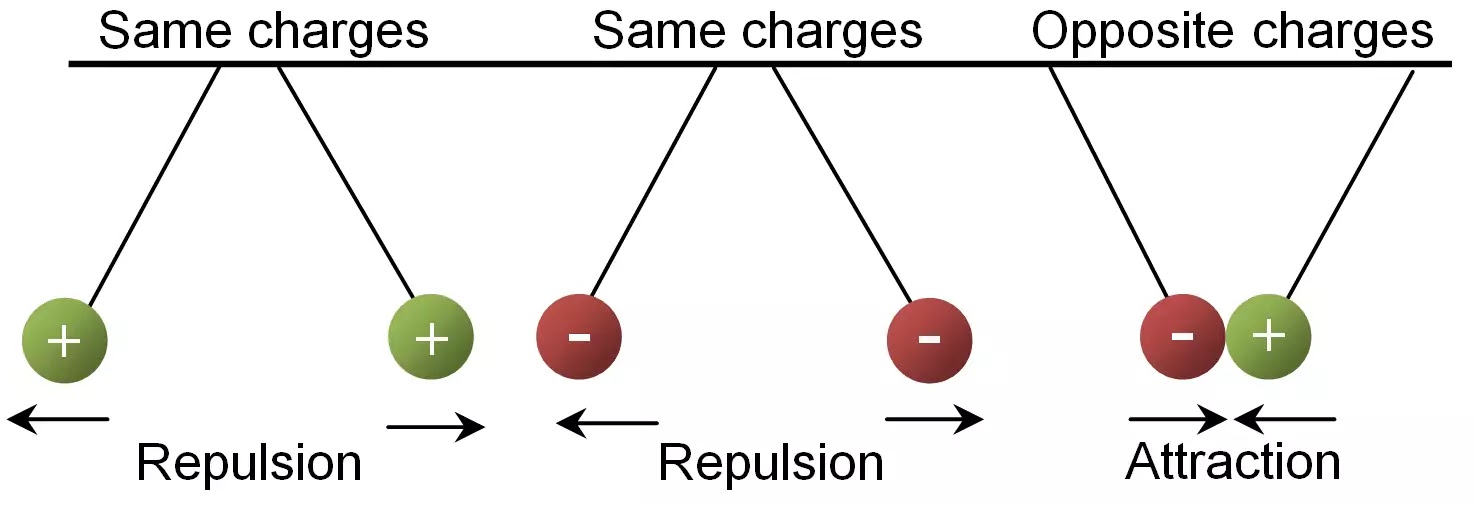
- Like charges repel each other.
- Unlike charges attract each other.
This applies to all charged objects, whether the charges are produced by friction, contact, or induction.
Like Charges (Repulsion)
When two objects have the same type of charge:
- Both positive (+ and +) or both negative (− and −).
- The objects push away from each other.
- This is called repulsion.
Example: Two negatively charged balloons move apart when brought close together.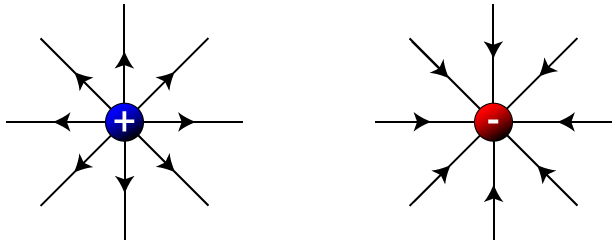
Unlike Charges (Attraction)
When two objects have different types of charge:
- One positive and one negative.
- The objects pull towards each other.
- This is called attraction.
Example: A positively charged rod attracts a negatively charged pith ball.
Why These Forces Occur
- Electric charges produce electric fields.
- Charges interact through these fields.
- The interaction causes attraction or repulsion.
Strength of Electrostatic Force
Qualitatively:
- Greater charge → stronger force.
- Greater separation → weaker force.
Relevant Relationship (for understanding)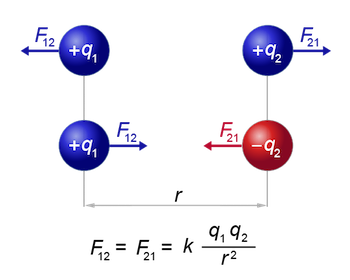
\( \mathrm{F \propto \dfrac{Q_1 Q_2}{r^2}} \)
- \( \mathrm{F} \) = electrostatic force
- \( \mathrm{Q_1, Q_2} \) = charges
- \( \mathrm{r} \) = distance between charges
(You are not required to calculate using this at IGCSE, but it explains the behaviour.)
Practical Evidence
- Charged balloons repelling each other.
- Pith balls moving apart or together.
- Hair standing up near a charged object.
Key Idea
- Like charges repel.
- Unlike charges attract.
- Electrostatic forces act without contact.
Important Points to Remember
- Forces act in pairs.
- Both objects experience the force.
- Charge is conserved.
Example
Two objects are both negatively charged. Describe the force between them.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The objects will repel each other.
This is because like charges repel.
Example
A positively charged rod is brought near a negatively charged object. State and explain what happens.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The objects attract each other.
This is because unlike charges attract.
