Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.6 Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.6 Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -2.6 Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
2.6 know the difference between mains electricity being alternating current (a.c.) and direct current (d.c.) being supplied by a cell or battery
Alternating Current (a.c.) and Direct Current (d.c.)
Electric current can flow in two different ways depending on the power supply. These are alternating current (a.c.) and direct current (d.c.).
Understanding the difference is important for recognising how electrical devices operate and how electricity is supplied in homes.
Direct Current (d.c.)
Direct current is a current that flows in one direction only.
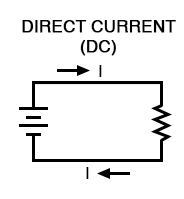
- Supplied by cells and batteries.
- The direction of current is constant.
- The size of the current may be constant or change slightly.
Examples of d.c. supplies include torches, mobile phones, and remote controls.
Alternating Current (a.c.)
Alternating current is a current that continually changes direction.
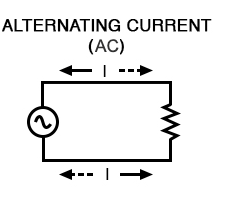
- Supplied by mains electricity.
- The current reverses direction many times each second.
- The size of the current also changes continuously.
In the UK, mains electricity has a frequency of \( \mathrm{50\ Hz} \).
Key Differences Between a.c. and d.c.
- d.c. flows in one direction; a.c. changes direction.
- d.c. is supplied by cells or batteries.
- a.c. is supplied by mains electricity.
- a.c. is suitable for long-distance transmission.
Current–Time Graphs
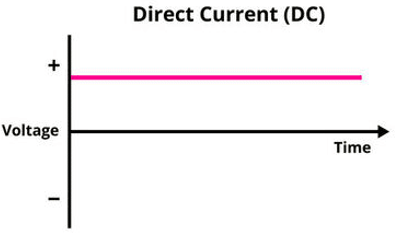
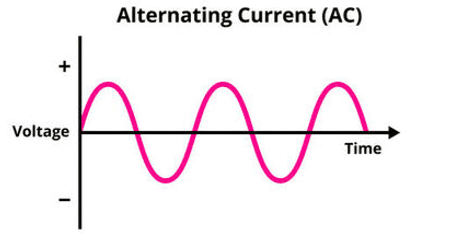
- d.c.: straight horizontal line (constant direction).
- a.c.: wave-like curve alternating above and below zero.
These graphs visually show how current behaves over time.
Why Mains Electricity Uses a.c.
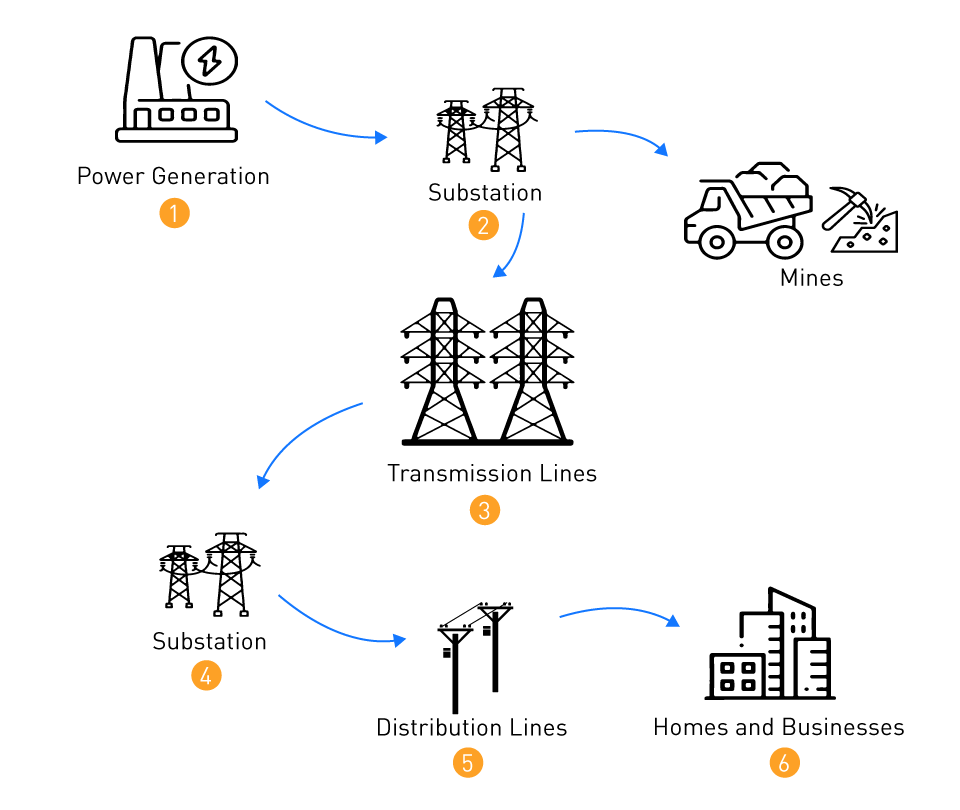
- a.c. voltage can be easily increased or decreased using transformers.
- High voltage reduces energy loss during transmission.
- This makes a.c. efficient for supplying electricity to homes.
Key Idea
- d.c. flows in one direction only.
- a.c. changes direction regularly.
- Different power sources supply different types of current.
Important Points to Remember
- Batteries supply d.c.
- Mains electricity is a.c.
- Many electronic devices convert a.c. to d.c. internally.
Example
State one difference between alternating current and direct current.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Direct current flows in one direction only, whereas alternating current changes direction.
Example
A mobile phone charger is plugged into the mains. Explain why the charger must convert a.c. to d.c.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Mains electricity is a.c., but the phone battery requires d.c.
The charger converts a.c. to d.c. to safely charge the battery.
