Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.10–3.11 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Its Order- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.10–3.11 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Its Order- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.10–3.11 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Its Order- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Light is part of a larger group of waves called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of electromagnetic waves with different wavelengths and frequencies.
All electromagnetic waves transfer energy and information and can travel through a vacuum.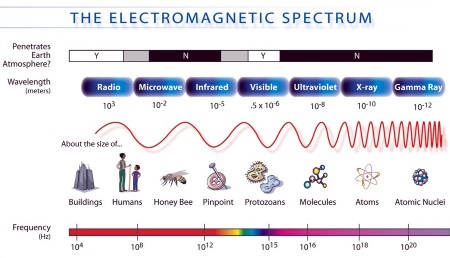
Key Idea
- Light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- All electromagnetic waves are transverse.
- All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in free space.
Speed of Electromagnetic Waves
In free space (vacuum), all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed:
\( \mathrm{c = 3.0 \times 10^8\ m/s} \)
- This speed is called the speed of light.
- It applies to radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum (in order of increasing frequency)
| Region | Typical Wavelength | Frequency | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio waves | > 1 m | Lowest | Broadcasting, communication |
| Microwaves | 1 m – 1 mm | Low | Cooking, satellites |
| Infrared | 1 mm – 700 nm | Low–medium | Heaters, thermal imaging |
| Visible light | 700 nm – 400 nm | Medium | Vision, photography |
| Ultraviolet | 400 nm – 10 nm | High | Sterilisation, fluorescent lamps |
| X-rays | 10 nm – 0.01 nm | Very high | Medical imaging |
| Gamma rays | < 0.01 nm | Highest | Cancer treatment, sterilisation |
Continuous Nature of the Spectrum
- There are no sharp boundaries between regions.

- Frequency and wavelength change gradually.
- Visible light is only a small part of the full spectrum.
Wave Relationship Used
All electromagnetic waves obey the wave equation:
\( \mathrm{c = f\lambda} \)
- \( \mathrm{c} \) = speed of light in free space (m/s)
- \( \mathrm{f} \) = frequency (Hz)
- \( \mathrm{\lambda} \) = wavelength (m)
If frequency increases, wavelength decreases.
Key Idea
- All EM waves travel at the same speed in vacuum.
- They differ only in frequency and wavelength.
- Light is one region of the EM spectrum.
Important Points to Remember
- EM waves do not require a medium.
- Higher frequency → higher energy.
- Correct order of the spectrum is essential for exams.
Example
State two similarities between radio waves and visible light.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Both are electromagnetic waves.
Both travel at the same speed in free space.
Example
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of \( \mathrm{6.0 \times 10^{14}\ Hz} \).
(a) Calculate its wavelength. (b) Identify the region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) Use \( \mathrm{c = f\lambda} \):
\( \mathrm{\lambda = \dfrac{3.0 \times 10^8}{6.0 \times 10^{14}}} \)
\( \mathrm{\lambda = 5.0 \times 10^{-7}\ m} \)
(b) This wavelength is in the visible light region.
Order of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is a continuous range of electromagnetic waves arranged according to their wavelength or frequency.
As wavelength decreases, frequency increases. All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in free space.
Key Relationship
The relationship between wave speed, frequency and wavelength is:
\( \mathrm{c = f\lambda} \)
- \( \mathrm{c} \) = speed of light in free space \( (3.0 \times 10^8\ m/s) \)
- \( \mathrm{f} \) = frequency (Hz)
- \( \mathrm{\lambda} \) = wavelength (m)
This shows that if frequency increases, wavelength must decrease.
Order of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
In order of decreasing wavelength and increasing frequency: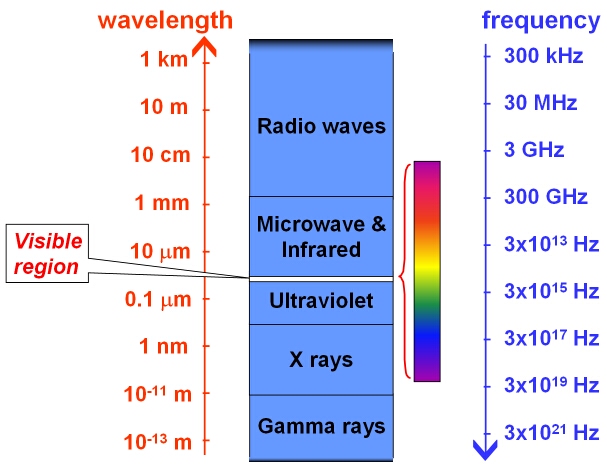
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
Memory aid: Raging Martians Invaded Venus Using X-ray Guns
Visible Light Spectrum
Visible light is the small part of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can detect.
Order of colours in visible light (decreasing wavelength):
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
Memory aid: ROYGBIV
Wavelength and Frequency Across Visible Light
- Red light → longest wavelength, lowest frequency.
- Violet light → shortest wavelength, highest frequency.
Key Idea
- Electromagnetic waves are ordered by wavelength or frequency.
- Wavelength decreases from radio waves to gamma rays.
- Frequency increases from radio waves to gamma rays.
Important Points to Remember
- All EM waves travel at the same speed in free space.
- Only wavelength and frequency change across the spectrum.
- Visible light is a very small part of the spectrum.
Example
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of increasing frequency:
Infrared, gamma rays, radio waves, visible light.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Radio waves → Infrared → Visible light → Gamma rays
Frequency increases in this order.
Example
(a) State the colour of visible light with the highest frequency. (b) State the colour with the longest wavelength.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) Violet has the highest frequency.
(b) Red has the longest wavelength.
