Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.12 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.12 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.12 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.12 explain some of the uses of electromagnetic radiations, including:
• radio waves: broadcasting and communications
• microwaves: cooking and satellite transmissions
• infrared: heaters and night vision equipment
• visible light: optical fibres and photography
• ultraviolet: fluorescent lamps
• X-rays: observing the internal structure of objects and materials, including for medical applications
• gamma rays: sterilising food and medical equipment
Uses of Electromagnetic Radiations
Electromagnetic (EM) radiations are used widely in everyday life, medicine, industry, and communication. Each region of the electromagnetic spectrum has different wavelengths, frequencies, and energies, making them suitable for specific applications.
Key Wave Relationship
All electromagnetic waves obey:
\( \mathrm{c = f\lambda} \)
- All EM waves travel at the same speed in free space.
- Higher frequency → higher energy.
- Shorter wavelength → greater penetration.
Radio Waves
Uses: Broadcasting and communications
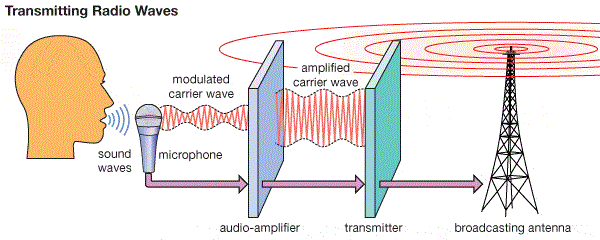
- Used for radio and television broadcasting.
- Used in mobile phone and long-distance communication.
- Long wavelengths allow radio waves to diffract around buildings and hills.
- Low energy makes them safe for everyday use.
Why suitable: Long wavelength and low frequency allow large-scale transmission over long distances.
Microwaves
Uses: Cooking and satellite transmissions
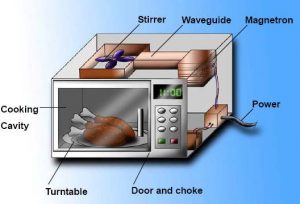
- Used in microwave ovens to heat food.
- Used for satellite communication and GPS.
- Pass easily through the atmosphere.
Why suitable:
- Absorbed by water molecules in food.
- Cause molecules to vibrate, producing heat.
- Shorter wavelength allows focused transmission to satellites.
Infrared Radiation
Uses: Heaters and night vision equipment

- Emitted by all warm objects.
- Used in infrared heaters.
- Used in night vision cameras and thermal imaging.
Why suitable:
- Transfers thermal energy efficiently.
- Can detect temperature differences in darkness.
Visible Light
Uses: Optical fibres and photography
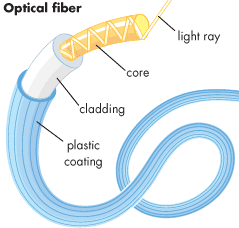
- Used in cameras and photography to form images.
- Used in optical fibres to transmit data.
- Can be focused using lenses.
Why suitable:
- Undergoes total internal reflection in optical fibres.
- Allows high-speed data transmission.
Ultraviolet Radiation
Uses: Fluorescent lamps
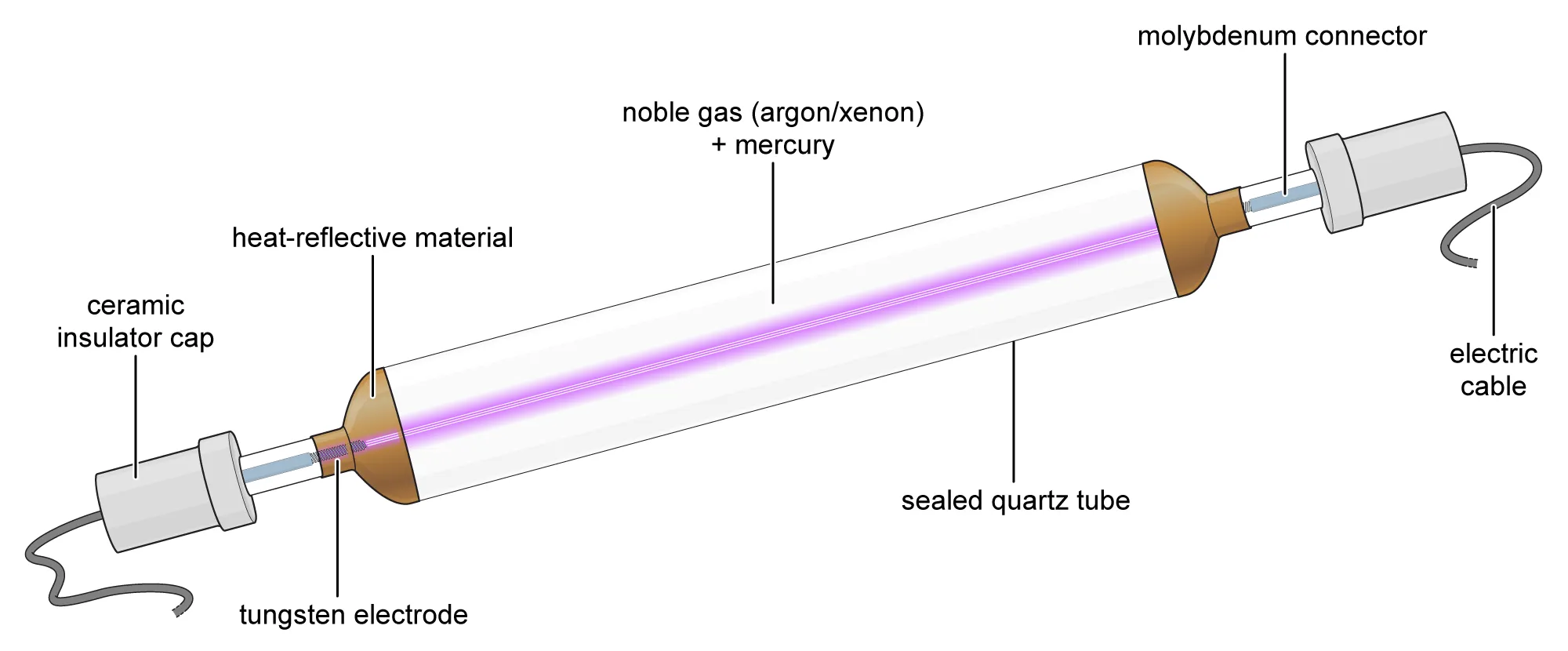
- Produced inside fluorescent lamps.
- Causes phosphor coatings to fluoresce and emit visible light.
- Has higher energy than visible light.
Why suitable: Can cause fluorescence, converting invisible UV into visible light.
X-Rays
Uses: Observing internal structures (medical and industrial)

- Used to image bones and teeth.
- Used to detect cracks in metal structures.
- Pass through soft tissue but are absorbed by dense materials.
Why suitable:
- High penetration power.
- Create clear contrast between materials of different density.
Gamma Rays
Uses: Sterilising food and medical equipment
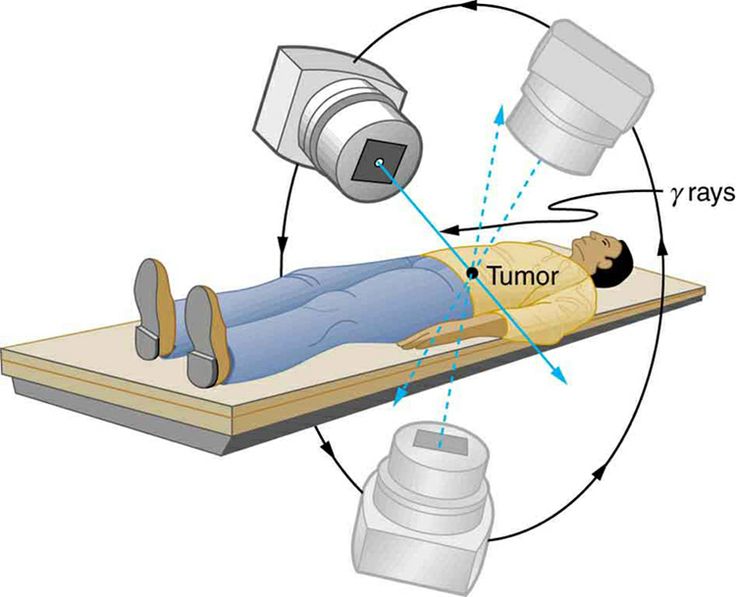
- Kill bacteria and microorganisms.
- Used to sterilise surgical instruments.
- Used in cancer treatment (radiotherapy).
Why suitable:
- Very high energy.
- Can destroy living cells.
Key Idea
- Different EM waves are used for different purposes.
- Uses depend on wavelength, frequency, and energy.
- Higher frequency waves are more penetrating and more dangerous.
Important Points to Remember
- All EM waves travel at the same speed in vacuum.
- Only wavelength and frequency change across the spectrum.
- Some EM waves require safety precautions.
Example
Explain why microwaves are suitable for cooking food.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Microwaves are absorbed by water molecules in food.
This causes the molecules to vibrate, increasing thermal energy and heating the food.
Example
X-rays are used in hospitals to image bones but not soft tissue.
Explain why X-rays are suitable for this use.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
X-rays pass through soft tissue but are absorbed by dense materials such as bone.
This creates a clear contrast on the image, allowing bones to be seen.
