Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.18 Refractive Index- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.18 Refractive Index- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.18 Refractive Index- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Refractive Index and Snell’s Law
When light travels from one medium to another, it changes speed and direction. This bending of light is called refraction. The amount by which light bends depends on the refractive index of the medium and the angles involved.
Refractive Index
The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much light slows down in that material.
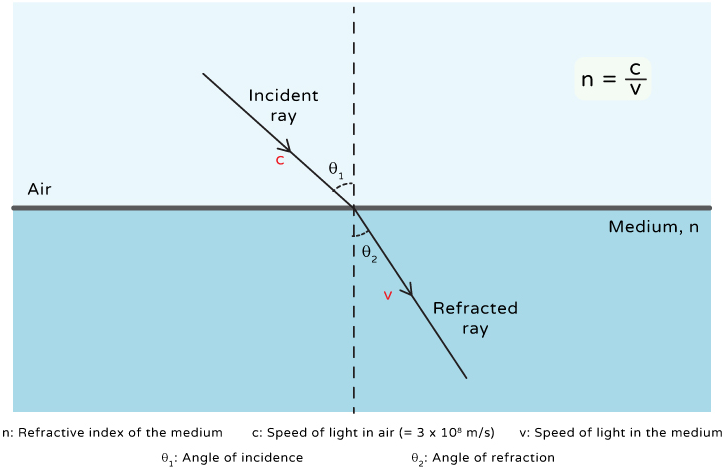
- It compares the speed of light in air (or vacuum) to its speed in the material.
- A higher refractive index means light travels more slowly.
- Refractive index has no unit.
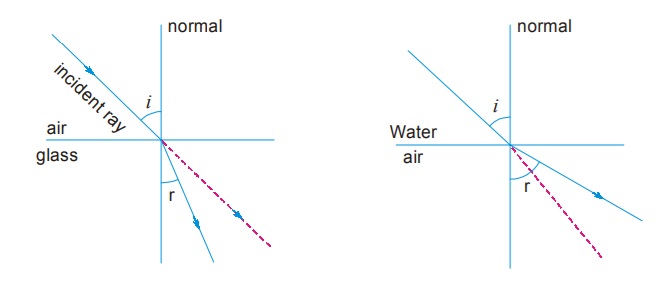
Angles in Refraction
- Angle of incidence (\( \mathrm{i} \)): the angle between the incident ray and the normal.
- Angle of refraction (\( \mathrm{r} \)): the angle between the refracted ray and the normal.
- Angles are always measured from the normal, not the surface.
Snell’s Law (Refractive Index Formula)
The relationship between refractive index, angle of incidence, and angle of refraction is:
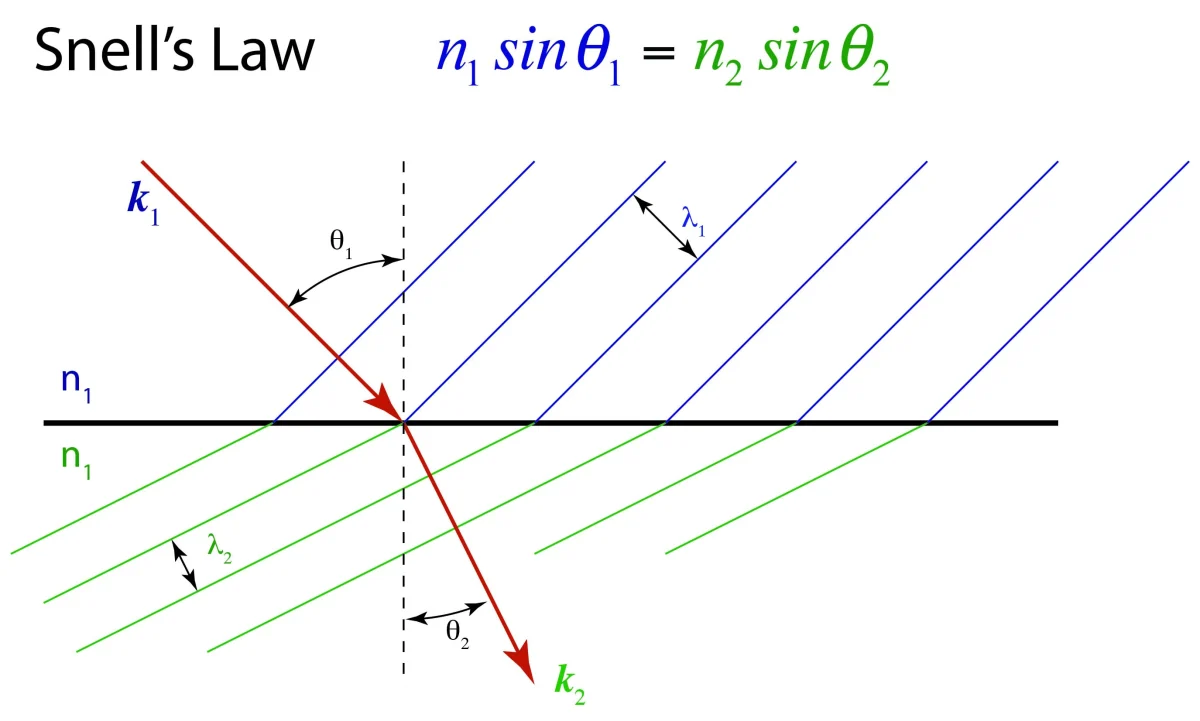
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}} \)
- \( \mathrm{n} \) = refractive index of the material
- \( \mathrm{i} \) = angle of incidence (°)
- \( \mathrm{r} \) = angle of refraction (°)
This formula applies when light travels from air into another medium.
Understanding the Relationship
- If \( \mathrm{n} \) is large, the refracted ray bends more towards the normal.
- A smaller angle of refraction means a higher refractive index.
- If there is no change in speed, there is no refraction.
Link to Wave Speed
Refractive index is also related to wave speed:
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{c}{v}} \)
- \( \mathrm{c} \) = speed of light in vacuum
- \( \mathrm{v} \) = speed of light in the medium
Higher refractive index → lower speed of light.
Key Idea
- Refractive index tells how much light bends.
- Snell’s law links angles to refractive index.
- Angles must always be measured from the normal.
Important Points to Remember
- Use degrees (°) for angles.
- Use sine values, not angles themselves.
- Refractive index has no units.
Example
A ray of light travels from air into glass.
The angle of incidence is \( \mathrm{40^\circ} \) and the angle of refraction is \( \mathrm{25^\circ} \).
Calculate the refractive index of the glass.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use Snell’s law:
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}} \)
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{\sin 40^\circ}{\sin 25^\circ}} \)
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{0.643}{0.423}} \)
\( \mathrm{n \approx 1.52} \)
Example
The refractive index of a block of glass is \( \mathrm{1.50} \).
If the angle of incidence is \( \mathrm{30^\circ} \), calculate the angle of refraction.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use Snell’s law:
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}} \)
Rearrange:
\( \mathrm{\sin r = \dfrac{\sin i}{n}} \)
\( \mathrm{\sin r = \dfrac{\sin 30^\circ}{1.50} = \dfrac{0.5}{1.5}} \)
\( \mathrm{\sin r = 0.333} \)
\( \mathrm{r \approx 19.5^\circ} \)
