Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.19 Core Practical: Refractive Index of Glass- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.19 Core Practical: Refractive Index of Glass- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.19 Core Practical: Refractive Index of Glass- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Practical: Investigating the Refractive Index of Glass
The refractive index of a material describes how much light slows down when it enters that material. In this experiment, a glass block is used to measure angles of incidence and refraction so that the refractive index of glass can be calculated.
Aim
To determine the refractive index of glass by measuring the angles of incidence and refraction of light passing through a glass block.
Apparatus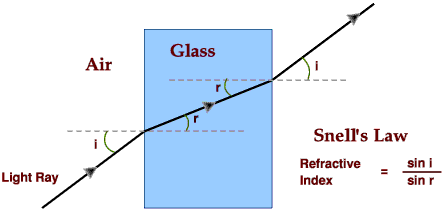
- Rectangular glass block
- Ray box with narrow slit (or laser)
- White paper
- Ruler
- Protractor
- Pencil
Theory / Formula
The refractive index of glass (relative to air) is given by Snell’s law:
\( \mathrm{n = \dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}} \)
- \( \mathrm{n} \) = refractive index of glass
- \( \mathrm{i} \) = angle of incidence (°)
- \( \mathrm{r} \) = angle of refraction (°)
Method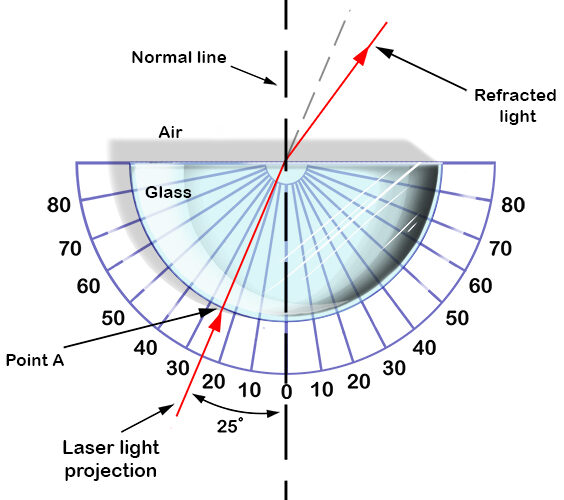
- Place the glass block on white paper and trace around it.
- Remove the block and draw a normal to one face.
- Replace the glass block exactly on its outline.
- Shine a narrow ray of light into the block at an angle.
- Mark the incident ray and the refracted ray.
- Remove the block and draw the full ray paths.
- Measure the angle of incidence and angle of refraction using a protractor.
- Repeat for at least three different angles of incidence.
Results Table (Sample)
| Angle of incidence, i (°) | Angle of refraction, r (°) | sin i | sin r | Refractive index, n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 19 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 1.52 |
An average value of refractive index is calculated from repeated readings.
Conclusion
- Light bends towards the normal when entering glass from air.
- The refractive index of glass is approximately 1.5.
- The value is consistent for different angles of incidence.
Sources of Error
- Thickness of pencil lines.
- Difficulty aligning the ray exactly.
- Inaccurate protractor readings.
Improvements
- Use a laser for a thinner ray.
- Repeat measurements and calculate an average.
- Ensure the glass block does not move during the experiment.
Safety Precautions
- Do not look directly into the ray box or laser.
- Handle the glass block carefully.
Key Idea
- Refraction occurs because light changes speed.
- Refractive index measures how much light slows down.
- Snell’s law links angles to refractive index.
Example
Why should the experiment be repeated for several different angles of incidence?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Repeating the experiment reduces random error.
It allows an average refractive index to be calculated for greater accuracy.
Example
Explain why the refracted ray bends towards the normal when light enters glass from air.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Light slows down when it enters glass.
This decrease in speed causes the ray to bend towards the normal.
