Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Waves transfer energy from one place to another without transferring matter. There are two main types of waves studied at IGCSE level: transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
Transverse Waves
A transverse wave is a wave in which the vibrations of the particles are perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
- Particles move up and down.
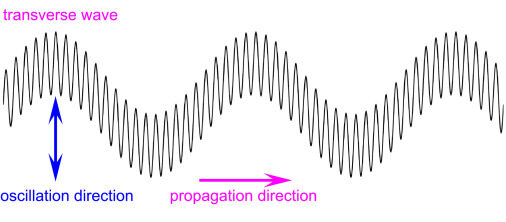
- Wave travels sideways.
- Has crests and troughs.
Examples of transverse waves:
- Water waves
- Light waves (electromagnetic waves)
- Waves on a string
Longitudinal Waves
A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the vibrations of the particles are parallel to the direction of wave travel.
- Particles vibrate back and forth.
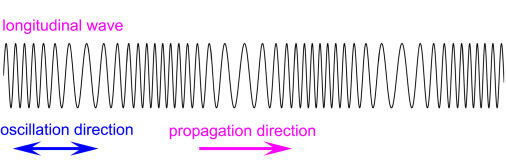
- Wave travels in the same direction.
- Has compressions and rarefactions.
Examples of longitudinal waves:
- Sound waves
- Seismic P-waves
Key Wave Relationship (Applies to Both)
\( \mathrm{wave\ speed = frequency \times wavelength} \)
\( \mathrm{v = f\lambda} \)
- \( \mathrm{v} \) = wave speed (m/s)
- \( \mathrm{f} \) = frequency (Hz)
- \( \mathrm{\lambda} \) = wavelength (m)
Difference Between Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
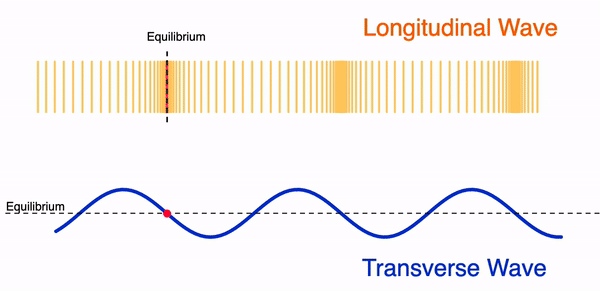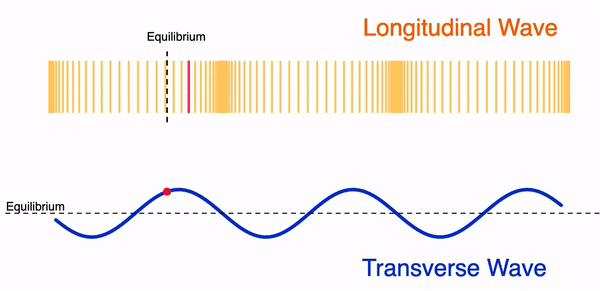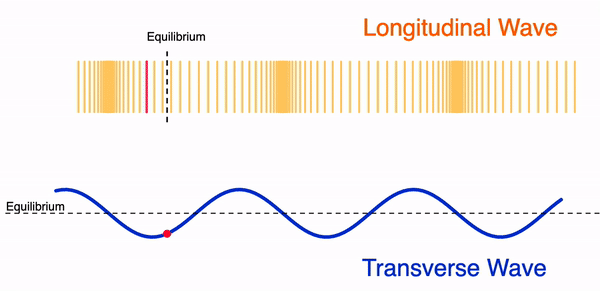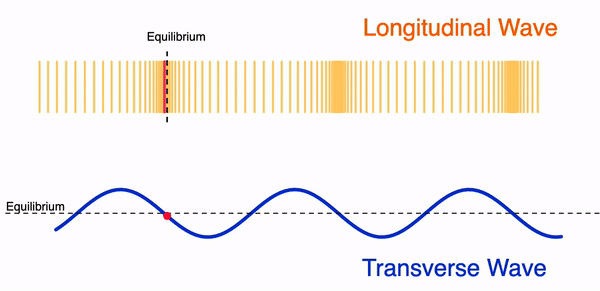
| Feature | Transverse Waves | Longitudinal Waves |
|---|---|---|
| Particle vibration | Perpendicular to wave direction | Parallel to wave direction |
| Wave features | Crests and troughs | Compressions and rarefactions |
| Examples | Light, water waves | Sound waves |
| Can travel in vacuum? | Yes (light) | No (sound) |
Key Idea
- Wave type depends on particle motion.
- Energy is transferred, not particles.
- Both types obey the wave equation.
Important Points to Remember
- Sound waves are always longitudinal.
- Light waves are always transverse.
- Particles vibrate about fixed positions.
Example
A wave travels through air and consists of compressions and rarefactions.
(a) Identify the type of wave. (b) Describe the motion of the particles.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) The wave is a longitudinal wave.
(b) The particles vibrate back and forth parallel to the direction of wave travel.
Example
A water wave has a frequency of \( \mathrm{2.0\ Hz} \) and a wavelength of \( \mathrm{0.50\ m} \).
(a) Calculate the wave speed. (b) State whether the wave is transverse or longitudinal.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) Use \( \mathrm{v = f\lambda} \):
\( \mathrm{v = 2.0 \times 0.50 = 1.0\ m/s} \)
(b) Water waves are transverse because particles move perpendicular to wave direction.
