Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.23 Sound Waves- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.23 Sound Waves- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.23 Sound Waves- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.23 know that sound waves are longitudinal waves that can be reflected and refracted
Sound Waves: Longitudinal Waves, Reflection and Refraction
Sound waves are a type of mechanical wave that require a medium, such as air, water, or solids, to travel. Sound waves are longitudinal waves and can undergo reflection and refraction, just like light waves.
Sound Waves as Longitudinal Waves
A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the vibrations of the particles of the medium are parallel to the direction of wave travel.
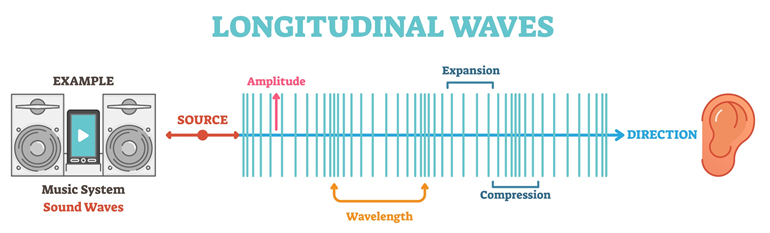
- Sound waves consist of compressions and rarefactions.
- Compressions are regions of high pressure.
- Rarefactions are regions of low pressure.
- Energy is transferred without transferring matter.
Reflection of Sound Waves
Reflection of sound occurs when sound waves bounce off a surface.
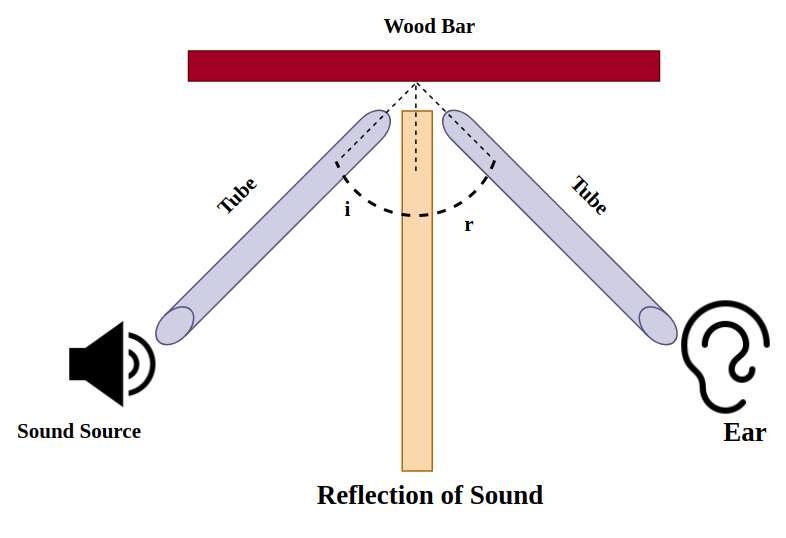
- Occurs at hard, flat surfaces such as walls or cliffs.
- Produces echoes.
- The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Application:
- Echo sounding
- Sonar
- Ultrasound imaging
Refraction of Sound Waves
Refraction of sound occurs when sound waves change speed as they travel through regions of air with different properties.
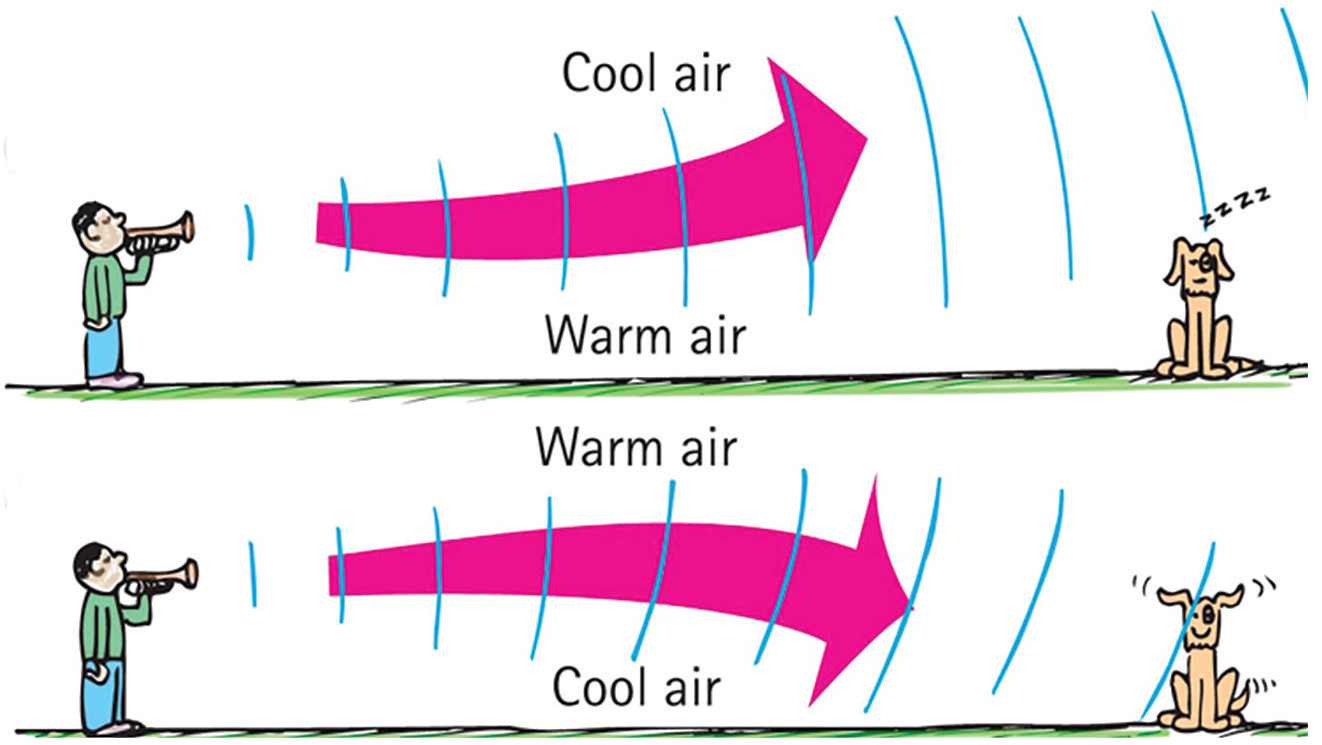
- Sound speed depends on temperature and density of air.
- Sound bends when speed changes.
- This often occurs in the atmosphere.
Examples:
- Sound travelling further at night.
- Sound bending due to temperature layers in air.
Wave Relationship Used
Sound waves obey the wave equation:
\( \mathrm{v = f\lambda} \)
- \( \mathrm{v} \) = speed of sound (m/s)
- \( \mathrm{f} \) = frequency (Hz)
- \( \mathrm{\lambda} \) = wavelength (m)
During refraction, frequency remains constant, but speed and wavelength change.
Key Idea
- Sound waves are longitudinal.
- They consist of compressions and rarefactions.
- Sound can be reflected and refracted.
Important Points to Remember
- Sound cannot travel in a vacuum.
- Reflection produces echoes.
- Refraction occurs due to speed changes.
Example
Explain why sound waves are described as longitudinal waves.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
In sound waves, particles vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel.
The wave consists of compressions and rarefactions.
Example
Explain how refraction allows sound to be heard more clearly at night.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
At night, cooler air near the ground causes sound to slow down.
This bends sound waves towards the ground, allowing them to travel further.
