Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.9 Reflection and Refraction of Waves- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.9 Reflection and Refraction of Waves- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -3.9 Reflection and Refraction of Waves- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
3.9 explain that all waves can be reflected and refracted
Reflection and Refraction of Waves
All waves including sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves—can undergo reflection and refraction when they meet a boundary between different media.
These behaviours occur because waves change direction when they interact with surfaces or when their speed changes.
Reflection of Waves
Reflection occurs when a wave bounces off a surface and changes direction while remaining in the same medium.
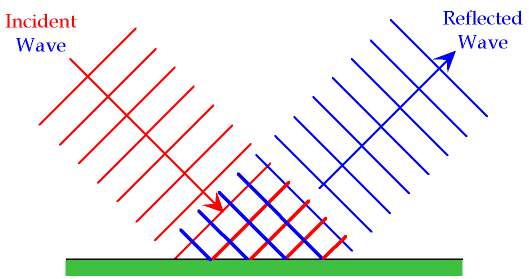
- The wave does not pass into a new medium.
- The speed and frequency remain the same.
- The direction of travel changes.
Law of Reflection (applies to all waves):
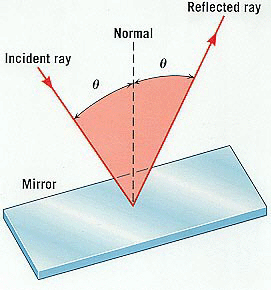
\( \mathrm{angle\ of\ incidence = angle\ of\ reflection} \)
This law applies to sound, water waves, and light waves.
Refraction of Waves
Refraction occurs when a wave enters a different medium and its speed changes, causing the wave to change direction.
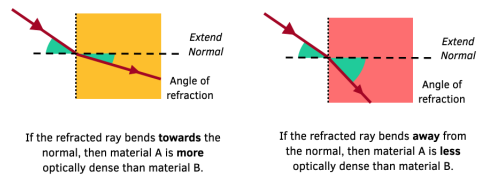
- The wave crosses a boundary.
- Wave speed changes.
- Wavelength changes.
- Frequency remains constant.
Why Refraction Occurs
- Different media affect wave speed differently.
- A change in speed causes bending of the wave.
- This bending is refraction.
Wave Relationship Used
The relationship between wave speed, frequency and wavelength is:
\( \mathrm{v = f\lambda} \)
- When a wave slows down, wavelength decreases.
- When a wave speeds up, wavelength increases.
- Frequency stays the same across boundaries.
Reflection and Refraction in Different Waves
- Water waves: reflect from barriers and refract in shallow water.
- Sound waves: reflect to form echoes and refract due to temperature changes.
- Light waves: reflect from mirrors and refract in glass or water.
Key Idea
- All waves can be reflected.
- All waves can be refracted.
- Refraction only occurs when wave speed changes.
Important Points to Remember
- Reflection does not change speed or frequency.
- Refraction changes speed and wavelength.
- Frequency never changes during refraction.
Example
A sound wave hits a large wall and an echo is heard.
(a) Name the wave behaviour involved. (b) State one property of the wave that remains unchanged.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) The wave behaviour is reflection.
(b) The frequency (and speed in air) remain unchanged.
Example
A water wave travels from deep water into shallow water at an angle.
(a) Describe what happens to the direction of the wave. (b) Explain this using wave speed.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
(a) The wave changes direction (bends).
(b) The wave slows down in shallow water, causing refraction.
