Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.10 Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfer- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.10 Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfer- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.10 Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfer- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfer (Insulation)
Unwanted energy transfer occurs when energy is transferred to the surroundings instead of being used for a useful purpose. Reducing this transfer makes systems more efficient, saves energy, and reduces costs.
Main Ways Energy Is Lost
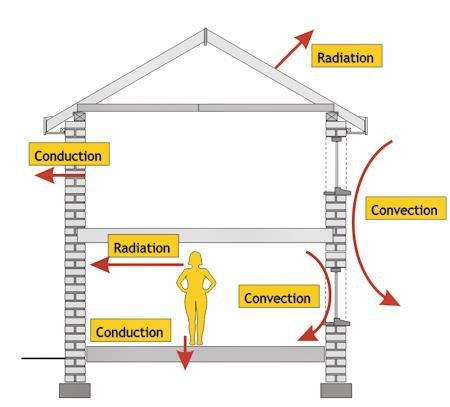
- By conduction through solids
- By convection in liquids and gases
- By radiation (infrared)
Insulation methods are designed to reduce one or more of these transfers.
Reducing Energy Transfer by Conduction
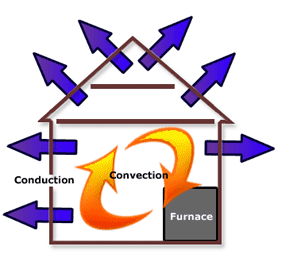
- Use materials with low thermal conductivity (insulators).
- Examples: wool, foam, plastic, air.
- Air is a poor conductor of heat.
Applications:
- Cavity wall insulation
- Loft insulation
- Foam insulation in buildings
Reducing Energy Transfer by Convection
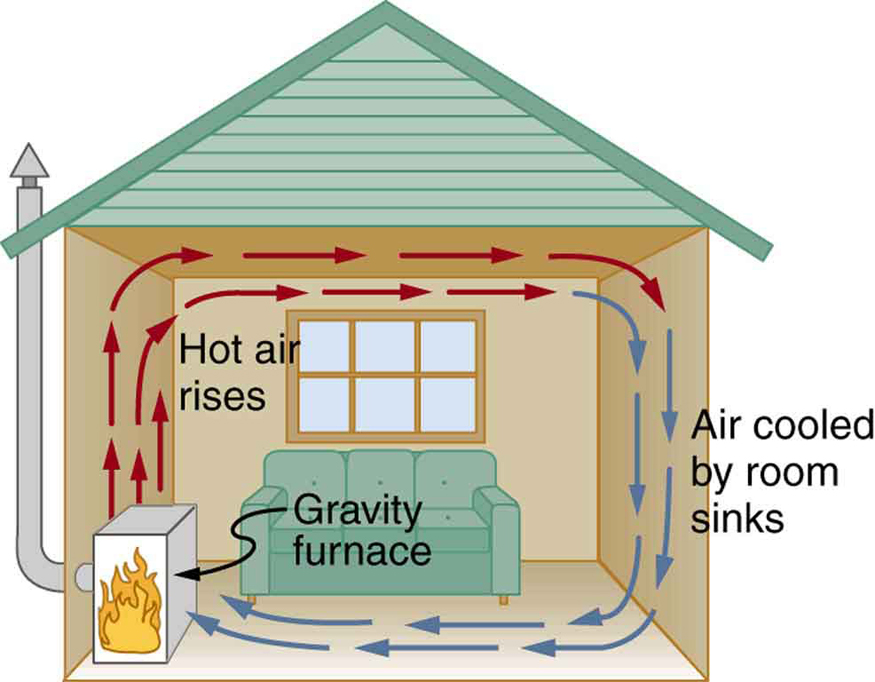
- Prevent movement of fluids.
- Trap air in small pockets.
- Use lids and sealed spaces.
Applications:
- Double glazing (traps air between glass panes)
- Vacuum flasks
- Draught excluders
Reducing Energy Transfer by Radiation
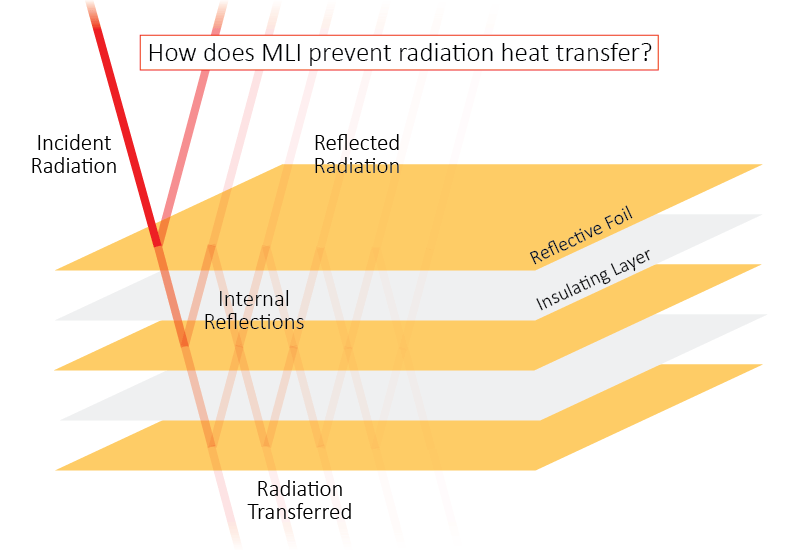
- Use shiny or reflective surfaces.
- Shiny surfaces reflect infrared radiation.
- They are poor emitters and absorbers.
Applications:
- Shiny foil behind radiators
- Silvered surfaces in vacuum flasks
- Emergency (space) blankets
Vacuum Flask: A Complete Example
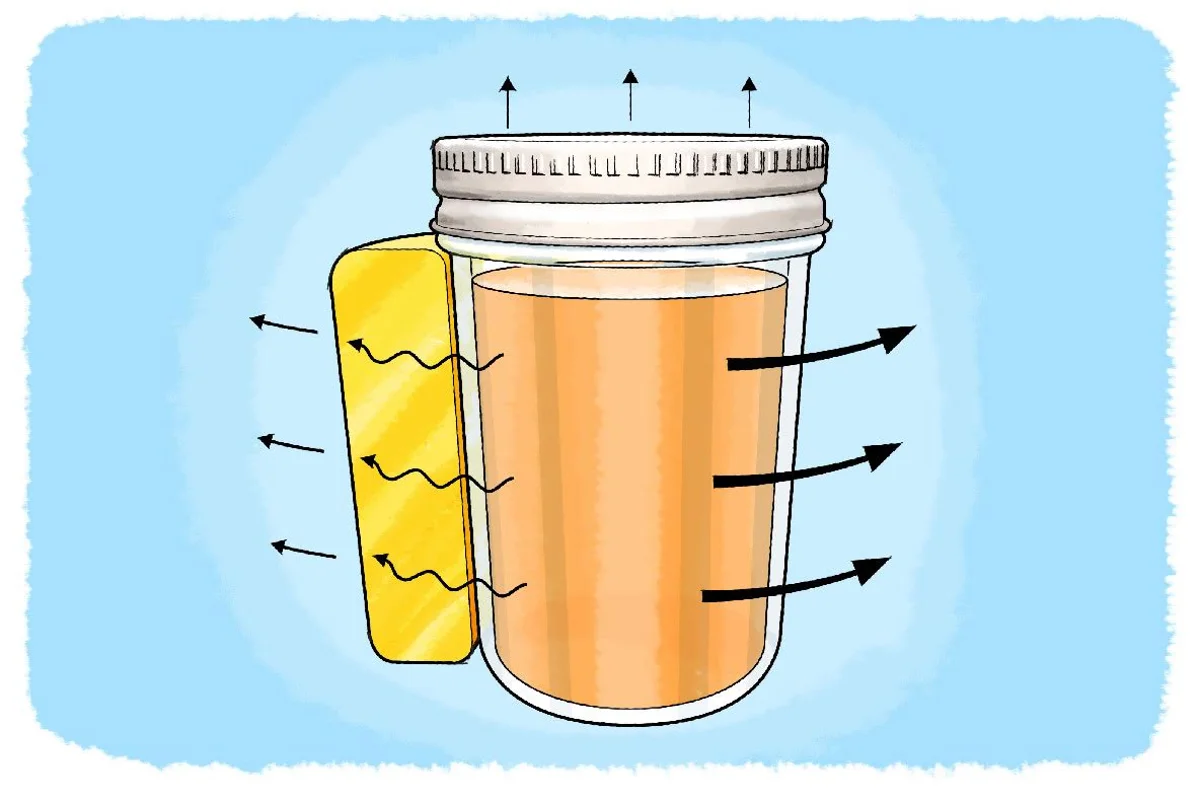
- Vacuum reduces conduction and convection.
- Silvered walls reduce radiation.
- Plastic stopper reduces conduction and convection.
This design greatly reduces unwanted energy transfer.
Key Idea
- Reducing energy loss increases efficiency.
- Different methods target different transfer processes.
- Most insulation uses trapped air.
Important Points to Remember
- Insulation does not stop energy transfer completely.
- It only reduces the rate of transfer.
- Good insulation saves energy and money.
Example
Explain how double glazing reduces energy loss from a house.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The air trapped between the glass panes is a poor conductor.
This reduces conduction.
The trapped air also prevents convection currents.
As a result, less thermal energy escapes.
Example
Explain how a vacuum flask keeps hot drinks hot for a long time.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The vacuum prevents conduction and convection.
The silvered surfaces reflect infrared radiation back into the liquid.
This greatly reduces unwanted energy transfer.
