Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.18–4.19P Electricity Generation from Energy Resources; Advantages and Disadvantages- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.18–4.19P Electricity Generation from Energy Resources; Advantages and Disadvantages- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.18–4.19P Electricity Generation from Energy Resources; Advantages and Disadvantages- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Energy Transfers in Electricity Generation
Electricity is generated by transferring energy from a primary energy source into electrical energy. Although the sources are different, many power stations use similar processes involving turbines and generators.
1. Wind Power
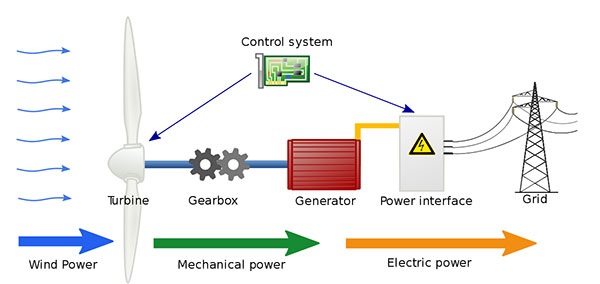
- Wind has kinetic energy.
- Wind turns the turbine blades.
- Kinetic energy → mechanical energy.
- The generator converts mechanical energy → electrical energy.
Energy transfers:
Kinetic (wind) → kinetic (turbine) → electrical
2. Water (Hydroelectric Power)
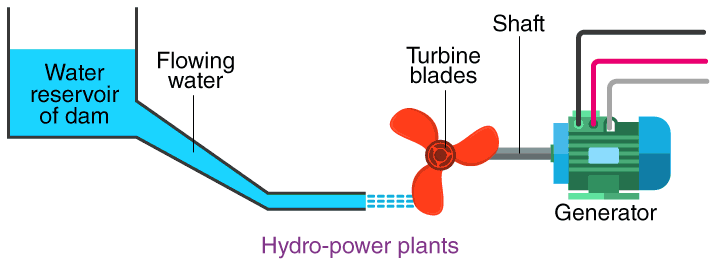
- Water stored behind a dam has gravitational potential energy.
- Falling water gains kinetic energy.
- Turbines rotate.
- Generators produce electricity.
Energy transfers:
Gravitational potential → kinetic → electrical
3. Geothermal Resources
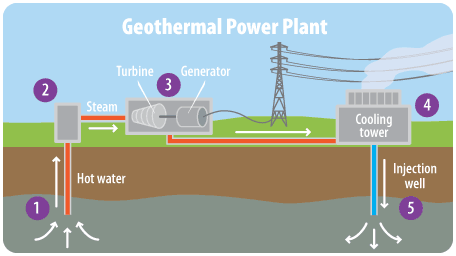
- Thermal energy stored inside the Earth.
- Hot water or steam rises to the surface.
- Steam turns a turbine.
- Generator produces electricity.
Energy transfers:
Thermal → kinetic → electrical
4. Solar Heating Systems

- Solar radiation transfers energy from the Sun.
- Energy heats water directly.
- No electricity is produced.
Energy transfers:
Radiation → thermal (water)
Note: This system produces heat, not electricity.
5. Solar Cells (Photovoltaic Cells)
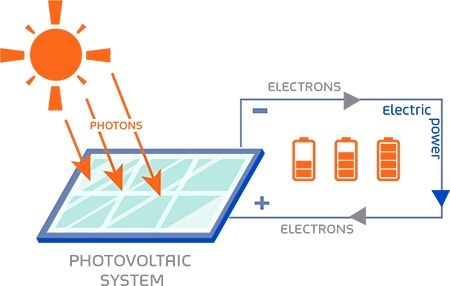
- Light energy from the Sun hits a solar cell.
- Electrons are released.
- An electric current is produced directly.
Energy transfers:
Radiation → electrical
No moving parts are involved.
6. Fossil Fuels (Coal, Oil, Gas)
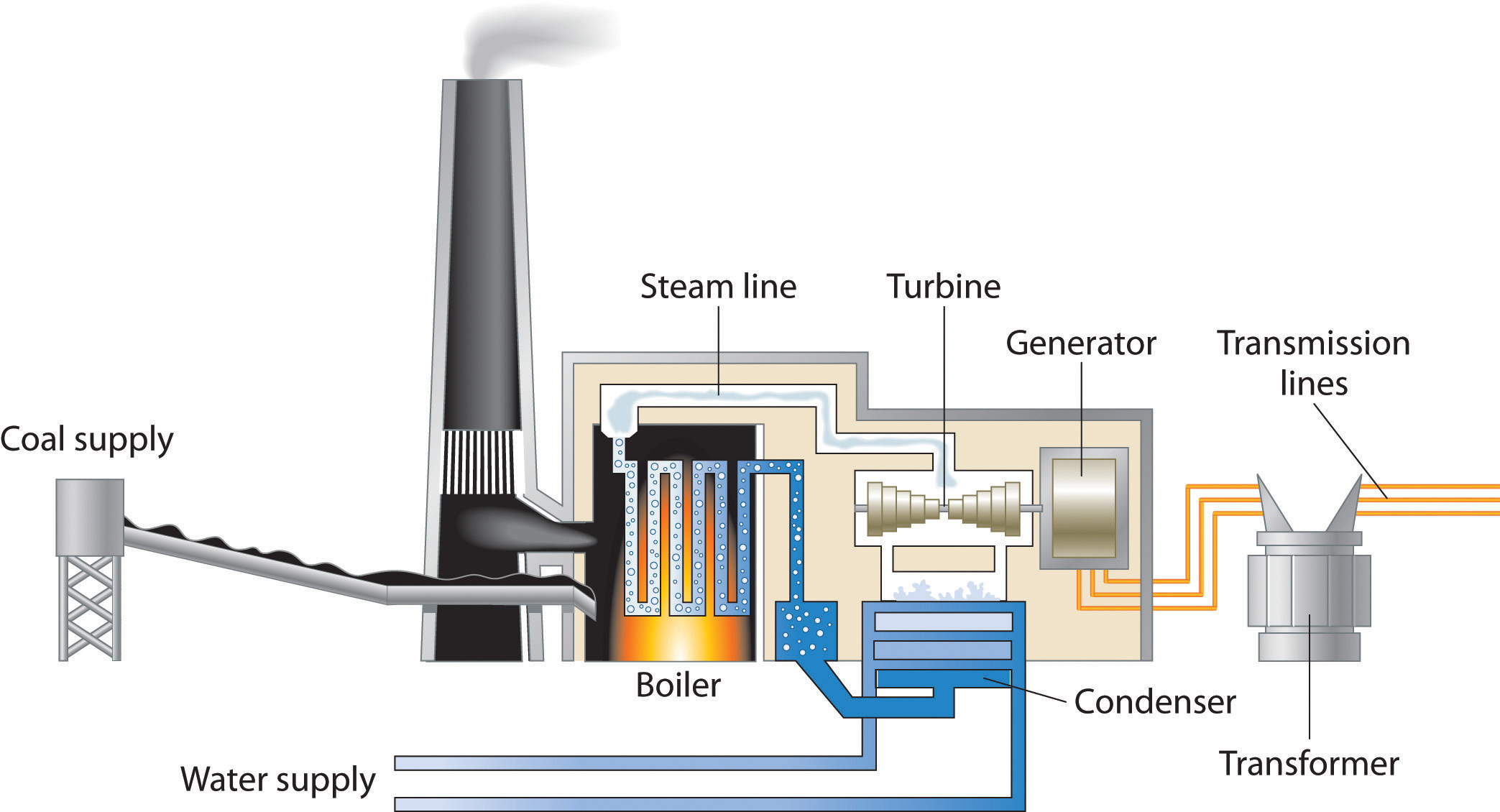
- Fuel contains chemical energy.
- Fuel is burned to heat water.
- Steam turns turbines.
- Generators produce electricity.
Energy transfers:
Chemical → thermal → kinetic → electrical
7. Nuclear Power
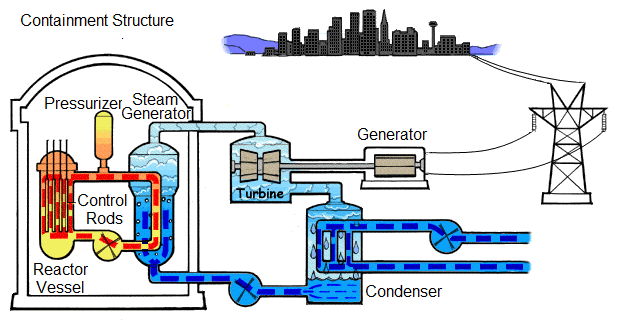
- Nuclear fuel releases energy by fission.
- Energy heats water.
- Steam turns turbines.
- Generators produce electricity.
Energy transfers:
Nuclear → thermal → kinetic → electrical
Common Feature of Most Power Stations
- Energy is used to spin a turbine.
- A generator converts kinetic energy to electrical energy.
- Some energy is always wasted as thermal energy.
Key Idea
- Different sources use different initial energy stores.
- Electrical energy is always the final useful output.
- Energy is conserved during generation.
Important Points to Remember
- Solar heating ≠ solar cells.
- Most stations use turbines and generators.
- Renewable sources do not run out.
Example
Describe the energy transfers that occur in a hydroelectric power station.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Water stored at height has gravitational potential energy.
As the water falls, this becomes kinetic energy.
The kinetic energy turns a turbine.
The generator converts this kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Example
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of using fossil fuels to generate electricity.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Advantage: Fossil fuels produce large amounts of electricity reliably.
Disadvantage: Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change.
Large-Scale Electricity Production: Advantages and Disadvantages
Electricity on a large scale can be generated using renewable and non-renewable energy resources. Each method has advantages and disadvantages related to reliability, environmental impact, cost, and energy output.
Renewable Energy Resources
1. Wind Power
Advantages
- Renewable and will not run out
- No greenhouse gas emissions during operation
- Low running costs
Disadvantages
- Unreliable — depends on wind speed
- Visual and noise pollution
- Large areas of land required
2. Hydroelectric Power
Advantages
- Renewable and reliable once built
- Very fast start-up time
- No air pollution
Disadvantages
- High initial construction cost
- Flooding of large areas of land
- Disrupts ecosystems and wildlife
3. Solar Power (Solar Cells)
Advantages
- Renewable and abundant
- No pollution during operation
- Low maintenance
Disadvantages
- Only works during daylight
- Weather dependent
- Large area needed for large-scale production
4. Geothermal Power
Advantages
- Reliable continuous energy source
- Very low greenhouse gas emissions
- Small land footprint
Disadvantages
- Limited to certain geographical locations
- High installation cost
- Risk of releasing underground gases
Non-Renewable Energy Resources
5. Fossil Fuels (Coal, Oil, Gas)
Advantages
- Reliable and controllable power output
- High energy output
- Established technology
Disadvantages
- Non-renewable — will run out
- Produces carbon dioxide (climate change)
- Causes air pollution and acid rain
6. Nuclear Power
Advantages
- Very high energy output
- No carbon dioxide during electricity generation
- Reliable base-load power
Disadvantages
- Radioactive waste disposal problem
- Risk of serious accidents
- High construction and decommissioning cost
Comparison
| Energy Source | Renewable? | Main Advantage | Main Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind | Yes | No fuel or emissions | Unreliable |
| Hydroelectric | Yes | Reliable | Environmental damage |
| Solar | Yes | Clean energy | Weather dependent |
| Fossil fuels | No | Reliable output | Pollution |
| Nuclear | No | High energy output | Radioactive waste |
Key Idea
- No single energy source is perfect.
- Countries use a mix of renewable and non-renewable resources.
- Environmental impact and reliability must be balanced.
Important Points to Remember
- Renewable ≠ always reliable.
- Non-renewable ≠ always polluting (e.g. nuclear).
- Exam answers must include both advantages and disadvantages.
Example
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of using wind turbines to generate electricity.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Advantage: Wind is renewable and produces no greenhouse gases during operation.
Disadvantage: Electricity generation is unreliable because wind speed varies.
Example
A country wants a reliable source of electricity with low carbon dioxide emissions.
Suggest a suitable method of electricity generation and justify your choice.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Nuclear power is suitable.
It produces large amounts of electricity reliably and does not release carbon dioxide during operation.
