Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.6–4.7 Thermal Energy Transfer and Convection in Everyday Phenomena- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.6–4.7 Thermal Energy Transfer and Convection in Everyday Phenomena- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -4.6–4.7 Thermal Energy Transfer and Convection in Everyday Phenomena- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
4.6 describe how thermal energy transfer may take place by conduction, convection and radiation
4.7 explain the role of convection in everyday phenomena
Thermal Energy Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Radiation
Thermal energy always transfers from a hotter region to a cooler region. This transfer can occur by conduction, convection, or radiation. Each process operates in different situations and materials.
1. Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through a material without the material itself moving. It occurs mainly in solids.

- Thermal energy is transferred by vibrating particles.
- Particles at the hot end vibrate more.
- They pass energy to neighbouring particles.
- Metals are good conductors of heat.
Conduction in Metals
- Metals contain free electrons.
- Free electrons move through the metal.
- They transfer energy quickly.
Insulators (such as plastic and wood) are poor conductors because they lack free electrons.
2. Convection
Convection is the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of fluids (liquids and gases).

- Fluid near the heat source warms up.
- Warm fluid becomes less dense.
- It rises.
- Cooler, denser fluid sinks.
- This sets up convection currents.
Convection does not occur in solids.
3. Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of thermal energy by electromagnetic waves, mainly infrared radiation.
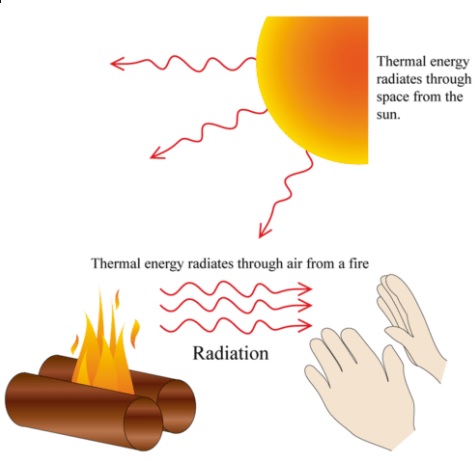
- Does not require a medium.
- Can occur through a vacuum.
- All objects emit and absorb radiation.
Surface Properties
- Black, dull surfaces are good emitters and absorbers.
- Shiny, light surfaces are poor emitters and absorbers.
Comparison of the Three Methods
| Method | Medium Required? | Where It Occurs |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Yes | Mainly solids |
| Convection | Yes | Liquids and gases |
| Radiation | No | All spaces |
Key Idea
- Thermal energy always flows from hot to cold.
- Different methods dominate in different situations.
- Radiation is the only method that works in a vacuum.
Important Points to Remember
- Conduction involves particle vibration.
- Convection involves bulk movement of fluid.
- Radiation involves infrared waves.
Example
Explain how thermal energy is transferred from the Sun to the Earth.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Thermal energy is transferred by radiation.
This is because there is a vacuum between the Sun and the Earth, so conduction and convection cannot occur.
Example
A metal spoon is placed in hot soup.
Explain how thermal energy travels along the spoon to the handle.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Thermal energy is transferred by conduction.
Particles and free electrons in the metal transfer energy from the hot end to the cooler handle.
Role of Convection in Everyday Phenomena
Convection is a method of thermal energy transfer that occurs in fluids (liquids and gases). It involves the movement of the fluid itself due to changes in temperature and density.
How Convection Works
- When a fluid is heated, its particles gain energy.
- The fluid expands and becomes less dense.
- The warmer, less dense fluid rises.
- Cooler, denser fluid sinks.
- This movement sets up convection currents.
Convection continues as long as there is a temperature difference.
Everyday Examples of Convection
1. Heating a Room
- Air near a radiator is heated.
- The warm air rises.
- Cooler air moves in to replace it.
- This circulates warm air around the room.
2. Boiling Water in a Pan
- Water at the bottom is heated first.
- Hot water rises and cooler water sinks.
- Convection currents distribute heat evenly.
3. Sea Breeze and Land Breeze
- Land heats up faster than the sea during the day.
- Warm air above land rises.
- Cool air from the sea moves in to replace it (sea breeze).
4. Chimneys and Ventilation
- Hot gases from a fire rise up the chimney.
- Cool air is drawn in to replace them.
- This maintains airflow.
Why Convection Is Important
- Transfers thermal energy efficiently in fluids.
- Explains weather patterns and ventilation.
- Used in heating and cooling systems.
Key Idea
- Convection involves bulk movement of fluids.
- It depends on temperature differences.
- It does not occur in solids.
Important Points to Remember
- Warm fluids rise because they are less dense.
- Cool fluids sink because they are more dense.
- Convection currents transfer energy.
Example
Explain how convection helps to heat a room using a radiator.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Air near the radiator is heated and becomes less dense.
This warm air rises and cooler air moves in to replace it.
A convection current is set up, circulating warm air around the room.
Example
Explain why smoke rises up a chimney when a fire is burning.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The hot gases produced by the fire are heated and become less dense.
They rise up the chimney.
Cooler air enters the fireplace, maintaining the convection current.
