Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.15 Gas Molecules and Pressure- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.15 Gas Molecules and Pressure- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.15 Gas Molecules and Pressure- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.15 explain how molecules in a gas have random motion and that they exert a force, and hence a pressure, on the walls of a container
Gas Molecules: Random Motion, Force and Pressure
Gases are made up of tiny molecules that are in constant random motion. This motion and the collisions of molecules with surfaces explain how gases exert forces and produce pressure.
Random Motion of Gas Molecules

- Gas molecules move rapidly in all directions.
- Their motion is random, meaning there is no fixed direction or pattern.
- Molecules travel in straight lines between collisions.
- Collisions occur between molecules and with container walls.
This behaviour is explained by the particle model of matter.
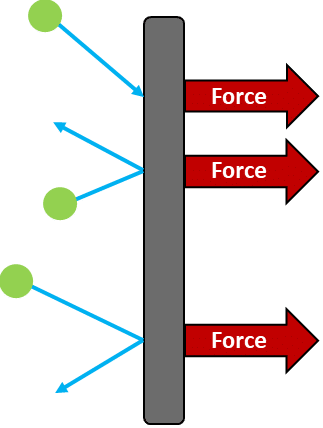
How Gas Molecules Exert a Force
- When gas molecules collide with the walls of a container, they bounce off.
- Each collision changes the molecule’s momentum.
- This change in momentum produces a force on the wall.
The force is always exerted perpendicular to the surface.
How Gas Pressure Is Produced
Pressure is the force exerted per unit area:
\( \mathrm{pressure = \dfrac{force}{area}} \)
\( \mathrm{P = \dfrac{F}{A}} \)
- Many molecular collisions occur every second.
- The combined effect of these collisions produces pressure.
- Pressure acts equally in all directions.
Effect of Temperature on Gas Pressure
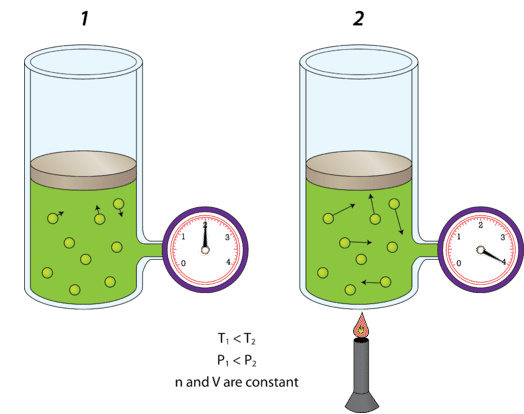
- Increasing temperature increases the kinetic energy of molecules.
- Molecules move faster.
- Collisions with the walls are more frequent and more forceful.
- Pressure increases if volume is constant.
Effect of Volume on Gas Pressure

- Reducing volume brings walls closer together.
- Molecules collide with walls more often.
- Pressure increases.
Everyday Examples
- A balloon stays inflated due to gas pressure.
- Aerosol cans feel harder when warmed.
- Car tyres have higher pressure after driving.
Key Idea
- Gas molecules move randomly.
- Pressure is caused by molecular collisions.
- Temperature and volume affect pressure.
Important Points to Remember
- Pressure acts on all container walls.
- More energetic molecules → higher pressure.
- Gas pressure is due to momentum change.
Example
Explain why a balloon becomes firmer when it is warmed.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Heating increases the kinetic energy of gas molecules.
The molecules move faster and collide with the walls more frequently.
This increases the force on the walls, so the pressure increases.
Example
A gas is sealed inside a rigid container.
Explain why the pressure increases when the gas is heated.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Heating increases the kinetic energy of the molecules.
The molecules collide with the container walls more often and with greater force.
This increases the pressure.
