Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.8P Energy Changes During Heating- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.8P Energy Changes During Heating- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -5.8P Energy Changes During Heating- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
5.8P explain why heating a system will change the energy stored within the system and raise its temperature or produce changes of state
Heating, Energy Stores, Temperature and Change of State
Heating a system transfers energy to it. This energy is stored in the system’s internal energy store, which is made up of the kinetic energy and potential energy of the particles.
Internal Energy
![]()
- Internal energy = total kinetic energy + total potential energy of particles.
- Heating increases the internal energy of a system.
- Cooling decreases the internal energy of a system.
Why Temperature Rises When a System Is Heated

- Heating transfers energy to particles.
- Particles move faster.
- Their kinetic energy increases.
- Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles.
Result: Increased kinetic energy → higher temperature.
Why Heating Can Cause a Change of State
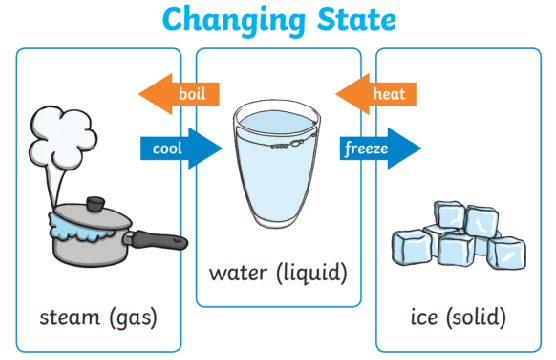
- During a change of state, temperature stays constant.
- Energy supplied is used to increase potential energy, not kinetic energy.
- Particles move further apart or break intermolecular bonds.
Examples of changes of state:
- Solid → liquid (melting)
- Liquid → gas (boiling or evaporation)
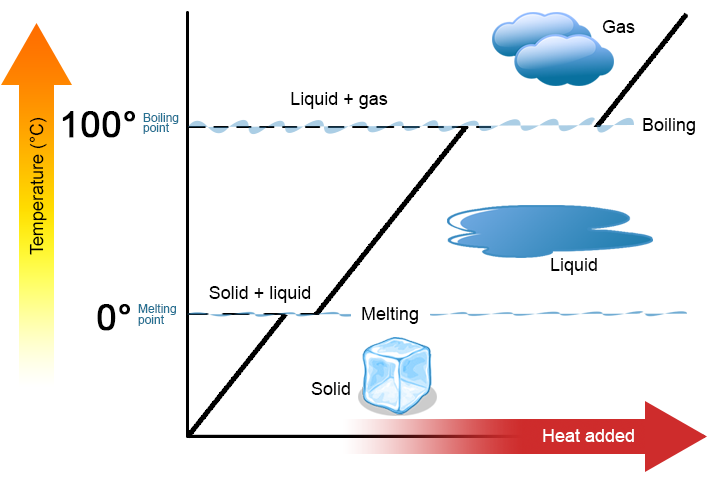
Heating Curve Explanation
- Sloping sections: temperature increases (kinetic energy increases).
- Flat sections: change of state (potential energy increases).
This explains why ice melts at 0°C without increasing in temperature.
Energy Transfer Summary![]()
- Heating → energy transfer to internal energy store.
- Temperature rise → increase in kinetic energy.
- Change of state → increase in potential energy.
Key Idea
- Heating always increases internal energy.
- Temperature does not always increase.
- Changes of state require energy.
Important Points to Remember
- Temperature measures average kinetic energy.
- Internal energy includes both kinetic and potential energy.
- Energy is conserved.
Example
Ice at 0°C is heated until it becomes water at 0°C.
Explain why the temperature does not change during this process.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The energy supplied is used to break bonds between particles.
This increases the potential energy of the particles.
The kinetic energy does not increase, so the temperature remains constant.
Example
A metal block is heated.
Explain why its temperature rises.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Heating transfers energy to the internal energy store.
The particles gain kinetic energy and move faster.
This increase in average kinetic energy causes the temperature to rise.
