Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.15 Induced Voltage - Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.15 Induced Voltage – Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.15 Induced Voltage – Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.15 know that a voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it and describe the factors that affect the size of the induced voltage
Electromagnetic Induction and Induced Voltage
A voltage can be produced in a conductor without a power supply if the conductor is placed in a changing magnetic environment. This process is known as electromagnetic induction.
Induced Voltage – Key Statement
Statement: A voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when:

- the conductor moves through a magnetic field, or
- the magnetic field through the conductor or coil changes.
Key idea: An induced voltage is produced only when the magnetic field experienced by the conductor is changing.
How an Induced Voltage Is Produced
- Moving a conductor through a magnetic field cuts magnetic field lines.
- Moving charges in the conductor experience a force.
- This causes charges to separate.
- A voltage is produced across the conductor.
Important point: If there is no change in the magnetic field through the conductor, no voltage is induced.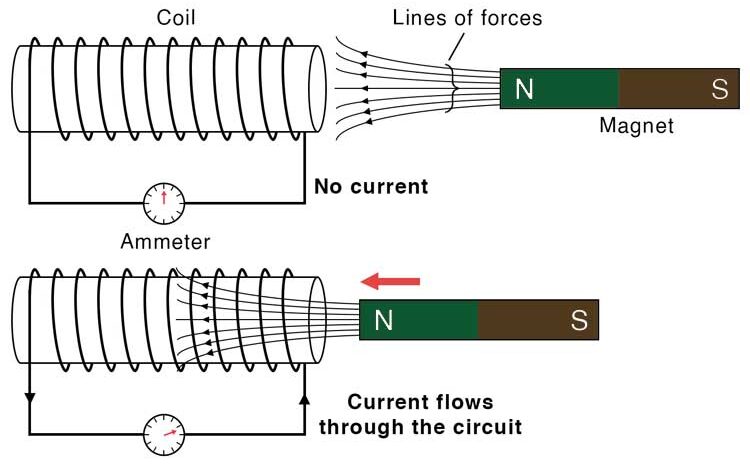
Induced Voltage in a Coil
A voltage can also be induced in a coil if the magnetic field through the coil changes.
- Moving a magnet into or out of a coil
- Moving the coil into or out of a magnetic field
- Changing the magnetic field strength around the coil
Key idea: The voltage is induced because the magnetic field lines linking the coil are changing.
Factors Affecting the Size of the Induced Voltage
The size of the induced voltage depends on how quickly the magnetic field through the conductor or coil changes.
- Speed of motion: Faster motion → larger induced voltage.
- Strength of magnetic field: Stronger field → larger induced voltage.
- Number of turns in a coil: More turns → larger induced voltage.
- Area of the coil: Larger area → larger induced voltage.
Key idea: A faster rate of change of magnetic field produces a larger induced voltage.
Direction of the Induced Voltage
- Reversing the direction of motion reverses the induced voltage.
- Reversing the magnetic field direction reverses the induced voltage.
Note: At IGCSE level, you only need to know that the direction depends on motion and field direction.
Example
A coil connected to a voltmeter shows a small voltage when a magnet is slowly pushed into it. The voltage increases when the magnet is pushed in faster. Explain this observation.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Moving the magnet changes the magnetic field through the coil.
- Pushing the magnet faster increases the rate of change of the magnetic field.
- A faster change induces a larger voltage.
- This produces a larger voltmeter reading.
Example
Two coils are identical except that one has twice as many turns as the other. Both are moved through the same magnetic field at the same speed. Explain which coil produces a larger induced voltage and why.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The coil with more turns has more wire cutting magnetic field lines.
- Each turn contributes to the induced voltage.
- More turns increase the total change in magnetic field linkage.
- The coil with twice as many turns produces a larger induced voltage.
