Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.2–6.3 Magnetic Forces, Materials, and Hard and Soft Magnetic Materials- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.2–6.3 Magnetic Forces, Materials, and Hard and Soft Magnetic Materials- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.2–6.3 Magnetic Forces, Materials, and Hard and Soft Magnetic Materials- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.2 know that magnets repel and attract other magnets and attract magnetic substances
6.3 describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials
Magnetic Effects: Attraction and Repulsion
Magnets produce a magnetic effect that allows them to attract certain materials and interact with other magnets through forces of attraction and repulsion.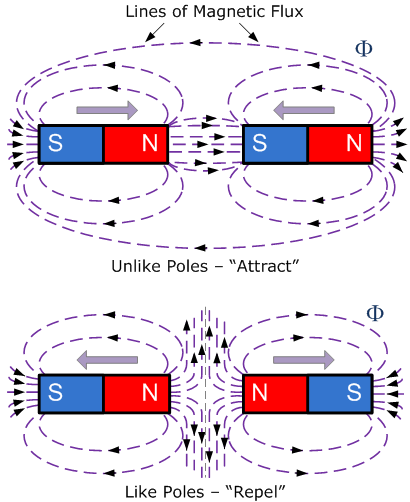
Magnets and Their Poles
Every magnet has two ends called magnetic poles:
- North pole (N)
- South pole (S)
Key rule: Magnetic poles always exist in pairs — cutting a magnet creates two smaller magnets, each with a north and a south pole.
Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets
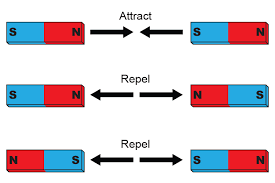
When two magnets are brought close together, they exert forces on each other.
Rules:
- Unlike poles attract each other (N–S).
- Like poles repel each other (N–N or S–S).
Meaning:
- Attraction pulls magnets together.
- Repulsion pushes magnets apart.
Magnetic Substances
Definition: Magnetic substances are materials that are attracted to a magnet.
Common magnetic substances:
- Iron
- Steel
- Nickel
- Cobalt
Important point: Magnets attract magnetic materials, but magnetic materials do not always repel or attract each other unless they are magnetised.
What Magnets Do NOT Attract
- Wood
- Plastic
- Glass
- Copper
- Aluminium
Key idea: Not all metals are magnetic.
Summary of Magnetic Interactions
- Magnets attract magnetic substances.
- Magnets attract or repel other magnets.
- Only magnets can repel.
- Magnetic forces act at a distance.
Example
A north pole of one magnet is brought close to the south pole of another magnet. Describe what happens.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- North and south poles are unlike poles.
- Unlike poles attract each other.
- The magnets move towards each other.
Example
A student brings a bar magnet close to a steel paper clip and then close to a plastic ruler. State what happens in each case.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The steel paper clip is attracted because steel is a magnetic material.
- The plastic ruler is not attracted because plastic is non-magnetic.
Magnetically Hard and Magnetically Soft Materials
Magnetic materials can be classified as magnetically hard or magnetically soft depending on how easily they become magnetised and how easily they lose their magnetism.
Magnetically Soft Materials
Definition: Magnetically soft materials are materials that are easily magnetised and easily demagnetised.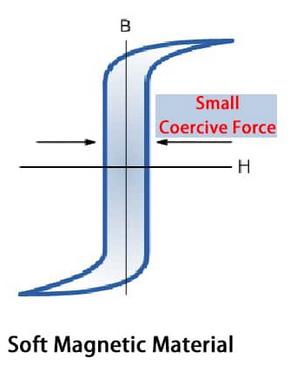
Key properties:
- Become magnetised quickly in a magnetic field.
- Lose magnetism quickly when the field is removed.
- Have low retentivity (do not stay magnetised).
- Have low coercivity (easy to demagnetise).
Examples:
- Soft iron
- Pure iron
Key idea: Magnetically soft materials are ideal where magnetism needs to be switched on and off.
Magnetically Hard Materials
Definition: Magnetically hard materials are materials that are difficult to magnetise but retain their magnetism once magnetised.
Key properties:
- Do not magnetise easily.
- Remain magnetised for a long time.
- Have high retentivity (stay magnetised).
- Have high coercivity (hard to demagnetise).
Examples:
- Steel
- Alnico
Key idea: Magnetically hard materials are used to make permanent magnets.
Comparison of Magnetic Properties
- Soft materials magnetise and demagnetise easily.
- Hard materials magnetise with difficulty but keep their magnetism.
- Choice of material depends on the application.
Uses of Magnetically Hard and Soft Materials
- Soft iron: electromagnets, transformers, relays.
- Steel: permanent magnets, compass needles.
Example
An electromagnet is designed to lift and then release scrap iron repeatedly. Explain why a magnetically soft material is used for the core instead of steel.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The core must become magnetised when current flows.
- It must lose magnetism quickly when the current is switched off.
- Magnetically soft materials have low retentivity.
- Steel would remain magnetised and not release the scrap iron easily.
Example
A student suggests using soft iron to make a permanent magnet. Explain why this is not suitable and state a better material.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Soft iron loses its magnetism easily.
- It has low retentivity and low coercivity.
- A permanent magnet must retain magnetism.
- Steel is more suitable because it is magnetically hard.
