Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.8–6.10P Magnetic Fields around Current-Carrying Conductors and Field Patterns- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.8–6.10P Magnetic Fields around Current-Carrying Conductors and Field Patterns- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -6.8–6.10P Magnetic Fields around Current-Carrying Conductors and Field Patterns- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
6.8 know that an electric current in a conductor produces a magnetic field around it
6.10P draw magnetic field patterns for a straight wire, a flat circular coil and a solenoid when each is carrying a current
Magnetic Field Around a Current-Carrying Conductor
When an electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around the conductor. This shows a direct link between electricity and magnetism.
Current-Carrying Conductor – Magnetic Effect
Statement: An electric current in a conductor produces a magnetic field around the conductor.
Key idea: The magnetic field exists only while the current is flowing.
Shape of the Magnetic Field
For a straight current-carrying conductor:
- Magnetic field lines form concentric circles around the wire.
- The conductor is at the centre of the circles.
- The field becomes weaker further from the wire.
Direction of the Magnetic Field
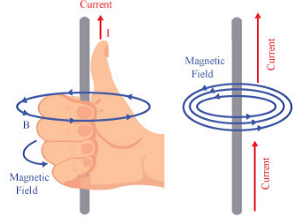
The direction of the magnetic field around a straight conductor is found using the right-hand grip rule.
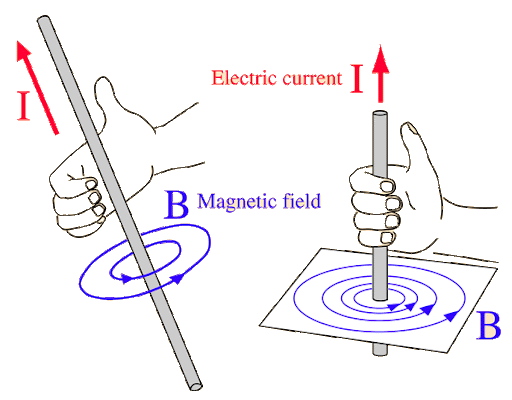
- Thumb points in the direction of the current.
- Curled fingers show the direction of the magnetic field.
Key point: Reversing the current reverses the direction of the magnetic field.
Factors Affecting the Magnetic Field Strength
- Increasing the current increases the magnetic field strength.
- Magnetic field strength decreases with distance from the conductor.
- Using a coil increases the strength of the magnetic field.
Evidence for the Magnetic Field
- A compass needle placed near the wire deflects.
- The deflection increases when current increases.
- No deflection occurs when current is switched off.
Example
A straight vertical wire passes through a piece of cardboard. A current flows upward through the wire. Describe the magnetic field pattern produced and explain how its direction can be determined.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The magnetic field forms concentric circles around the wire.
- The wire is at the centre of the circles.
- The right-hand grip rule is used.
- The thumb points upward (direction of current).
- The curled fingers show the field direction.
Example
A student increases the current in a straight wire while observing a nearby compass. Explain what happens to the compass deflection and why.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Increasing the current increases the magnetic field strength.
- A stronger magnetic field exerts a larger force on the compass needle.
- The compass deflects through a greater angle.
- This confirms that current produces a magnetic field.
Magnetic Field Patterns of Current-Carrying Conductors
When an electric current flows, it produces a magnetic field. The shape of the magnetic field depends on the shape of the conductor. You must be able to draw and interpret the magnetic field patterns for different current-carrying conductors.
Magnetic Field Around a Straight Wire

Pattern:
- Magnetic field lines form concentric circles around the wire.
- The wire is at the centre of the circles.
- Field strength decreases with distance from the wire.
Direction:
- Use the right-hand grip rule.
- Thumb points in direction of current.
- Curled fingers show field direction.
Magnetic Field Around a Flat Circular Coil
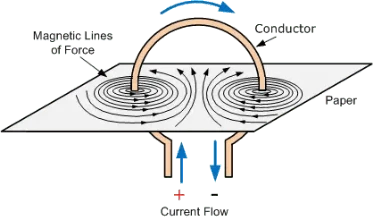
Pattern:
- Field lines form circles around each part of the wire.
- Inside the coil, field lines combine to form a stronger field.
- The field is strongest at the centre of the coil.
Direction:
- Use the right-hand rule.
- Fingers follow current direction around the coil.
- Thumb points in direction of the magnetic field through the centre.
Magnetic Field Around a Solenoid

Pattern:
- Magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet.
- Inside the solenoid, field lines are straight, parallel, and evenly spaced.
- This shows a strong, uniform magnetic field inside.
Polarity:
- One end acts as a north pole.
- The other end acts as a south pole.
- Reversing the current reverses the poles.
Comparing the Three Field Patterns
- Straight wire → circular field lines.
- Circular coil → concentrated field at centre.
- Solenoid → strong, uniform internal field.
Key idea: The solenoid produces the most useful magnetic field for applications such as electromagnets.
Example
A student draws magnetic field lines around a solenoid and notices that the lines inside the solenoid are straight and evenly spaced. Explain what this shows about the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Straight lines show the field has a constant direction.
- Even spacing shows constant field strength.
- This indicates a uniform magnetic field.
- The field inside the solenoid is strong.
Example
A current flows anticlockwise in a flat circular coil when viewed from above. State the direction of the magnetic field at the centre of the coil and explain your answer.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Use the right-hand rule.
- Fingers curl in the direction of the current.
- The thumb points upward.
- The magnetic field at the centre is upwards.
