Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.18–7.20 Nuclear Fission: Products, Chain Reaction- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.18–7.20 Nuclear Fission: Products, Chain Reaction- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.18–7.20 Nuclear Fission: Products, Chain Reaction- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.18 understand how a nucleus of U-235 can be split (the process of fission) by collision with a neutron and that this process releases energy as kinetic energy of the fission products
7.19 know that the fission of U-235 produces two radioactive daughter nuclei and a small number of neutrons
7.20 describe how a chain reaction can be set up if the neutrons produced by one fission strike other U-235 nuclei
Nuclear Fission of Uranium-235
Nuclear fission is a process in which a heavy nucleus splits into smaller nuclei. Uranium-235 is an important fuel because it can undergo fission when it collides with a neutron.
Key Statement
Statement: A nucleus of uranium-235 can be split by collision with a neutron, and this fission process releases energy as the kinetic energy of the fission products.
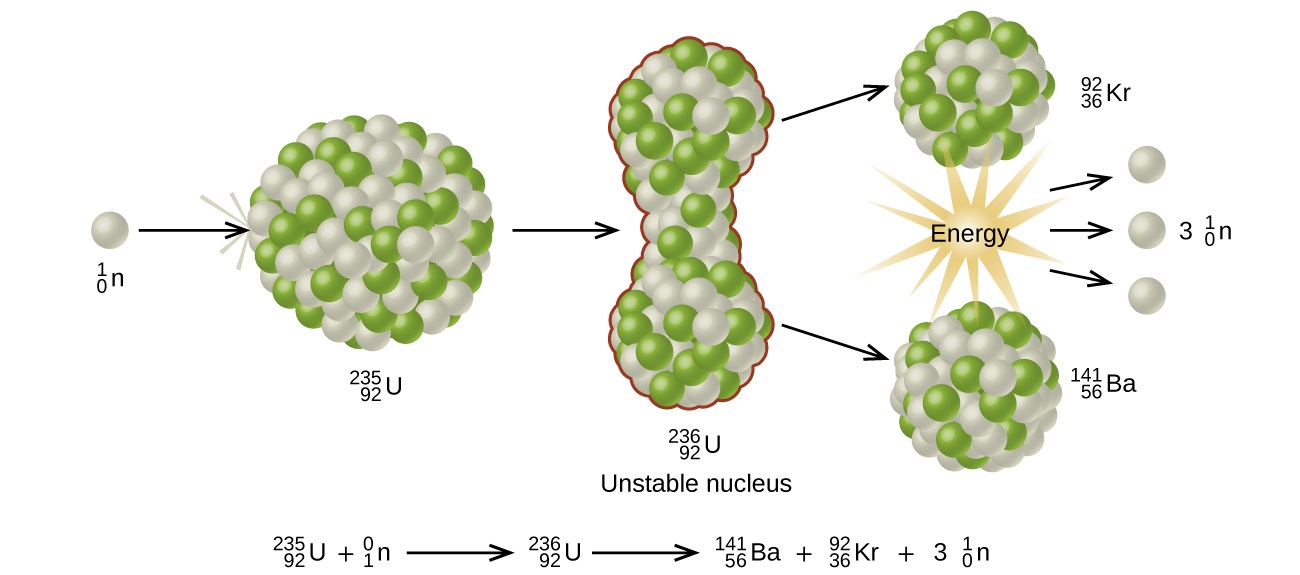
Structure of a U-235 Nucleus
- U-235 is a large, heavy nucleus.
- It is relatively unstable.
- It can absorb a slow-moving neutron.
Key idea: U-235 is fissile — it can undergo fission easily.
The Fission Process

Step-by-step description:
- A neutron collides with a U-235 nucleus.
- The nucleus absorbs the neutron.
- The nucleus becomes unstable.
- It splits into two smaller nuclei (fission products).
- Additional neutrons are released.
\( \mathrm{^{235}_{92}U + ^1_0n \rightarrow fission\ products + neutrons} \)
Energy Released in Fission![]()
How energy is released:
- The fission products move apart at high speed.
- This motion gives them large kinetic energy.
- This kinetic energy is the main energy released.
Key idea: The energy released is mainly the kinetic energy of the fission products.
Important:
- A small amount of mass is converted into energy.
- This energy appears as kinetic energy.
Neutrons and Chain Reactions
- More than one neutron is released during fission.
- These neutrons can cause further fissions.
- This can lead to a chain reaction.
Key idea: Controlling the neutrons controls the energy release.
Example
Describe how the fission of a U-235 nucleus occurs when it collides with a neutron and explain how energy is released.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- A neutron is absorbed by the U-235 nucleus.
- The nucleus becomes unstable.
- It splits into two smaller nuclei.
- The fission products move apart rapidly.
- Their kinetic energy is the energy released.
Example
Explain why the energy released in nuclear fission is described as kinetic energy rather than heat energy.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The fission products move at very high speeds.
- Moving objects have kinetic energy.
- The kinetic energy is later transferred as heat.
- The initial energy release is kinetic.
Products of U-235 Nuclear Fission
When a nucleus of uranium-235 undergoes nuclear fission, it does not split evenly. Instead, it forms two smaller radioactive nuclei (called daughter nuclei) and releases a small number of neutrons.
Key Statement
Statement: The fission of a U-235 nucleus produces two radioactive daughter nuclei and a small number of neutrons.
Key idea: Both the daughter nuclei and the emitted neutrons are important for energy release and chain reactions.
What Happens During Fission
Step-by-step:
- A slow neutron collides with a U-235 nucleus.
- The nucleus absorbs the neutron.
- The nucleus becomes unstable.
- It splits into two smaller nuclei.
- Two or three neutrons are released.
\( \mathrm{^{235}_{92}U + ^1_0n \rightarrow ^{A_1}_{Z_1}X + ^{A_2}_{Z_2}Y + 2\ or\ 3\ ^1_0n} \)
Daughter Nuclei
- The daughter nuclei are radioactive.
- They have roughly half the mass of the original nucleus.
- They are different elements from uranium.
- They may later undergo radioactive decay.
Key idea: Fission products are unstable because their neutron–proton ratio is not ideal.
Neutrons Released
- A small number of neutrons (usually 2 or 3) are released.
- These neutrons have high kinetic energy.
- They can cause further fission reactions.
Important: These neutrons make a chain reaction possible.
Why This Is Important
- Daughter nuclei release energy as kinetic energy.
- Neutrons allow sustained energy production.
- Controlled fission is used in nuclear reactors.
Example
State two products of the fission of a U-235 nucleus and explain why the daughter nuclei are radioactive.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Two smaller daughter nuclei are produced.
- Several neutrons are also released.
- The daughter nuclei have unstable neutron–proton ratios.
- This makes them radioactive.
Example
Explain why the neutrons released during U-235 fission are important in a nuclear reactor.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Neutrons can cause further fission of U-235 nuclei.
- This produces a chain reaction.
- The chain reaction releases continuous energy.
- Controlling neutrons controls the reactor output.
Chain Reactions in U-235 Nuclear Fission
A chain reaction occurs when the neutrons released from one nuclear fission event go on to cause further fissions. This process is central to how nuclear reactors produce energy.
Key Statement
Statement: A chain reaction can be set up if the neutrons produced by one fission strike other U-235 nuclei, causing them to undergo fission as well.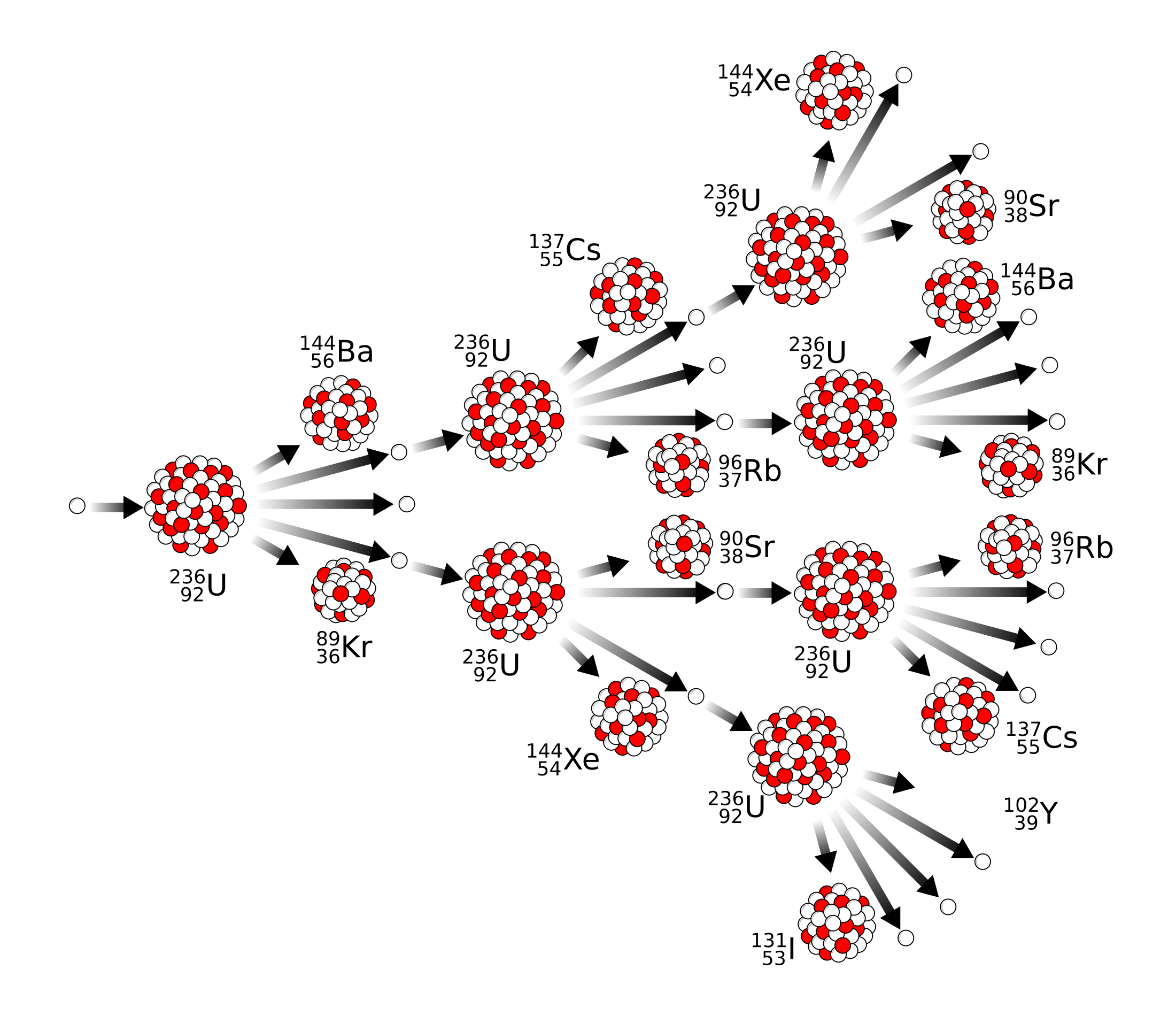
Key idea: Each fission can trigger more fissions.
How a Chain Reaction Starts
Step-by-step description:
- A slow neutron is absorbed by a U-235 nucleus.
- The nucleus undergoes fission.
- Two radioactive daughter nuclei are formed.
- Energy and several neutrons are released.
- These neutrons move away from the fission site.
Setting Up the Chain Reaction
- The emitted neutrons strike nearby U-235 nuclei.
- Each neutron may cause another fission.
- More neutrons are released.
- The process repeats continuously.
Key condition: Enough neutrons must cause further fission for the reaction to continue.
Why the Reaction Can Grow Rapidly
- Each fission releases more than one neutron.
- The number of fissions can increase rapidly.
- This leads to a large release of energy.
Important: If too many neutrons escape without causing fission, the chain reaction stops.
Controlled and Uncontrolled Chain Reactions
- In a nuclear reactor, the chain reaction is controlled.
- Control rods absorb excess neutrons.
- This keeps the reaction steady and safe.
Key idea: Controlling the number of neutrons controls the rate of energy release.
Example
Describe how a chain reaction is produced during the fission of U-235.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- A neutron causes a U-235 nucleus to split.
- The fission releases more neutrons.
- These neutrons strike other U-235 nuclei.
- Further fissions occur.
- The process repeats, forming a chain reaction.
Example
Explain why a chain reaction does not continue if too many neutrons escape from the fuel.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Escaping neutrons cannot cause further fission.
- Fewer U-235 nuclei are split.
- The number of neutrons decreases.
- The chain reaction dies out.
