Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.21 - 7.22 Control Rods, Moderators, and Shielding- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.21 – 7.22 Control Rods, Moderators, and Shielding- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.21 – 7.22 Control Rods, Moderators, and Shielding- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.21 describe the role played by the control rods and moderator in the fission process
7.22 understand the role of shielding around a nuclear reactor
Role of the Moderator and Control Rods in Nuclear Fission
In a nuclear reactor, the energy released by the fission of U-235 must be carefully controlled. This is achieved using two key components: the moderator and the control rods.
Key Statement
Statement: The moderator slows down neutrons so they can cause further fission, while the control rods absorb neutrons to control the rate of the chain reaction.
Key idea: The fission process must be controlled to release energy safely and steadily.
The Moderator
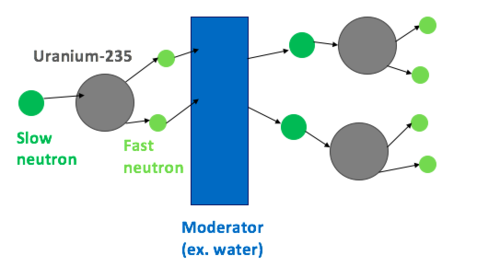
Role:
- Slows down fast-moving neutrons.
- Allows neutrons to be absorbed by U-235 nuclei.
- Helps maintain a steady chain reaction.
Why slowing neutrons is important:
- Fast neutrons are less likely to cause fission.
- Slow (thermal) neutrons are more effective.
Common moderator materials:
- Graphite
- Water
The Control Rods
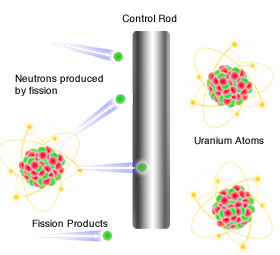
Role:
- Absorb excess neutrons.
- Control the rate of the chain reaction.
- Prevent the reaction from becoming too fast.
How they work:
- Lowered into the reactor → more neutrons absorbed.
- Raised out of the reactor → fewer neutrons absorbed.
Common control rod materials:
- Boron
- Cadmium
Comparison: Moderator vs Control Rods
| Feature | Moderator | Control rods |
|---|---|---|
| Main function | Slow down neutrons | Absorb neutrons |
| Effect on chain reaction | Helps sustain reaction | Controls reaction rate |
| Typical materials | Graphite, water | Boron, cadmium |
| Movement | Fixed in reactor | Moved in and out |
Why Both Are Needed
- The moderator increases the chance of fission.
- Control rods prevent the reaction becoming uncontrollable.
- Together they allow safe, continuous energy production.
Example
Explain why a moderator is required in a nuclear reactor using U-235 fuel.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Fission produces fast neutrons.
- Fast neutrons are less likely to cause fission.
- The moderator slows the neutrons.
- Slow neutrons are more likely to be absorbed by U-235.
- This allows the chain reaction to continue.
Example
Describe how control rods are used to reduce the power output of a nuclear reactor.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Control rods are lowered further into the reactor.
- More neutrons are absorbed.
- Fewer neutrons cause fission.
- The rate of the chain reaction decreases.
- The power output is reduced.
Role of Shielding Around a Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor produces large amounts of ionising radiation during fission. To protect people and the environment, the reactor is surrounded by shielding.
Key Statement
Statement: Shielding around a nuclear reactor is used to absorb ionising radiation and reduce exposure to safe levels.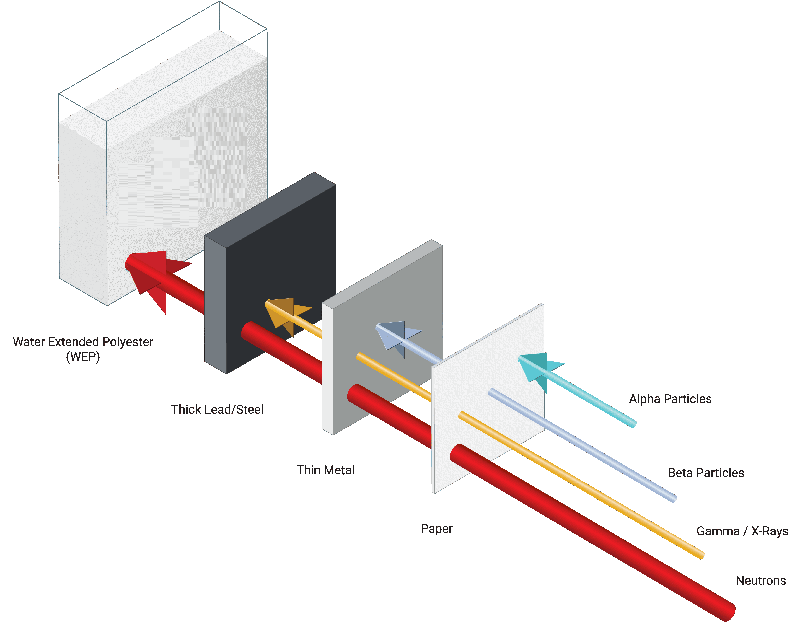
Key idea: Shielding prevents harmful radiation from escaping the reactor.
Why Shielding Is Needed
- Nuclear fission produces gamma radiation and neutrons.
- These radiations are highly penetrating.
- Unshielded radiation would be dangerous to humans.
Important: Shielding protects both reactor workers and the surrounding environment.
How Shielding Works
- Shielding materials absorb or scatter radiation.
- The intensity of radiation decreases as it passes through shielding.
- Thicker shielding provides greater protection.
Key idea: Radiation intensity decreases with increased absorption.
Materials Used for Shielding
| Material | Radiation reduced | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Gamma rays, neutrons | Thick, dense, contains hydrogen |
| Lead | Gamma rays | Very dense material |
| Water | Neutrons | Slows and absorbs neutrons |
Shielding and Reactor Safety
- Shielding surrounds the reactor core.
- It forms part of the reactor containment structure.
- It reduces radiation to background or safe levels outside the reactor.
Key idea: Shielding allows nuclear power to be used safely.
What Shielding Does NOT Do
- It does not slow down neutrons for fission (that is the moderator’s role).
- It does not control the reaction rate (that is the control rods’ role).
- It only protects by reducing radiation exposure.
Example
Explain why thick concrete shielding is placed around the core of a nuclear reactor.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Nuclear fission produces penetrating radiation.
- Concrete absorbs gamma rays and neutrons.
- Thick concrete greatly reduces radiation intensity.
- This protects workers and the environment.
Example
A nuclear reactor has insufficient shielding. Describe two possible dangers.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Ionising radiation could escape.
- Workers could receive harmful radiation doses.
- Radiation could damage living tissue.
- There could be long-term environmental contamination.
