Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.24–7.26 Nuclear Fusion, Stars as Energy Sources, and Fusion Conditions- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.24–7.26 Nuclear Fusion, Stars as Energy Sources, and Fusion Conditions- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.24–7.26 Nuclear Fusion, Stars as Energy Sources, and Fusion Conditions- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.24 describe nuclear fusion as the creation of larger nuclei resulting in a loss of mass from smaller nuclei, accompanied by a release of energy
7.25 know that fusion is the energy source for stars
7.26 explain why nuclear fusion does not happen at low temperatures and pressures, due to electrostatic repulsion of protons
Nuclear Fusion and Energy Release
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction in which small nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. During this process, some mass is lost and converted into energy.
Key Statement
Statement: Nuclear fusion is the creation of larger nuclei from smaller nuclei, resulting in a loss of mass that is accompanied by a release of energy.
Key idea: A small loss of mass produces a very large amount of energy.
What Happens During Nuclear Fusion
Step-by-step description:
- Two small nuclei move very close together.
- They overcome the repulsive force between them.
- The nuclei join to form a larger nucleus.
- The mass of the new nucleus is less than the total original mass.
- The missing mass is released as energy.
Loss of Mass in Fusion
- The total mass before fusion is slightly greater than after fusion.
- This difference is called the mass defect.
- The mass defect is converted into energy.
Key idea: Mass is converted into energy during fusion.
Energy Released in Fusion
- The energy released appears mainly as kinetic energy.
- The fusion products move at very high speeds.
- This kinetic energy can be transferred as heat.
Important: Fusion releases more energy per kilogram of fuel than fission.
Conditions Required for Fusion
- Extremely high temperature.
- Extremely high pressure.
- Nuclei must have enough energy to overcome repulsion.
Key idea: These conditions occur naturally in stars.
Where Nuclear Fusion Occurs
- In the Sun and other stars.
- Hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium.
- This provides energy that makes stars shine.
Example
Explain why nuclear fusion releases energy even though no fuel is burned.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Fusion joins small nuclei to form a larger nucleus.
- The mass of the product nucleus is less than the original mass.
- The missing mass is converted into energy.
- This energy is released during the fusion reaction.
Example
Describe how nuclear fusion in the Sun provides energy and explain why high temperatures are required.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium.
- A small amount of mass is lost.
- This mass is converted into energy.
- High temperatures give nuclei enough energy to overcome repulsion.
Nuclear Fusion as the Energy Source for Stars
Nuclear fusion is the process that provides the energy output of stars, including the Sun. This energy is released from the nuclei of atoms under extreme conditions.
Key Statement
Statement: Nuclear fusion is the energy source for stars.
Key idea: Stars shine because energy is released during fusion reactions in their cores.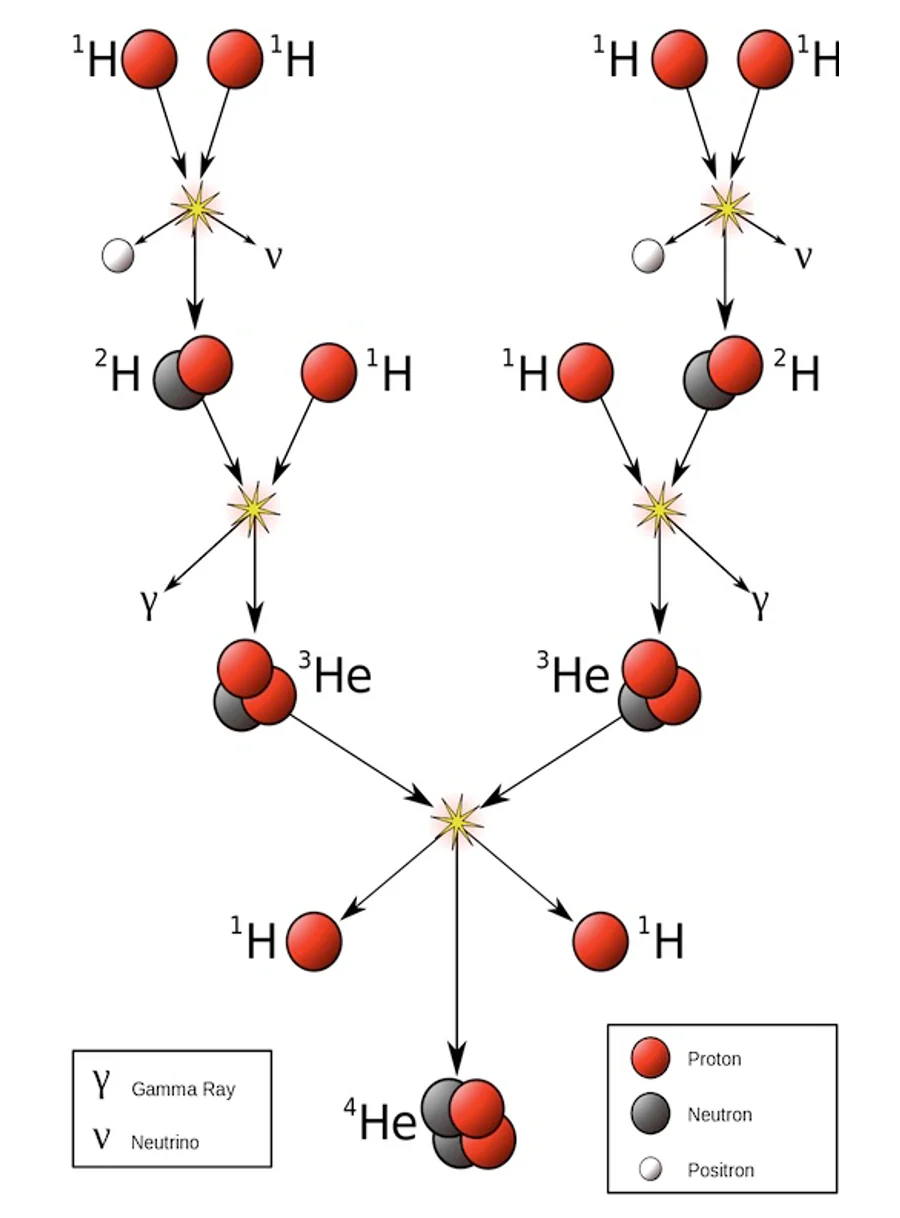
Fusion Reactions in Stars
- Stars contain very hot gases called plasma.
- Hydrogen nuclei move at extremely high speeds.
- These nuclei collide and fuse together.
- A larger nucleus is formed.
Important: In most stars, hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium.
Why Fusion Releases Energy in Stars
- The helium nucleus has less mass than the original hydrogen nuclei.
- The missing mass is converted into energy.
- This energy is released mainly as kinetic energy.
Key idea: A very small loss of mass produces a very large amount of energy.
Conditions Inside a Star
- Extremely high temperature (millions of degrees).
- Extremely high pressure.
- Strong gravitational forces.
Why these conditions are needed:
- They allow nuclei to overcome repulsive forces.
- This makes fusion possible.
How Fusion Energy Reaches Earth
- Energy produced in the core moves outward.
- It eventually reaches the surface of the star.
- Energy is emitted as light and heat.
Key idea: Sunlight is energy released from nuclear fusion.
Example
Explain why nuclear fusion is the energy source of the Sun.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Hydrogen nuclei fuse together in the Sun’s core.
- This forms helium nuclei.
- The mass of the products is less than the original mass.
- The missing mass is converted into energy.
- This energy is released as light and heat.
Example
Explain why nuclear fusion can occur in stars but is difficult to carry out on Earth.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Stars have extremely high temperatures and pressures.
- Gravity provides strong confinement.
- These conditions allow nuclei to overcome repulsion.
- Such conditions are difficult to achieve and maintain on Earth.
Why Nuclear Fusion Does Not Occur at Low Temperatures and Pressures
Nuclear fusion requires extremely high temperatures and pressures. At low temperatures and pressures, fusion cannot occur because of the electrostatic repulsion between protons.
Key Statement
Statement: Nuclear fusion does not happen at low temperatures and pressures because positively charged protons repel each other, preventing them from getting close enough to fuse.
Key idea: Fusion requires nuclei to overcome electrostatic repulsion.
Electrostatic Repulsion Between Protons

- Protons have a positive electric charge.
- Like charges repel each other.
- This repulsion is called electrostatic repulsion.
Important: Electrostatic repulsion acts over relatively long distances compared to nuclear forces.
What Is Needed for Fusion to Occur
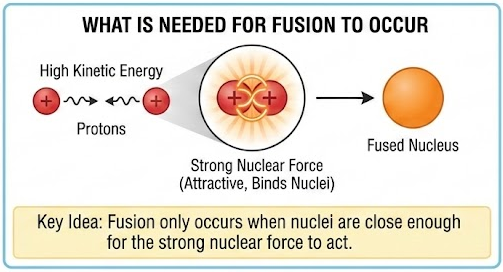
- Protons must get extremely close together.
- At very short distances, the strong nuclear force becomes attractive.
- This force can bind the nuclei together.
Key idea: Fusion only occurs when nuclei are close enough for the strong nuclear force to act.
Why Low Temperature Prevents Fusion

- Low temperature means low kinetic energy.
- Protons move slowly.
- They cannot overcome electrostatic repulsion.
Result: The protons repel each other before they can fuse.
Why Low Pressure Prevents Fusion
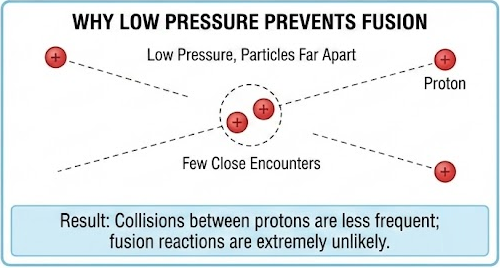
- Low pressure means particles are far apart.
- Collisions between protons are less frequent.
- Few close encounters occur.
Result: Fusion reactions are extremely unlikely.
Conditions Required to Overcome Repulsion
- Very high temperature → high kinetic energy.
- Very high pressure → nuclei forced close together.
- Strong gravitational forces (in stars).
Key idea: These conditions exist in the cores of stars.
Example
Explain why nuclear fusion does not occur at room temperature.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- At room temperature, protons have low kinetic energy.
- They cannot overcome electrostatic repulsion.
- The protons do not get close enough to fuse.
- Therefore, fusion does not occur.
Example
Stars have very high core temperatures and pressures. Explain why both are needed for nuclear fusion.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- High temperature gives protons high kinetic energy.
- This helps overcome electrostatic repulsion.
- High pressure forces protons close together.
- This allows the strong nuclear force to act.
- Fusion can then occur.
