Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.8 Balancing Nuclear Equations- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.8 Balancing Nuclear Equations- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.8 Balancing Nuclear Equations- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.8 understand how to balance nuclear equations in terms of mass and charge
Balancing Nuclear Equations
Nuclear equations describe radioactive decay and nuclear reactions. These equations must be balanced so that both mass number and charge are conserved.
Key Principle
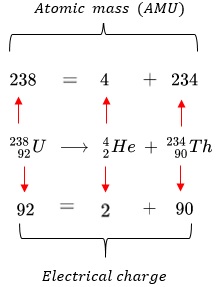
Statement: In a nuclear equation, the total mass number and the total atomic (proton) number must be the same on both sides of the equation.
Key idea: Nuclear reactions obey conservation laws.
What Must Be Balanced
- Mass number (A) → total number of nucleons
- Atomic number (Z) → total charge (number of protons)
Important: Electrons involved in beta decay are included in charge balancing.
General Nuclear Notation
\( \mathrm{^{A}_{Z}X} \)
- \( \mathrm{A} \) = mass number
- \( \mathrm{Z} \) = atomic (proton) number
- \( \mathrm{X} \) = element symbol
Balancing Alpha Decay
Alpha particle:
\( \mathrm{^4_2\alpha} \)
Rule:
- Mass number decreases by 4
- Atomic number decreases by 2
General form:
\( \mathrm{^{A}_{Z}X \rightarrow ^{A-4}_{Z-2}Y + ^4_2\alpha} \)
Balancing Beta (β⁻) Decay
Beta particle:
\( \mathrm{^0_{-1}\beta} \)
Rule:
- Mass number remains unchanged
- Atomic number increases by 1
General form:
\( \mathrm{^{A}_{Z}X \rightarrow ^{A}_{Z+1}Y + ^0_{-1}\beta} \)
Balancing Gamma Decay
Gamma ray:
\( \mathrm{^0_0\gamma} \)
Rule:
- No change in mass number
- No change in atomic number
General form:
\( \mathrm{^{A}_{Z}X^* \rightarrow ^{A}_{Z}X + \gamma} \)
Balancing Neutron Emission
Neutron:
\( \mathrm{^1_0n} \)
Rule:
- Mass number decreases by 1
- Atomic number unchanged
General form:
\( \mathrm{^{A}_{Z}X \rightarrow ^{A-1}_{Z}Y + ^1_0n} \)
Step-by-Step Method (Exam Technique)
- Write the incomplete nuclear equation.
- Add up mass numbers on both sides.
- Add up atomic numbers on both sides.
- Adjust the unknown nucleus so both totals match.
- Check both mass and charge are conserved.
Example
Complete and balance the following nuclear equation:
\( \mathrm{^{210}_{84}Po \rightarrow \; ? \; + ^4_2\alpha} \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Mass number:
\( \mathrm{210 – 4 = 206} \)
Atomic number:
\( \mathrm{84 – 2 = 82} \)
Balanced equation:
\( \mathrm{^{210}_{84}Po \rightarrow ^{206}_{82}Pb + ^4_2\alpha} \)
Example
A nucleus undergoes beta decay and changes from \( \mathrm{^{14}_{6}C} \) to nitrogen. Write the balanced nuclear equation.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Mass number stays the same:
\( \mathrm{A = 14} \)
Atomic number increases by 1:
\( \mathrm{Z = 7} \)
Balanced equation:
\( \mathrm{^{14}_{6}C \rightarrow ^{14}_{7}N + ^0_{-1}\beta} \)
