Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.9 Detection of Ionising Radiation- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.9 Detection of Ionising Radiation- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -7.9 Detection of Ionising Radiation- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
7.9 know that photographic film or a Geiger–Müller detector can detect ionising radiations
Detecting Ionising Radiation
Ionising radiation cannot be seen directly, but it can be detected using suitable devices. Two commonly used detectors are photographic film and the Geiger–Müller detector.
Key Statement
Statement: Photographic film and a Geiger–Müller detector can be used to detect ionising radiations.
Key idea: These detectors work because ionising radiation affects matter.
Photographic Film 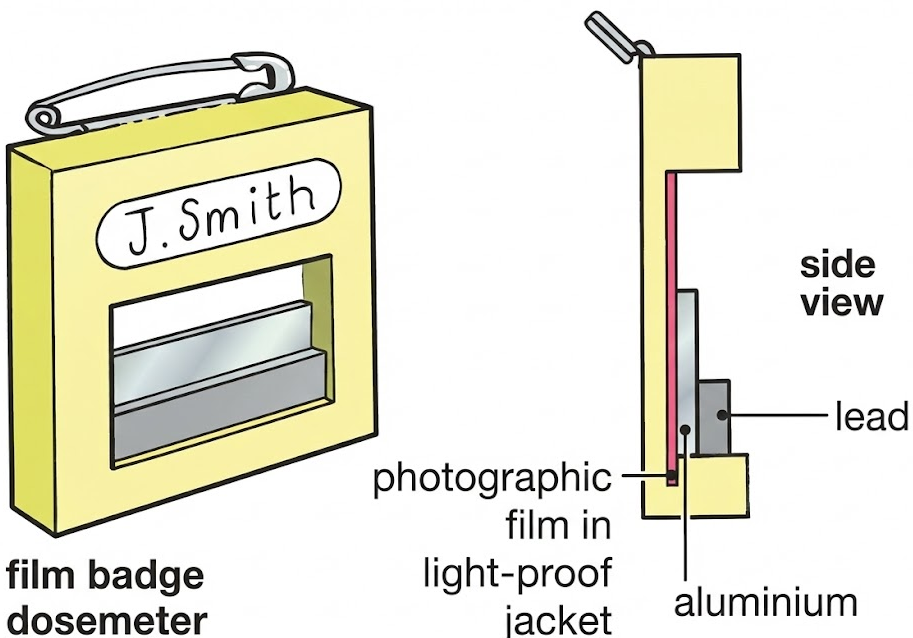
How it works:
- Photographic film is sensitive to ionising radiation.
- Radiation darkens the film by ionising atoms in the emulsion.
- Greater exposure produces darker film.
Uses:
- Monitoring radiation exposure of workers.
- Personal dosimeters worn over long periods.
Limitation:
- Does not give immediate readings.
- Must be developed to see results.
Geiger–Müller Detector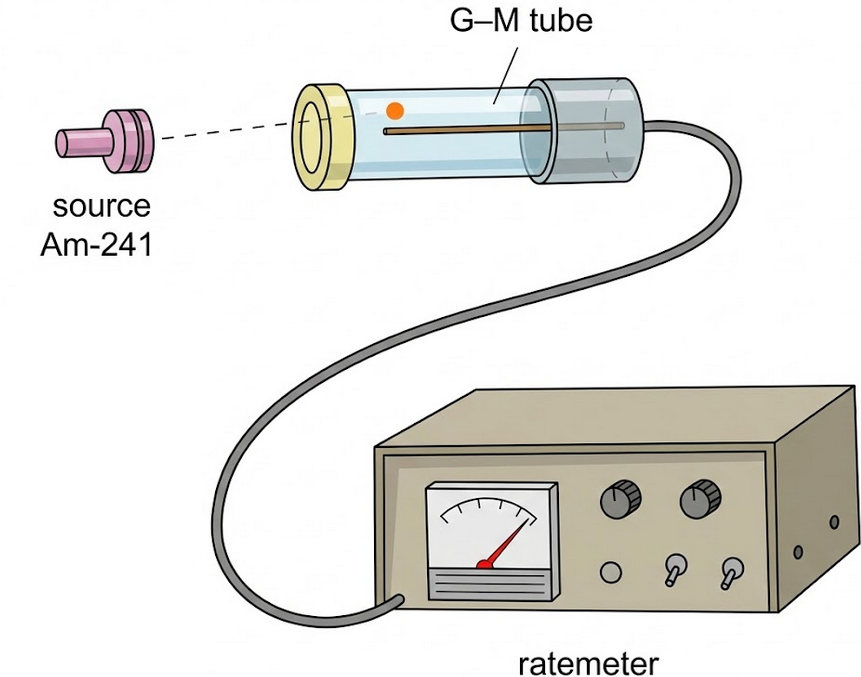
How it works:
- Contains gas at low pressure inside a tube.
- Ionising radiation enters the tube.
- The gas becomes ionised.
- This produces an electrical pulse.
Output:
- Each pulse represents a detection event.
- Pulses can be counted electronically.
- Results are obtained immediately.
Key idea: Higher count rate → higher radiation intensity.
Comparing the Two Detectors
- Photographic film gives cumulative exposure.
- Geiger–Müller detector gives instant readings.
- Both rely on ionisation.
Example
A laboratory technician wears a photographic film badge while working with radioactive sources. Explain why this method is suitable for monitoring exposure.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The badge records cumulative radiation exposure.
- Ionising radiation darkens the film.
- The darkness indicates total exposure over time.
- This helps ensure safe working limits are not exceeded.
Example
A Geiger–Müller detector is used to investigate radiation near a source. Explain why it is more suitable than photographic film for this experiment.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The detector gives immediate readings.
- The count rate changes as distance changes.
- This allows real-time measurements.
- Photographic film cannot show instant results.
