Edexcel iGCSE Physics -8.5 Orbits of Comets, Moons, and Planets- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -8.5 Orbits of Comets, Moons, and Planets- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel iGCSE Physics -8.5 Orbits of Comets, Moons, and Planets- Study Notes -Edexcel iGCSE Physics – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
update
Differences in the Orbits of Comets, Moons, and Planets
Although comets, moons, and planets all move in orbits due to gravitational force, their orbits differ in shape, size, and the object they orbit.
Key Statement
Statement: Moons orbit planets, planets orbit the Sun in near-circular paths, and comets orbit the Sun in highly elliptical paths.
Key idea: The shape of an orbit depends on the object’s speed and distance from the body providing the gravitational force.
Orbits of Moons

- Moons orbit planets.
- The orbit is usually nearly circular.
- The gravitational force comes from the planet.
- The distance from the planet is relatively small.
Key idea: The planet’s gravity provides the centripetal force keeping the moon in orbit.
Orbits of Planets

- Planets orbit the Sun.
- Planetary orbits are almost circular.
- The Sun’s large mass provides a strong gravitational force.
- Planets remain at roughly constant distance from the Sun.
Key idea: Stable, near-circular orbits result from a balance between forward motion and gravitational attraction.
Orbits of Comets
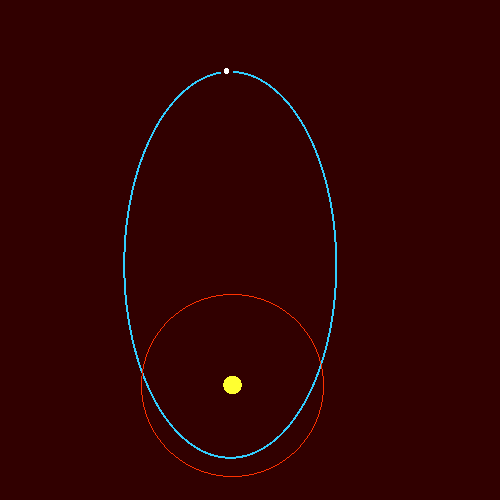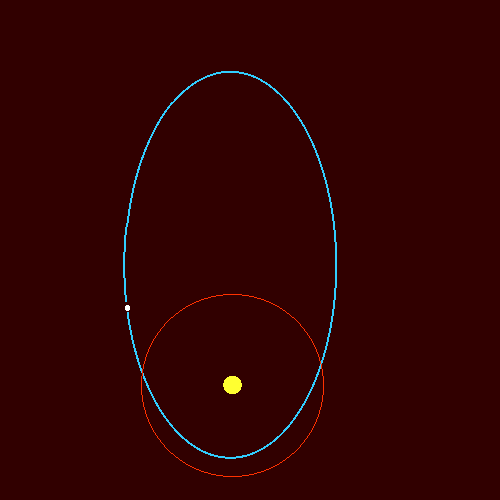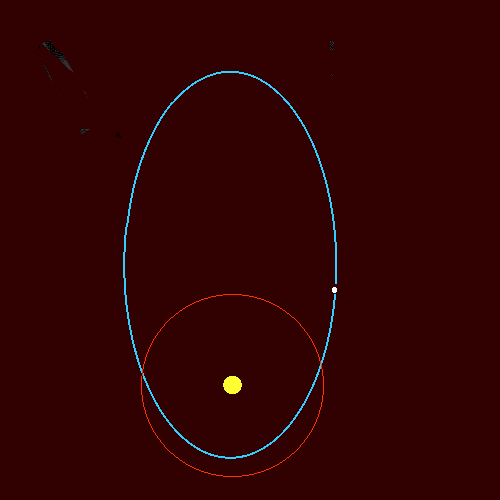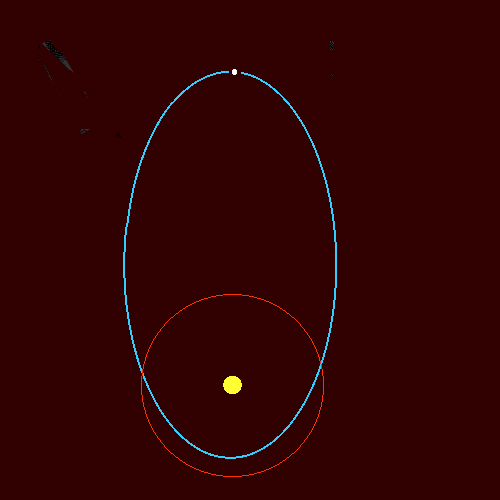
- Comets orbit the Sun.
- Their orbits are highly elliptical.
- They travel very close to the Sun and then very far away.
- Their speed changes greatly during the orbit.

Key idea: Comets move fastest when close to the Sun and slowest when far away.
Comparison of Orbits
| Feature | Moons | Planets | Comets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object orbited | Planet | Sun | Sun |
| Orbit shape | Nearly circular | Nearly circular | Highly elliptical |
| Distance variation | Small | Small | Very large |
| Speed change | Almost constant | Almost constant | Large variation |
Why These Differences Occur
- Planets and moons formed in rotating discs, leading to circular paths.
- Comets originate from distant regions of the solar system.
- Comets have lower average speeds and weaker gravitational binding.
Key idea: Weaker gravitational control leads to more elongated orbits.
Example
Explain why the orbit of a comet is highly elliptical while the orbit of a planet is nearly circular.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- Comets originate far from the Sun.
- They have a wide range of distances from the Sun.
- The Sun’s gravitational force changes greatly along the orbit.
- This results in a highly elliptical path.
- Planets remain at nearly constant distance, giving circular orbits.
Example
A moon and a comet both move under gravitational attraction. Explain why the moon’s speed remains nearly constant while the comet’s speed varies greatly.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
- The moon’s distance from its planet is nearly constant.
- The gravitational force on the moon is almost constant.
- This leads to nearly constant orbital speed.
- The comet’s distance from the Sun changes greatly.
- The gravitational force changes, causing large speed variation.
