Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.10 Atherosclerosis - Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.10 Atherosclerosis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.10 Atherosclerosis- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand the course of events that leads to atherosclerosis (endothelial dysfunction, inflammatory response, plaque formation, raised blood pressure)
Atherosclerosis
🌱 Introduction
Atherosclerosis is the progressive narrowing and hardening of arteries caused by the build-up of plaques, which can affect blood flow and raise blood pressure.
🧩 Course of Events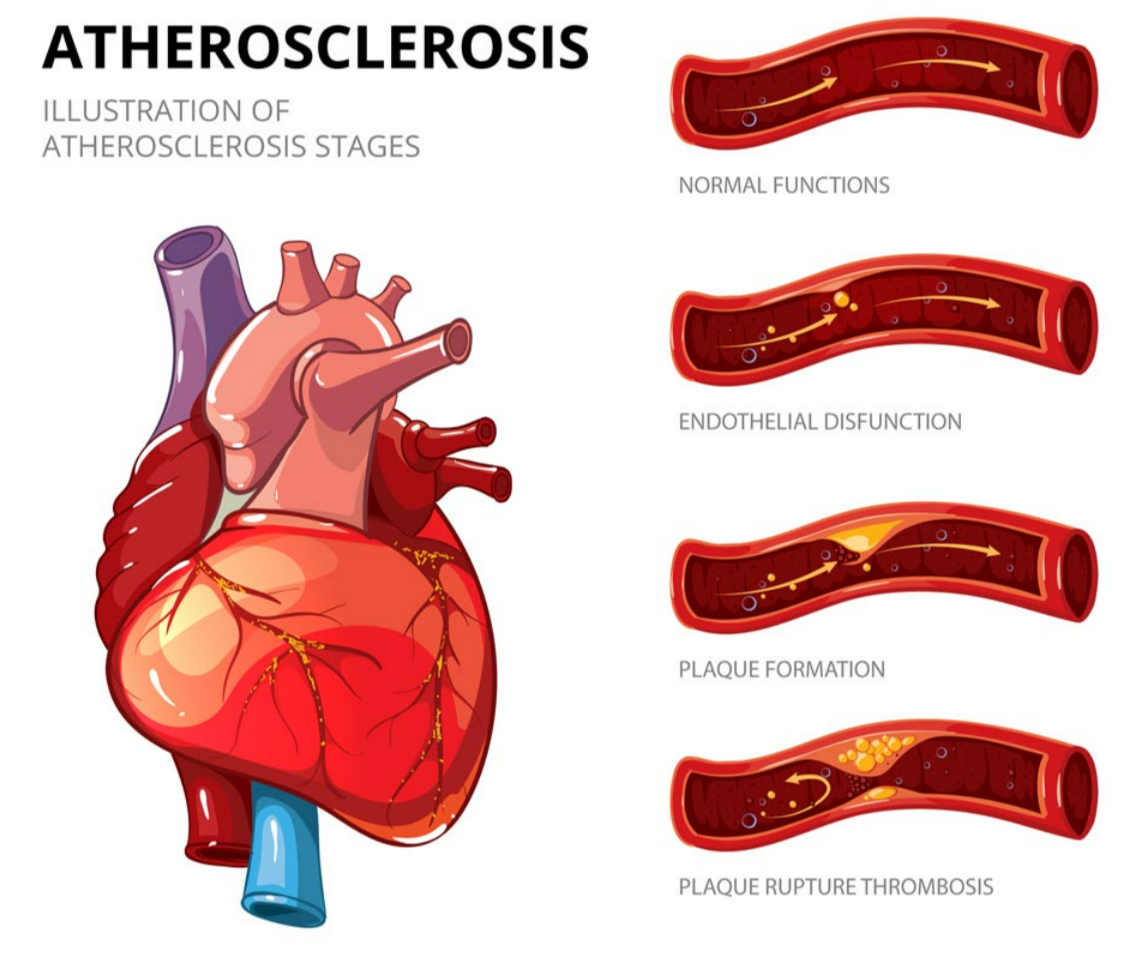
- Endothelial Dysfunction
The inner lining of arteries (endothelium) is damaged.
Causes include high blood pressure, smoking, toxins, or high blood cholesterol.
Damage allows lipids (fats) to enter the artery wall. - Inflammatory Response
The body reacts to lipid deposits as harmful.
White blood cells (macrophages) move in and ingest lipids → form foam cells.
Chemicals released during inflammation further damage arterial walls. - Plaque Formation
Lipids, fibrous tissue, calcium, and dead cells accumulate → form atheromatous plaques.
Plaques narrow the artery, making it less flexible. - Raised Blood Pressure
Narrowed arteries → blood flows under higher pressure.
High pressure can damage arteries further and increase the risk of clot formation.
⚡ Key Points
- Atherosclerosis starts with endothelial damage
- Inflammation promotes plaque development
- Plaques reduce artery diameter → increases blood pressure
- Ruptured plaques → blood clots → can cause heart attack or stroke
💡 Quick Recap
| Step | Event |
|---|---|
| 1 | Endothelial damage |
| 2 | Inflammatory response (macrophages → foam cells) |
| 3 | Plaque formation (lipids + fibrous tissue + calcium) |
| 4 | Raised blood pressure → risk of clots & cardiovascular events |
