Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.11 Blood Clotting - Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.11 Blood Clotting- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.11 Blood Clotting- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- understand the blood clotting process (thromboplastin release, conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin) and its role in cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Blood Clotting & Cardiovascular Disease
🌱 Introduction
Blood clotting (haemostasis) is a vital process that prevents excessive blood loss after injury. However, abnormal clotting inside blood vessels can lead to cardiovascular disease (CVD).
🧩 Stages of Blood Clotting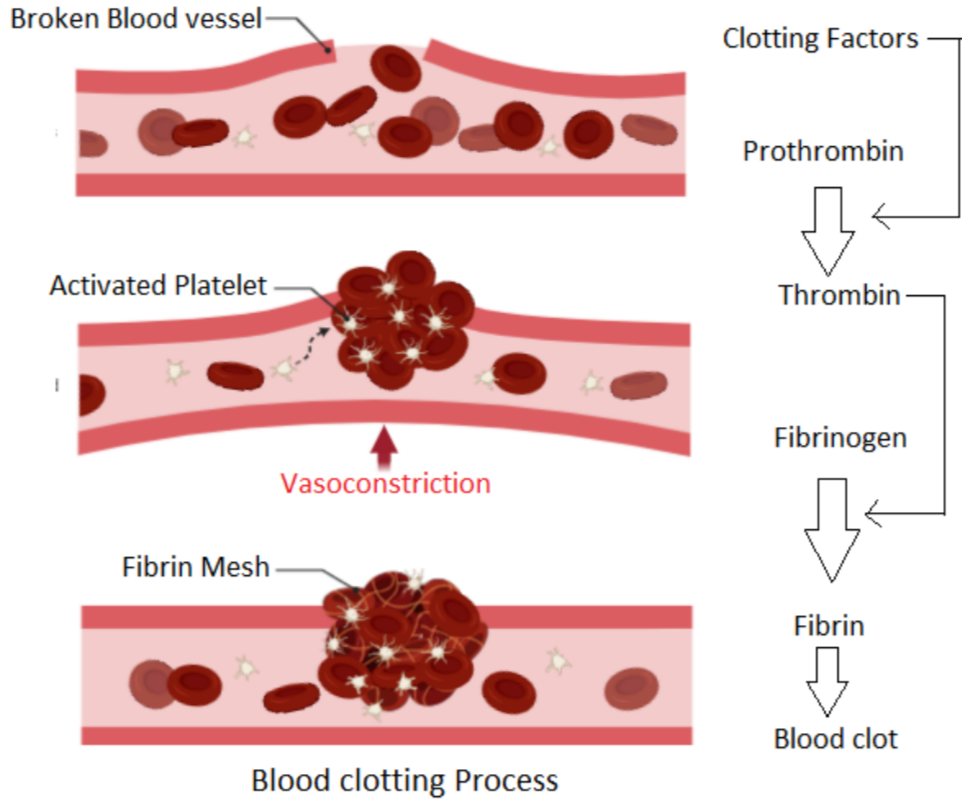
- Thromboplastin Release
When a blood vessel is damaged, cells in the vessel wall release thromboplastin (an enzyme).
Thromboplastin initiates a chain reaction that leads to clot formation. - Conversion of Prothrombin to Thrombin
Thromboplastin, along with calcium ions, converts prothrombin (a plasma protein) into thrombin (an active enzyme). - Conversion of Fibrinogen to Fibrin
Thrombin converts fibrinogen (soluble protein in plasma) into fibrin (insoluble threads).
Fibrin threads form a mesh, trapping red blood cells and platelets → blood clot forms.
⚡ Role in Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
- Normal clotting: protects the body after injury.
- Abnormal clotting inside arteries (especially in narrowed arteries due to atherosclerosis) can:
- Block blood flow → heart attack or stroke.
- Cause ischemia (lack of oxygen to tissues).
- Risk factors: smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, inactivity.
💡 Quick Recap
| Stage | Event |
|---|---|
| 1 | Thromboplastin release → starts clotting cascade |
| 2 | Prothrombin → Thrombin (with Ca²⁺ ions) |
| 3 | Fibrinogen → Fibrin → mesh traps blood cells → clot |
| CVD Link | Abnormal clots in arteries → blocked blood flow, heart attack, stroke |
