Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.13 Dietary Antioxidants & CVD- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.13 Dietary Antioxidants & CVD- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.13 Dietary Antioxidants & CVD- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 1.13 understand the link between dietary antioxidants and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Understanding the Link Between Dietary Antioxidants and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
🌱 Introduction
CVD often begins with damage to the inner lining (endothelium) of arteries.
This damage is worsened by free radicals – unstable molecules that attack cell membranes and DNA.
Antioxidants in our diet protect the body from these free radicals, helping lower the risk of atherosclerosis and CVD.
⚛️ What Are Free Radicals?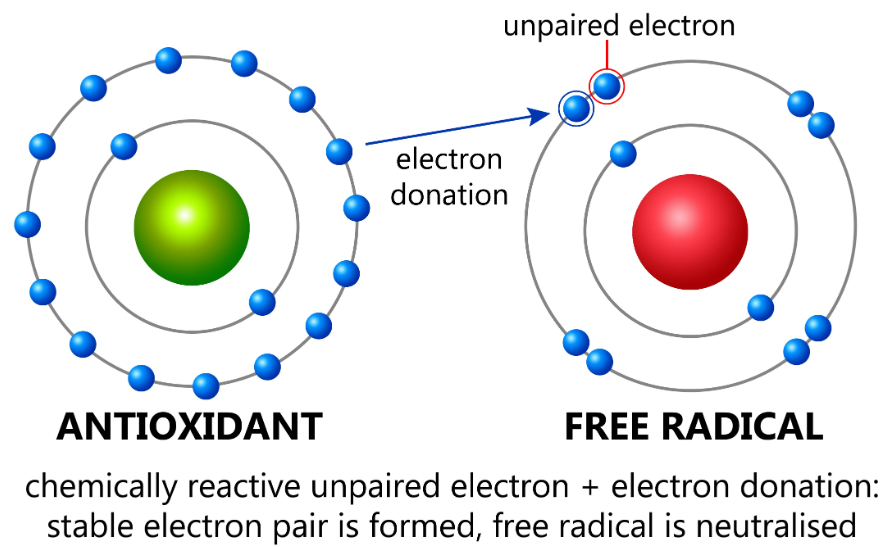
- Free radicals = atoms or molecules with unpaired electrons.
- Formed naturally during metabolism (respiration) or from pollution, smoking, radiation.
- Because they are unstable, they oxidize (damage) cell components such as:
- Lipids in cell membranes
- Proteins
- DNA
- Endothelial cells of blood vessels
Think: “Free radicals = rust for your arteries.”
🍊 What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are molecules that neutralize free radicals by donating electrons without becoming unstable themselves.
This prevents oxidative damage to cells and tissues.
🧩 Major Dietary Antioxidants
| Nutrient | Common Sources |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, strawberries, peppers |
| Vitamin E | Nuts, seeds, vegetable oils |
| Beta-carotene (provitamin A) | Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach |
| Polyphenols | Green tea, dark chocolate, berries |
❤️ How Antioxidants Reduce CVD Risk
- Protect Endothelium: Prevent oxidation of arterial lining → less endothelial dysfunction.
- Reduce LDL Oxidation: Stops oxidized LDL from sticking → slows plaque formation.
- Prevent Inflammation: Free radicals trigger inflammation; antioxidants lower it → arteries stay flexible.
- Improve HDL Function: Enhances HDL → better cholesterol removal from arteries.
📊 Summary Table
| Process | Without Antioxidants | With Antioxidants |
|---|---|---|
| Free radical formation | High | Neutralized |
| Endothelial damage | Increases | Reduced |
| LDL oxidation | Prominent | Prevented |
| Atherosclerosis risk | Increases | Decreases |
| Overall CVD risk | High | Lower |
⚡ Quick Recap
Key Idea: “Free radicals cause oxidation → antioxidants stop oxidation → healthier arteries.”
Good Antioxidant Sources: Citrus fruits, Berries, Nuts, Green tea, Leafy greens
Simple Rule: More antioxidants = less oxidation = lower CVD risk.
