Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.8 The Cardiac Cycle - Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.8 The Cardiac Cycle- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.8 The Cardiac Cycle- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- know the cardiac cycle (atrial systole, ventricular systole and cardiac diastole) and relate the structure and operation of the mammalian heart, including the major blood vessels, to its function
The Cardiac Cycle & Mammalian Heart
🌱 Introduction
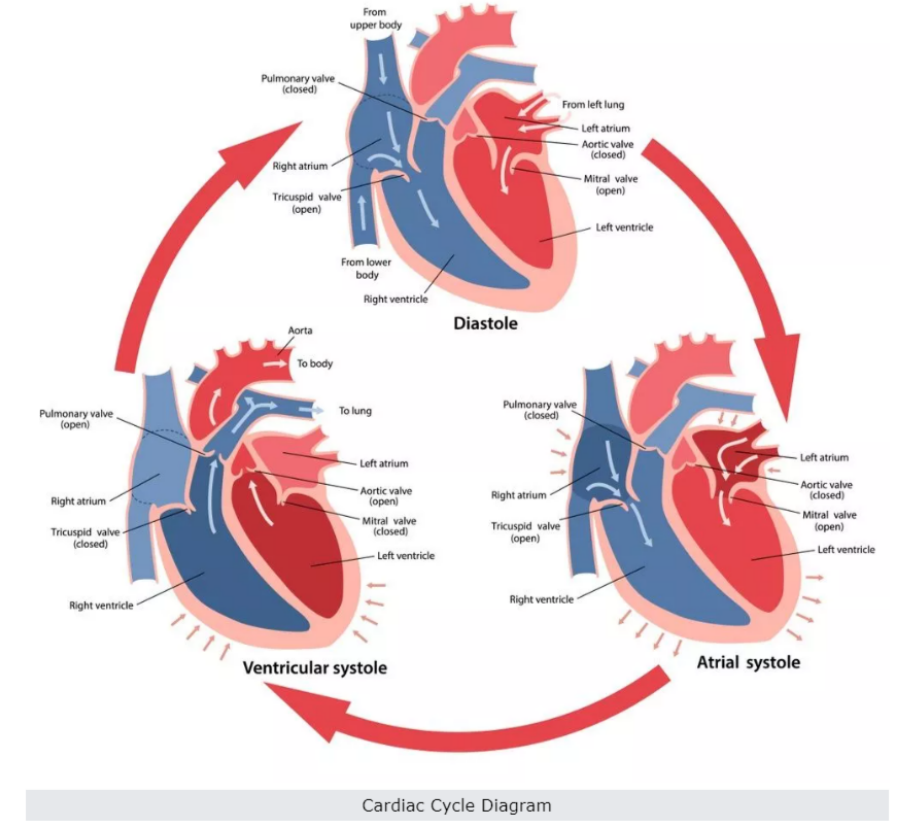
The heart is a muscular pump that moves blood through the body.
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in one heartbeat: atrial systole → ventricular systole → cardiac diastole.
Major blood vessels are linked structurally to support blood flow efficiently.
🧩 Cardiac Cycle Stages
- Atrial Systole
Atria contract → push blood into the ventricles
AV (atrioventricular) valves open, semilunar valves closed
Ventricles are relaxed - Ventricular Systole
Ventricles contract → push blood into arteries (aorta & pulmonary artery)
AV valves close, semilunar valves open
Atria relax, filling with blood from veins - Cardiac Diastole
Heart muscles relax → chambers refill with blood
AV valves open, semilunar valves closed
Ensures continuous circulation
🩺 Structure of Mammalian Heart & Relation to Function
| Feature | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Chambers | 2 atria (thin walls), 2 ventricles (thicker walls, left thicker than right) | Separate oxygenated & deoxygenated blood; thicker walls in ventricles → pump blood under high pressure |
| Valves | AV valves (tricuspid & bicuspid), semilunar valves (aortic & pulmonary) | Prevent backflow, ensure one-way blood flow |
| Major Blood Vessels | – Vena cava → brings deoxygenated blood to right atrium – Pulmonary artery → sends blood to lungs – Pulmonary vein → returns oxygenated blood to left atrium – Aorta → carries oxygenated blood to body | Connect heart to circulatory system efficiently |
| Muscular walls | Left ventricle thickest, right thinner | Generate high pressure to circulate blood; left ventricle pumps to whole body, right pumps to lungs |
| Septum | Muscular wall between left & right sides | Prevents mixing of oxygenated & deoxygenated blood |
⚡ Key Points
- Cardiac cycle ensures continuous, unidirectional blood flow
- Systole: contraction (atria → ventricles → arteries)
- Diastole: relaxation (filling phase)
- Structure of heart & vessels matches function of pumping blood efficiently
💡 Quick Recap
Atrial systole: atria contract → ventricles fill
Ventricular systole: ventricles contract → blood to arteries
Diastole: heart relaxes → chambers refill
Left ventricle thicker: pumps blood to entire body
Valves: prevent backflow → one-way flow
