Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.9 The Role of Haemoglobin - Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.9 The Role of Haemoglobin- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -1.9 The Role of Haemoglobin- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- (i) understand the role of haemoglobin in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- (ii) understand the oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin, the Bohr effect and the significance of the oxygen affinity of fetal haemoglobin compared with adult haemoglobin
Haemoglobin & Gas Transport
🌱 Introduction
Haemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen (O₂) from lungs to tissues and helping carry carbon dioxide (CO₂) from tissues back to lungs.
🧩 Role of Haemoglobin
- Oxygen Transport
Each haemoglobin molecule can bind up to 4 oxygen molecules.
Forms oxyhaemoglobin in high O₂ environments (lungs).
Releases O₂ in low O₂ environments (tissues). - Carbon Dioxide Transport
 CO₂ binds to haemoglobin forming carbaminohaemoglobin.
CO₂ binds to haemoglobin forming carbaminohaemoglobin.
Helps carry CO₂ from tissues to lungs for exhalation.
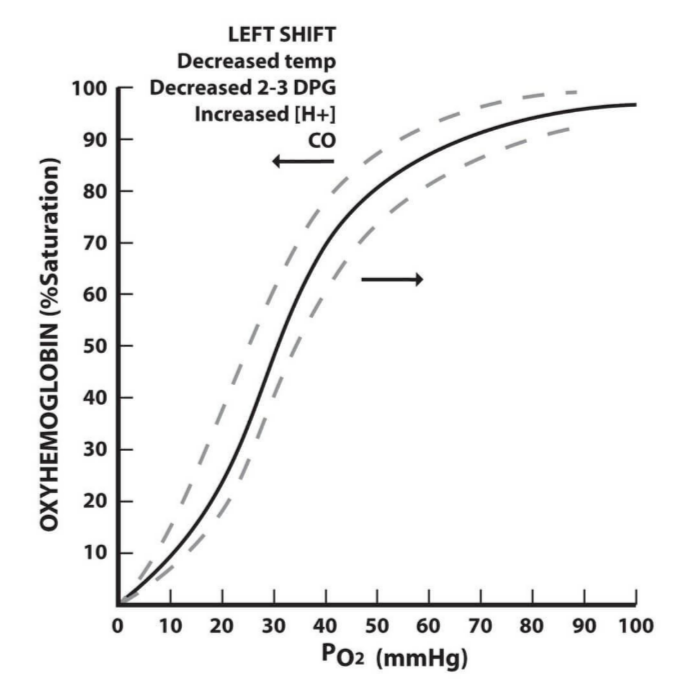
📈 Oxygen Dissociation Curve
- Graph shows percentage saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen vs partial pressure of O₂ (pO₂).
- Sigmoid (S-shaped) curve:
– At high pO₂ → haemoglobin binds O₂ readily (lungs)
– At lower pO₂ → haemoglobin releases O₂ easily (tissues) - Bohr Effect
Increased CO₂ or lower pH → haemoglobin releases more O₂.
Significance: tissues with high respiration (more CO₂) get more oxygen.
👶 Fetal vs Adult Haemoglobin
| Feature | Adult Haemoglobin | Fetal Haemoglobin | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen affinity | Lower | Higher | Fetus can absorb O₂ from mother’s blood efficiently |
| Dissociation curve | Right-shifted | Left-shifted | Left shift → higher O₂ binding at lower pO₂ |
⚡ Key Points
- Haemoglobin = main O₂ & CO₂ transporter
- Oxygen dissociation curve shows how O₂ loading/unloading changes with pO₂
- Bohr effect helps active tissues get more O₂
- Fetal haemoglobin has higher O₂ affinity → ensures effective O₂ transfer from mother
💡 Quick Recap
Haemoglobin: binds O₂ in lungs, releases in tissues
CO₂ transport: forms carbaminohaemoglobin
Bohr effect: ↑ CO₂ → more O₂ released
Fetal Hb: binds O₂ better than adult → fetal survival
