Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.14 Mutations- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.14 Mutations- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.14 Mutations- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 2.14 (i) understand how errors in DNA replication can give rise to mutations (substitution, insertion and deletion of bases)
(ii) know that some mutations will give rise to cancer or genetic disorders, but that many mutations will have no observable effect
Mutations – Errors in DNA Replication
🌱 Introduction
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence.
They usually occur due to errors in DNA replication or external factors like radiation or chemicals.
Mutations can affect proteins, leading to changes in cell function.
(i) Types of Mutations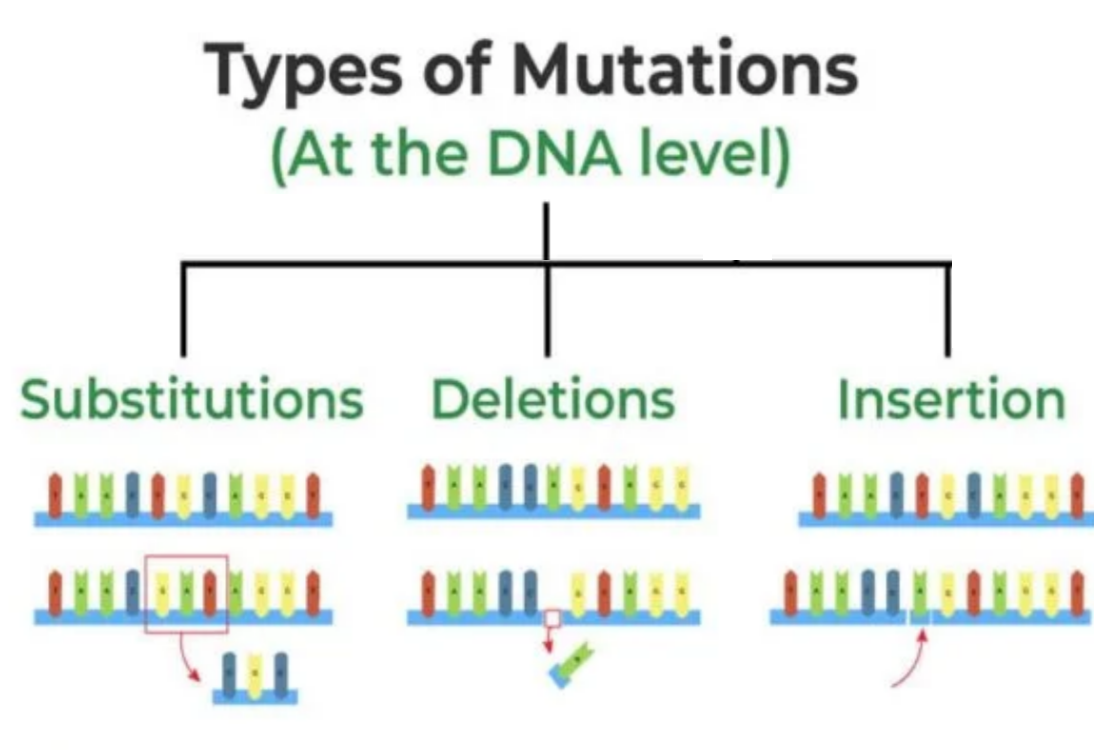
Mutations arise when bases are incorrectly copied during replication:
- Substitution (Point Mutation): One base is replaced by another.
Example: A → G
Effect: May change one amino acid (missense) or may have no effect (silent mutation). - Insertion: Extra base(s) added.
Shifts reading frame → frameshift mutation.
Usually drastic effect, changing all downstream codons. - Deletion: One or more bases removed.
Also frameshift → changes all downstream amino acids.
(ii) Consequences of Mutations
| Type of Effect | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Harmful | Can disrupt protein function → disease or cancer | Mutation in p53 gene → cancer |
| Neutral / No effect | Mutation does not change amino acid or protein function | Silent mutation in non-critical region |
| Beneficial (rare) | Provides evolutionary advantage | Mutation in bacteria → antibiotic resistance |
Many mutations have no observable effect due to the degenerate nature of the genetic code or occur in non-coding DNA.
Some mutations cause genetic disorders (e.g., cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia).
Mutations in regulatory genes can cause uncontrolled cell division → cancer.
💡 Memory Tip
- Substitution → swap
- Insertion → add
- Deletion → remove
- Frameshift → reading frame changes → bigger effect
🧠 Quick Recap
| Feature | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Mutation | Change in DNA sequence due to replication error |
| Substitution | One base replaced, may or may not affect protein |
| Insertion / Deletion | Adds/removes bases, usually frameshift → major effect |
| Effect on organism | Neutral, harmful (disease/cancer), or rarely beneficial |
| Cause | DNA replication errors, mutagens, radiation, chemicals |
In short: Errors in DNA replication can alter the genetic code. Some mutations are harmless, while others can cause disorders or cancer, depending on their location and type.
