Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.9 Nucleotides, DNA & RNA, Base Pairing- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.9 Nucleotides, DNA & RNA, Base Pairing- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -2.9 Nucleotides, DNA & RNA, Base Pairing- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 2.9 (i) know the basic structure of mononucleotides (deoxyribose or ribose linked to a phosphate and a base, including thymine, uracil, adenine, cytosine or guanine) and the structures of DNA and RNA (polynucleotides composed of mononucleotides linked by condensation reactions to form phosphodiester bonds)
(ii) know how complementary base pairing and the hydrogen bonding between two complementary strands are involved in the formation of the DNA double helix
Nucleic Acids – Mononucleotides, DNA & RNA
🌱 (i) Structure of Mononucleotides
Mononucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids.
Components of a Mononucleotide: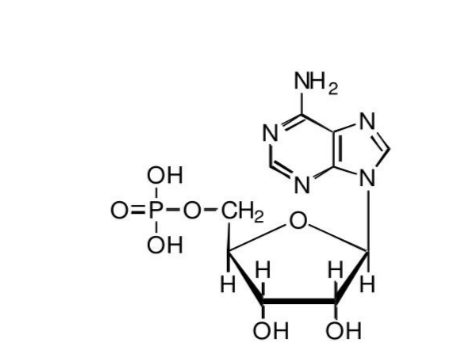
- Sugar: Ribose in RNA; Deoxyribose in DNA (lacks 1 oxygen at 2′ carbon)
- Phosphate group: Attached to 5′ carbon of sugar
- Nitrogenous base: Attached to 1′ carbon of sugar
- DNA bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
- RNA bases: Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
General Formula: Phosphate – Sugar – Base
Example: Deoxyribonucleotide = deoxyribose + phosphate + base
Polynucleotide Formation:
Mononucleotides link together to form polynucleotides (DNA or RNA).
- Condensation reaction between phosphate of one nucleotide and sugar of another → phosphodiester bond
- Structure: sugar-phosphate backbone (repeating units), bases stick out from backbone
🌱 (ii) DNA Structure & Complementary Base Pairing
Double Helix: DNA is made of two polynucleotide strands twisted into a double helix. Strands are antiparallel → one runs 5′ → 3′, other 3′ → 5′.
Complementary Base Pairing:
- Hydrogen bonds hold strands together:
- Adenine (A) ↔ Thymine (T) → 2 H-bonds
- Guanine (G) ↔ Cytosine (C) → 3 H-bonds
- Ensures accurate replication & genetic coding
DNA vs RNA:
| Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Strands | Double | Single |
| Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
| Function | Genetic storage | Protein synthesis & regulation |
Key Points:
- Mononucleotides = phosphate + sugar + base
- Polymers = phosphodiester bonds link nucleotides
- DNA = double helix, complementary strands, hydrogen-bonded bases
- Base pairing: A-T (2 H-bonds), G-C (3 H-bonds)
- DNA stability from hydrogen bonding + hydrophobic base stacking
🧠 Quick Recap
Mononucleotide: Sugar + Phosphate + Base (DNA: A,T,G,C; RNA: A,U,G,C)
Phosphodiester Bond: Links sugar-phosphate backbone → condensation reaction
DNA Structure: Double helix, antiparallel strands, bases inside, sugar-phosphate outside
Base Pairing: A-T (2 H-bonds), G-C (3 H-bonds)
RNA: Single-stranded, ribose sugar, uracil replaces thymine
