Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.14 The Cell Cycle & Mitosis- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.14 The Cell Cycle & Mitosis- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.14 The Cell Cycle & Mitosis- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 3.14 understand the role of mitosis and the cell cycle in producing genetically identical daughter cells for growth and asexual reproduction
Mitosis & the Cell Cycle: Producing Genetically Identical Cells
🌱 Introduction
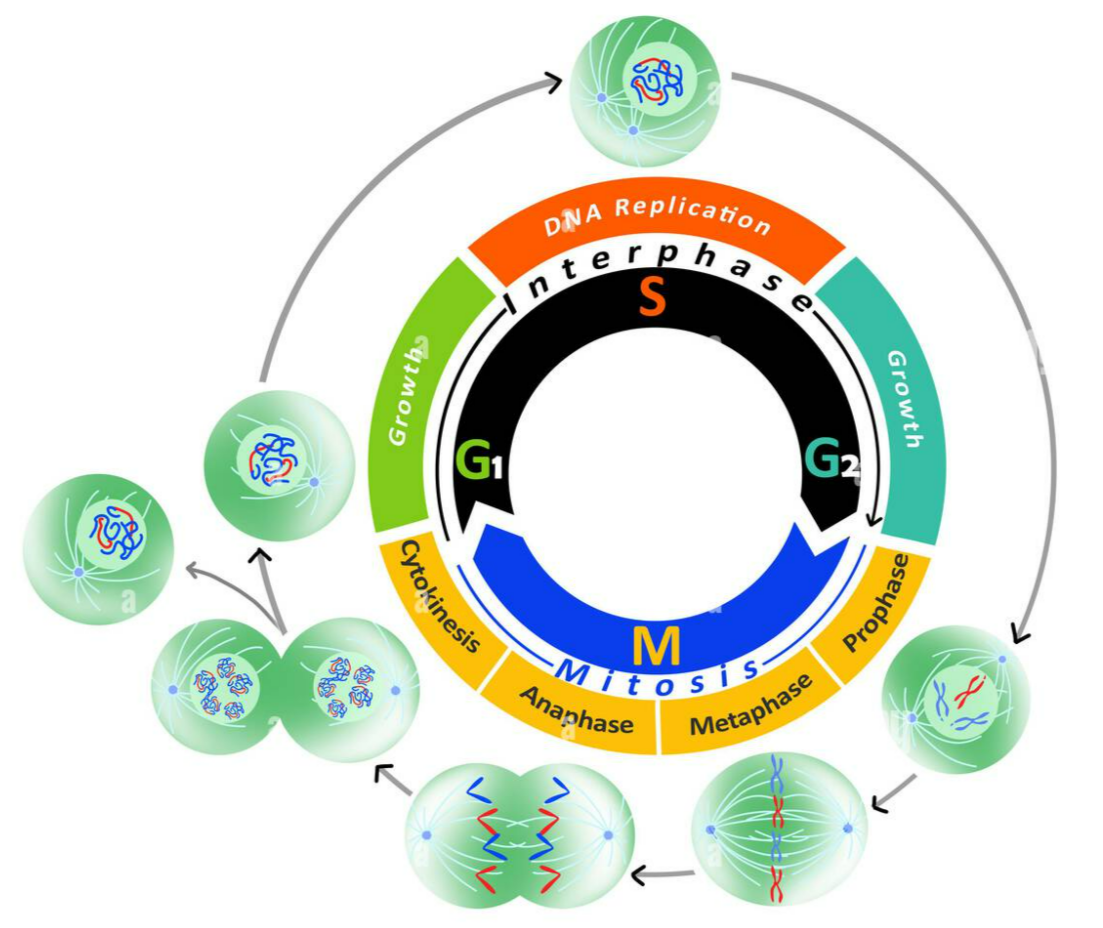
Mitosis is a type of eukaryotic cell division producing two genetically identical daughter cells.
Essential for:
- Growth of tissues & organisms
- Repair & replacement of damaged cells
- Asexual reproduction in some organisms
It is controlled by the cell cycle.
🟢 The Cell Cycle
The sequence of events a cell undergoes from one division to the next:
| Stage | Description | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Interphase | Cell grows & prepares for division | G₁ → growth & protein synthesis, S → DNA replication, G₂ → organelle synthesis & check for errors |
| Mitosis (M phase) | Nuclear division | Produces two genetically identical nuclei |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasmic division | Splits cell into two daughter cells |
📌 Key Point: Interphase ensures DNA is duplicated & cell is ready for division.
🟢 Mitosis Process
Purpose: Divide duplicated chromosomes equally into two nuclei.
| Phase | Key Features | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Prophase | Chromosomes condense, spindle fibres form | Chromosomes visible |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align at equator | Ensures equal segregation |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids pulled to opposite poles | Each nucleus gets identical DNA |
| Telophase | Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes decondense | Two nuclei present in one cell |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasm divides | Two genetically identical daughter cells |
Tip: Mitosis conserves chromosome number (diploid → diploid).
Role of Mitosis
- Growth: Adds new cells to increase organism size.
- Repair & Replacement: Replaces damaged cells with identical healthy cells.
- Asexual Reproduction: Produces offspring genetically identical to parent (e.g., budding in Hydra, vegetative propagation in plants).
Key Points for Genetics
- Daughter cells are genetically identical → same DNA sequence.
- Chromosome number maintained (diploid in humans).
- Ensures organismal stability and proper function.
⚡ Quick Recap
Mitosis → produces 2 identical daughter cells.
Cell cycle = Interphase + Mitosis + Cytokinesis.
Interphase → growth, DNA replication, organelle prep.
Mitosis → equal DNA distribution.
Roles: growth, repair, asexual reproduction.
Chromosome number stays constant; DNA identical.
