Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.3 Eukaryotic Cells- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.3 Eukaryotic Cells- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.3 Eukaryotic Cells- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 3.3 (i) know the ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells, including nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, centrioles, lysosomes and Golgi apparatus
(ii) understand the function of the organelles listed in (i)
Ultrastructure & Functions of Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
🌱 Introduction
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells with membrane-bound organelles, each performing specific functions. Understanding their structure (ultrastructure) and function is key for biology exams.
1. Nucleus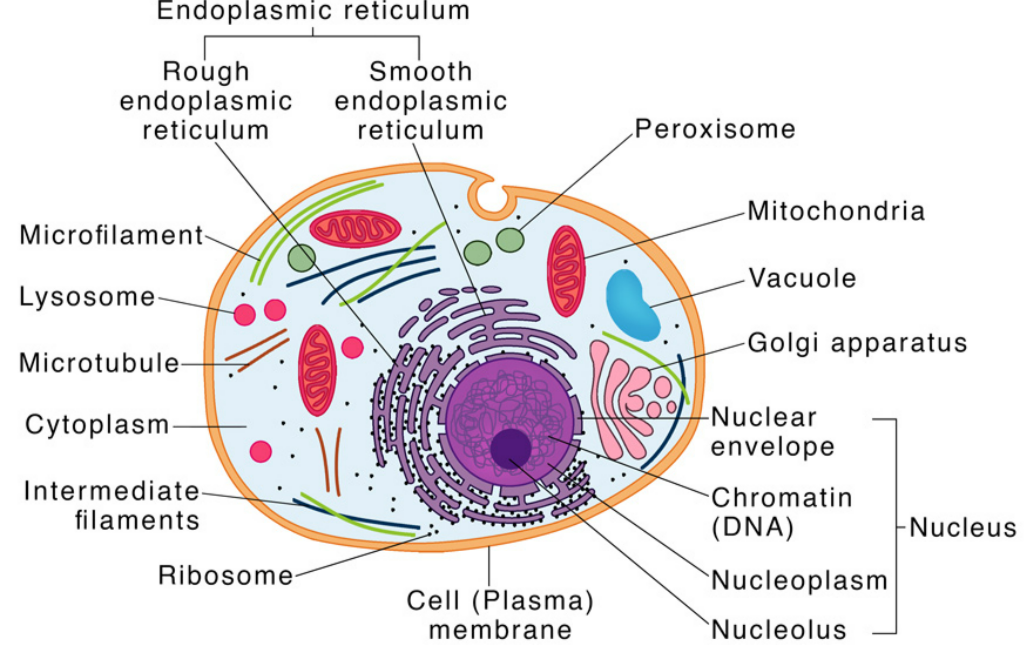
- Ultrastructure: Surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope with pores. Contains chromatin (DNA + proteins) and nucleolus.
- Function: Controls cell activities (growth, metabolism, reproduction). Stores genetic material. Nucleolus → site of ribosome synthesis.
2. Nucleolus
- Ultrastructure: Dense, spherical structure inside the nucleus.
- Function: Produces rRNA and assembles ribosome subunits.
3. Ribosomes
- Ultrastructure: Small particles, non-membrane-bound. Made of rRNA + proteins. Can be free in cytoplasm or bound to rough ER.
- Function: Site of protein synthesis.
4. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- Ultrastructure: Membranous network with ribosomes on surface.
- Function: Synthesizes proteins (especially for secretion or membrane insertion).
5. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
- Ultrastructure: Membranous network without ribosomes.
- Function: Synthesizes lipids & steroids. Detoxifies drugs and poisons. Stores calcium ions in muscle cells.
6. Mitochondria
- Ultrastructure: Double membrane: outer smooth, inner folded (cristae). Internal fluid: matrix containing enzymes & DNA.
- Function: Powerhouse of the cell → ATP production via cellular respiration. Self-replicating; contains its own DNA & ribosomes.
7. Centrioles
- Ultrastructure: Cylinder-shaped, made of microtubules (9×3 arrangement). Usually found in pairs, near the nucleus.
- Function: Organizes spindle fibers during cell division. Involved in formation of cilia and flagella.
8. Lysosomes
- Ultrastructure: Spherical, membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes.
- Function: Digests waste and cellular debris. Breaks down old organelles, pathogens, and macromolecules.
9. Golgi Apparatus
- Ultrastructure: Stacked, flattened membranous sacs (cisternae). Has cis face (receives from ER) and trans face (ships out).
- Function: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins & lipids. Forms lysosomes. Involved in secretion.
📊 Summary Table
| Organelle | Ultrastructure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Double membrane, chromatin, nucleolus | Controls cell, stores DNA |
| Nucleolus | Dense structure inside nucleus | Ribosome synthesis |
| Ribosomes | Small particles (rRNA + proteins) | Protein synthesis |
| Rough ER | Membranous network with ribosomes | Protein synthesis (for secretion/membrane) |
| Smooth ER | Membranous network without ribosomes | Lipid synthesis, detox, Ca²⁺ storage |
| Mitochondria | Double membrane, cristae, matrix | ATP production, cellular respiration |
| Centrioles | Cylindrical, 9×3 microtubules | Spindle formation, cilia/flagella |
| Lysosomes | Membrane-bound, digestive enzymes | Digestion, waste breakdown |
| Golgi Apparatus | Stacked cisternae with cis/trans faces | Protein/lipid modification & secretion |
⚡ Quick Recap
Nucleus → control center, stores DNA.
Nucleolus → ribosome factory.
Ribosomes → make proteins.
RER → protein production & transport.
SER → lipid synthesis & detox.
Mitochondria → ATP powerhouse.
Centrioles → spindle organization, cilia/flagella.
Lysosomes → cell’s digestive system.
Golgi → modify, package, ship proteins/lipids.
