Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.4 The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.4 The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -3.4 The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 3.4 understand the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) and the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within cells, including their role in the formation of extracellular enzymes
Protein Transport in Cells: Role of RER & Golgi Apparatus
🌱 Introduction
Proteins synthesized in the cell are not always used immediately inside the cytoplasm. Many are secreted as extracellular enzymes, embedded in the membrane, or sent to organelles like lysosomes. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Golgi apparatus work together in a protein transport pathway to ensure correct folding, modification, and delivery.
1. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- Ultrastructure: Membranous network with ribosomes on the surface. Continuous with the nuclear envelope.
- Functions in Protein Transport:
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes on RER synthesize secretory proteins, membrane proteins, and lysosomal enzymes.
- Folding and Quality Control: Proteins enter the RER lumen as they are synthesized. Chaperone proteins help fold them correctly. Misfolded proteins are retained or degraded.
- Initial Modification: Addition of sugar groups (glycosylation) → forms glycoproteins.
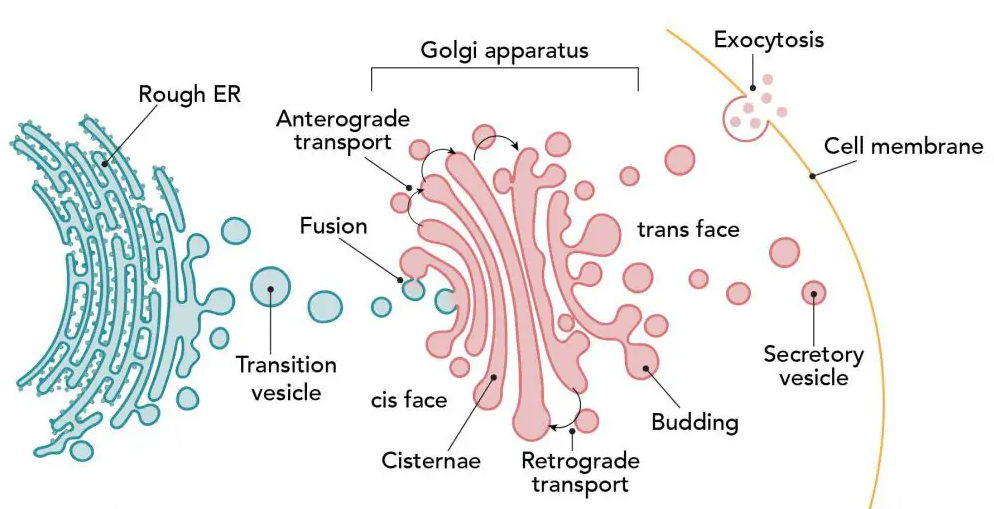 Vesicle Formation: Proteins are packaged into transport vesicles. Vesicles bud off from the RER membrane and move to the Golgi apparatus.
Vesicle Formation: Proteins are packaged into transport vesicles. Vesicles bud off from the RER membrane and move to the Golgi apparatus.
- Key Point: RER is the “factory” where proteins are synthesized and prepped for transport.
2. Golgi Apparatus
- Ultrastructure: Flattened, stacked membranous cisternae. Cis face → receives vesicles from RER. Trans face → sends vesicles to their destination.
- Functions in Protein Transport:
- Receiving Proteins: Transport vesicles from RER fuse at the cis face of the Golgi.
- Modification: Further glycosylation, sulfation, or phosphorylation of proteins. Proteins are packaged correctly for their specific destinations.
- Sorting and Packaging: Golgi sorts proteins into vesicles for secretion outside the cell (extracellular enzymes, hormones), plasma membrane insertion, or lysosomes.
- Vesicle Delivery: Vesicles bud off from the trans face and are delivered to cell membrane, extracellular space, or organelles like lysosomes.
- Key Point: Golgi acts as the “post office”, modifying, sorting, and shipping proteins to their correct destinations.
3. Role in Extracellular Enzyme Formation
- Synthesis → Ribosomes on RER synthesize the enzyme protein.
- Folding & Glycosylation → Protein enters RER lumen → folded and partially glycosylated.
- Transport to Golgi → Packaged into vesicles from RER → fuse with Golgi cis face.
- Modification in Golgi → Further processing and targeting signals added.
- Secretion → Vesicles bud off from Golgi trans face → fuse with plasma membrane → enzyme released outside the cell.
- Example: Digestive enzymes like amylase from pancreatic cells follow this pathway.
📊 Summary Table
| Organelle | Role in Protein Transport | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| RER | Protein synthesis, folding, initial glycosylation, vesicle formation | “Protein factory” |
| Golgi | Protein modification, sorting, packaging, vesicle delivery | “Protein post office” |
| Outcome | Extracellular enzymes, membrane proteins, lysosomal enzymes | Ensures correct folding & delivery |
⚡ Quick Recap
RER → synthesizes & folds proteins, adds initial sugar groups.
Golgi → modifies, sorts, packages, and delivers proteins.
Extracellular enzymes → synthesized in RER, processed in Golgi, secreted via vesicles.
Analogy → RER = factory, Golgi = post office, vesicles = delivery trucks.
