Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.1 -4.2 Plant Cell Structure- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.1 -4.2 Plant Cell Structure- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.1 -4.2 Plant Cell Structure- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 4.1 (i) know the structure and ultrastructure of plant cells including cell wall, chloroplast, amyloplast, vacuole, tonoplast, plasmodesmata, pits and middle lamella and be able to compare it with animal cells
(ii) understand the function of the structures listed in (i) - 4.2 be able to recognise the organelles in 4.1 from electron microscope (EM) images
Plant Cell Structure & Ultrastructure (and comparison with animal cells)
📌 Introduction
Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. However, plant cells have additional structures that give them support, storage, and photosynthetic ability.
🧫 (i) Structure & Ultrastructure of Plant Cells
| Organelle | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Rigid outer layer made of cellulose microfibrils | Provides mechanical strength, protection, and shape, freely permeable to water & solutes |
| Middle Lamella | Thin layer rich in pectin between two adjacent cell walls | Acts as a cement, holding neighboring plant cells together |
| Pits | Thin regions in the cell wall where the cell wall is not thickened | Allow water and solute movement between adjacent cells (esp. in xylem) |
| Plasmodesmata | Narrow cytoplasmic connections between adjacent cells | Enable cell-to-cell communication and transport of substances |
| Chloroplasts | Double membrane organelle containing chlorophyll and internal thylakoid membranes (grana + stroma) | Site of photosynthesis; converts light energy → chemical energy |
| Amyloplasts | Colorless plastids storing starch grains | Act as energy stores and can convert starch back to sugar when needed |
| Vacuole | Large, membrane-bound (by tonoplast) fluid-filled sac | Stores cell sap, maintains turgor pressure, supports the cell |
| Tonoplast | The membrane surrounding the vacuole | Controls movement of ions and molecules into and out of the vacuole |
🌾 (ii) Comparison: Plant Cell vs Animal Cell
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (cellulose) | Absent |
| Chloroplasts | Present in photosynthetic cells | Absent |
| Vacuole | Large, central, permanent | Small or temporary |
| Tonoplast | Present | Absent |
| Amyloplast | Present (for starch storage) | Absent |
| Plasmodesmata | Present | Absent |
| Pits | Present in xylem & other cells | Absent |
| Centrioles | Usually absent (except in lower plants) | Present |
| Shape | Regular / rectangular | Irregular / rounded |
| Energy storage | Starch (in amyloplasts) | Glycogen (in cytoplasm) |
🧩 Internal View of Plant Cell (Ultrastructure Overview)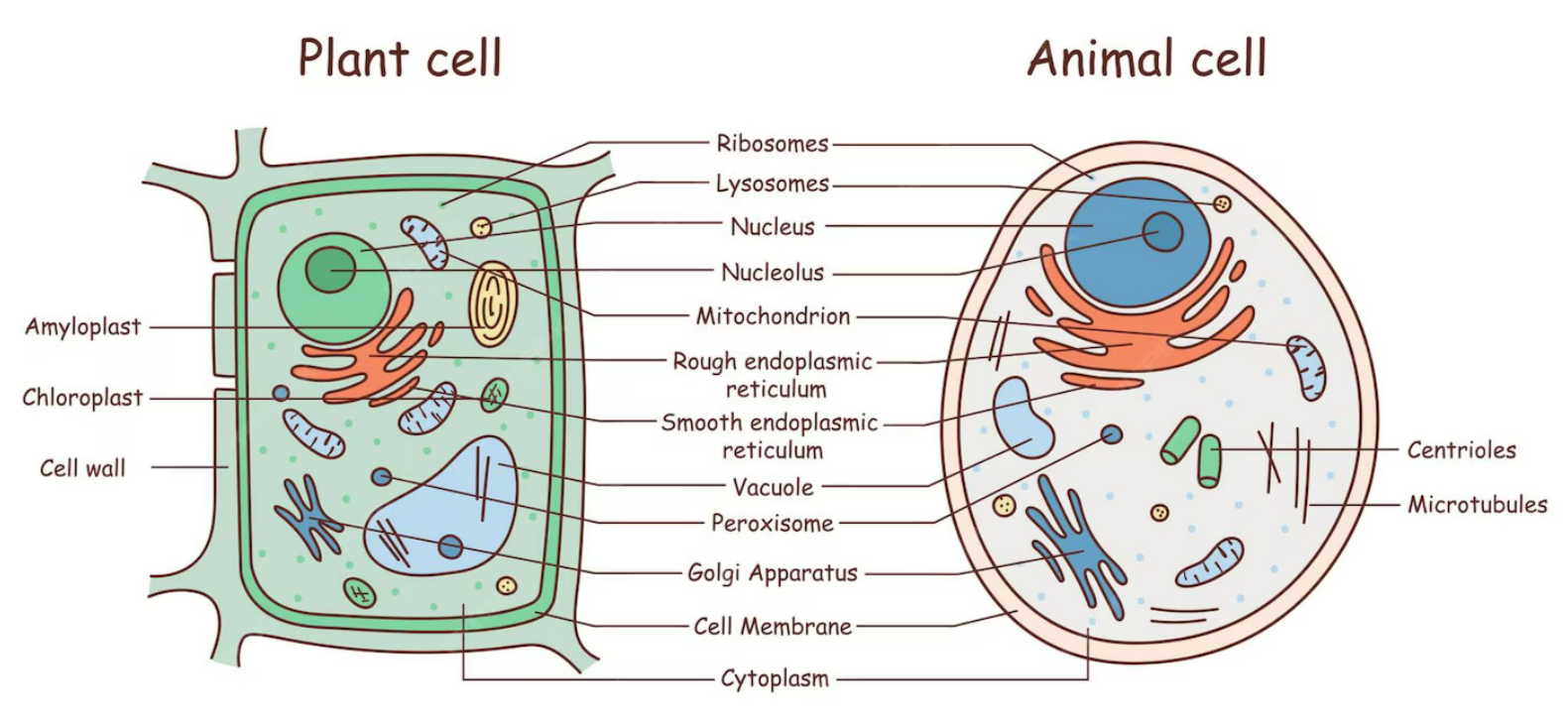
- Nucleus → Controls cell activities.
- Cytoplasm → Site of metabolic reactions.
- Mitochondria → Energy release via respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER & SER) → Protein & lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus → Protein modification & packaging.
- Ribosomes → Protein synthesis.
- Cell Surface Membrane → Selectively permeable barrier.
- Unique structures: Chloroplast, Amyloplast, Cell Wall, Large Vacuole.
🧬 Special Mentions
🌞 Chloroplast structure summary:
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Grana (stacks of thylakoids) | Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis |
| Stroma | Enzymes for light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) |
| Lamellae | Connect grana |
| Own DNA & ribosomes | Allow partial self-replication |
Cell wall + Middle lamella + Plasmodesmata work together to form a continuous living system between cells – called the symplast pathway.
🌻 Summary Table
| Organelle | Present in Plant? | Present in Animal? | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | ✓ | ✗ | Support, protection |
| Middle Lamella | ✓ | ✗ | Binds cells |
| Pits | ✓ | ✗ | Transport between cells |
| Plasmodesmata | ✓ | ✗ | Cytoplasmic connections |
| Chloroplast | ✓ | ✗ | Photosynthesis |
| Amyloplast | ✓ | ✗ | Starch storage |
| Vacuole & Tonoplast | ✓ Large & Permanent | ✓ Small/Temporary | Storage, turgor |
| Centrioles | ✗ (mostly) | ✓ | Spindle formation |
| Lysosomes | Less common | ✓ | Digestion of waste |
⚡ Quick Recap
Plant Cell = Animal Cell + Extra Support + Photosynthesis Tools
Cell Wall → Structure
Chloroplast → Photosynthesis
Vacuole & Tonoplast → Storage & Pressure
Plasmodesmata → Communication
Amyloplast → Starch storage
🧠 Remember: “Plant cells are green, rigid, and full of sap; animal cells are flexible, round, and active!”
Recognising Plant Cell Organelles from EM Images
📌 Introduction
Electron microscopes (EM) provide high magnification and resolution, allowing us to see ultrastructural details of plant cells. Each organelle has a distinct appearance under EM – knowing these shapes helps you identify them quickly in diagrams or photos.
🧫 Key Organelles & Their EM Features
| Organelle | EM Appearance | Function / Tip to Recognise |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Thick, outer dark boundary around the cell, appears layered | Rigid structure made of cellulose microfibrils, gives support |
| Middle Lamella | Thin line between two adjacent cell walls, often lighter | “Cement” layer – holds neighbouring cells together |
| Pits | Small gaps or depressions in the cell wall | Allow movement of water between cells (common in xylem walls) |
| Plasmodesmata | Tiny thread-like connections passing through cell walls | Link cytoplasm of adjacent cells (often seen as fine lines) |
| Chloroplast | Oval organelle with double membrane, inside – stacks of dark discs (grana) and lighter stroma regions | Site of photosynthesis, grana = thylakoid stacks |
| Amyloplast | Round or oval, with dense starch grains (dark spots), no internal membranes like chloroplast | Storage of starch, no pigments |
| Vacuole | Large clear (white) space taking up most of cell volume | Contains cell sap, maintains turgor |
| Tonoplast | Thin membrane line around vacuole | Separates vacuole from cytoplasm |
| Nucleus | Large, round or oval, darker nucleolus inside, double membrane (nuclear envelope) with pores | Controls cell activities |
| Mitochondria | Small, bean-shaped, double membrane, inner folds = cristae | Site of aerobic respiration |
| Rough ER | Flattened sacs with dots (ribosomes) on surface | Protein synthesis and transport |
| Golgi Apparatus | Stack of flattened curved sacs (no ribosomes), often with vesicles nearby | Modifies and packages proteins |
🧠 Easy Visual Mnemonics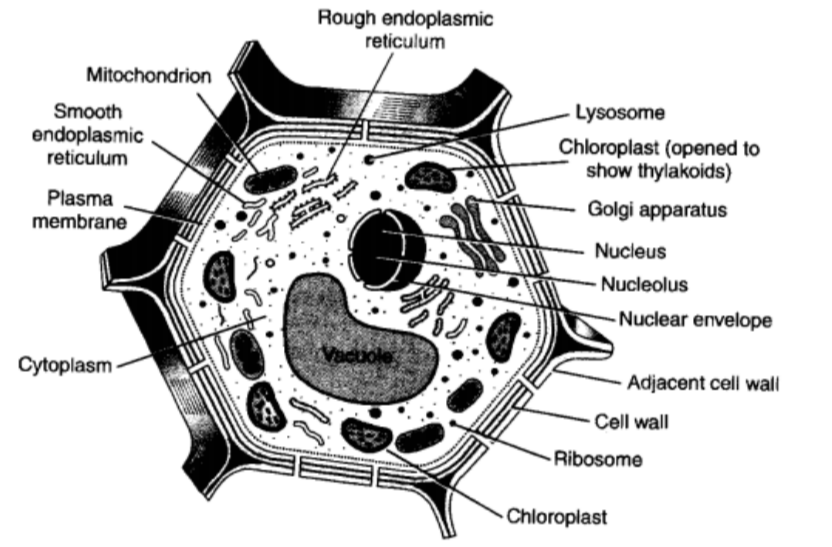
| Organelles | Mnemonic / Tip |
|---|---|
| Chloroplast | Think “pancake stacks” → grana = thylakoid stacks |
| Amyloplast | Looks like smooth jelly with dark starch grains |
| Cell Wall | Thick solid frame, more defined than cell membrane |
| Vacuole | Huge empty space (looks white on EM) |
| Plasmodesmata | Tiny tunnels crossing walls – very fine lines |
| Golgi | “WiFi shape” – stacked curved sacs |
| Mitochondria | Bean with zigzag folds (cristae) inside |
🌾 Comparison Tip
| EM View | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Regular / rectangular | Round / irregular |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplasts | Present | Absent |
| Large Vacuole | Present | Absent / small |
| Pits + Plasmodesmata | Present | Absent |
⚡ Quick Recap
Identify by EM Clue → Organelle
Pancake stacks (grana) → Chloroplast
Big empty area → Vacuole
Thick rigid outline → Cell Wall
Smooth plastid with dark starch → Amyloplast
Thin line between walls → Middle Lamella
Tiny thread between cells → Plasmodesmata
Bean with inner folds → Mitochondria
Stack of sacs → Golgi Apparatus
