Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.10 Bacterial Growth Conditions- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.10 Bacterial Growth Conditions- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.10 Bacterial Growth Conditions- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 4.10 understand the conditions required for bacterial growth
Understanding the Conditions Required for Bacterial Growth
🌱 Introduction
Bacteria are unicellular organisms that can reproduce rapidly under suitable conditions.
Their growth means an increase in number of cells (population size), not in cell size.
Most bacteria divide by binary fission – one cell splits into two identical cells.
⚙️ Factors Affecting Bacterial Growth
| Factor | Why It’s Needed | What Happens If Missing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Enzymes work best at optimum temp (25–40°C) for most species. | Too low → enzymes inactive; Too high → enzymes denature. |
| Nutrients | Source of carbon, nitrogen, and minerals for building cell components. | Without nutrients → no growth or reproduction. |
| Oxygen | Needed for aerobic respiration (in aerobes). Anaerobes may not need it. | Absence of O₂ kills aerobes; presence of O₂ kills strict anaerobes. |
| pH level | Most bacteria prefer neutral pH (~7). | Extreme pH damages enzymes and membranes. |
| Water availability | Required for metabolic reactions and transport. | Without water → cytoplasm dries → cells die. |
| Absence of toxins | Toxic substances (like antibiotics or alcohol) can inhibit enzyme activity. | Growth stops or bacteria die. |
🔬 Types of Bacteria by Oxygen Requirement
| Type | Oxygen Need | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Obligate aerobes | Must have O₂ | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Obligate anaerobes | Killed by O₂ | Clostridium botulinum |
| Facultative anaerobes | Can grow with or without O₂ | E. coli |
📈 Bacterial Growth Curve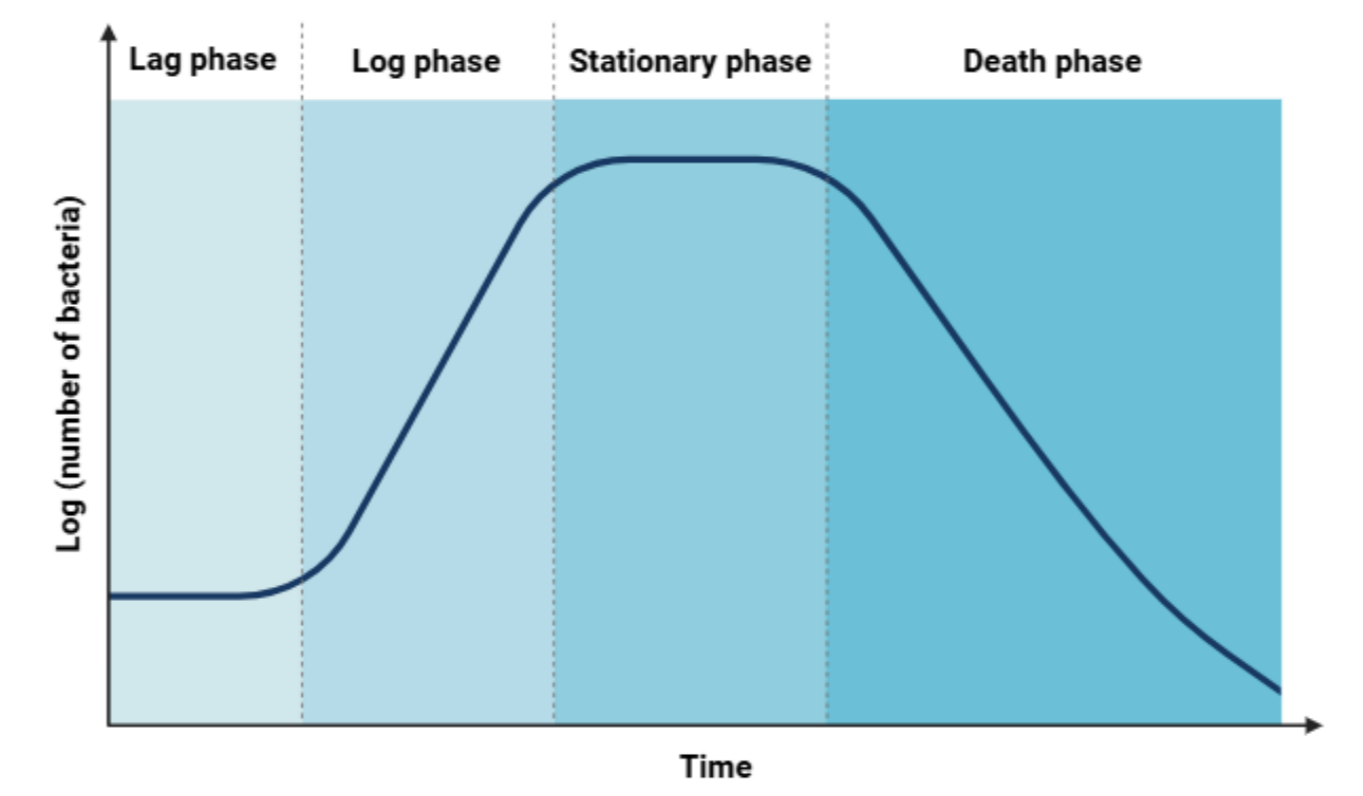
When bacteria are grown in a nutrient medium, their population follows four main phases:
- Lag phase: Cells adapt to new environment; enzymes start synthesizing.
- Log (exponential) phase: Rapid cell division; maximum growth rate.
- Stationary phase: Nutrients start depleting; growth rate = death rate.
- Death phase: Toxins accumulate; cells die faster than they divide.
🧩 Example: Ideal Growth Conditions for E. coli
- Temperature: 37°C (body temperature)
- pH: 7
- Medium: Moist nutrient medium with glucose + amino acids
- Oxygen: Aerobic or facultative environment
📦 Quick Recap
| Condition | Why It Matters | Memory Trick |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Controls enzyme activity | “Too hot kills, too cold chills” |
| Nutrients | Provide building materials and energy | “Food = Fuel for Fission” |
| Oxygen | Needed for respiration (aerobes) | “O₂ loves aerobes, hates anaerobes” |
| pH | Maintains enzyme structure | “Neutral is natural” |
| Water | Essential for chemical reactions | “No water, no life” |
