Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.14 The Three Domain System- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.14 The Three Domain System- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.14 The Three Domain System- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 4.14(i) understand that classification is a means of organising the variety of life based on relationships between organisms using differences and similarities in phenotypes and in genotypes, and is built around the species concept
(ii) understand the process and importance of critical evaluation of new data by the scientific community leading to new taxonomic groupings, based on molecular evidence, including the three-domain system (Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya)
Classification of Living Organisms & the Three-Domain System
🌱 Introduction
The Earth is home to millions of species, all different yet connected. To study them effectively, scientists classify organisms based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
Modern classification combines visible traits (phenotypes) and genetic information (genotypes) to reveal how organisms are related.
🧬 (i) Understanding Classification
What is Classification?
Classification means arranging organisms into groups based on similarities and differences.
It helps scientists organise biodiversity, identify new species, and understand evolution.
Two Key Bases for Classification:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Phenotypic classification | Based on observable features (morphology, anatomy, physiology, behaviour) | Vertebrates → fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals |
| Genotypic classification | Based on DNA, RNA, and protein sequence similarities | Humans and chimpanzees share ~98% of DNA |
Species Concept
- A species is a group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
- They share similar genetics and morphology.
- Each species has a unique binomial name (Genus + species).
- Examples: Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes
Why It Matters:
Species is the basic unit of classification – all higher taxonomic ranks (genus, family, order, etc.) are built around it.
🧩 (ii) Modern Classification & Molecular Evidence
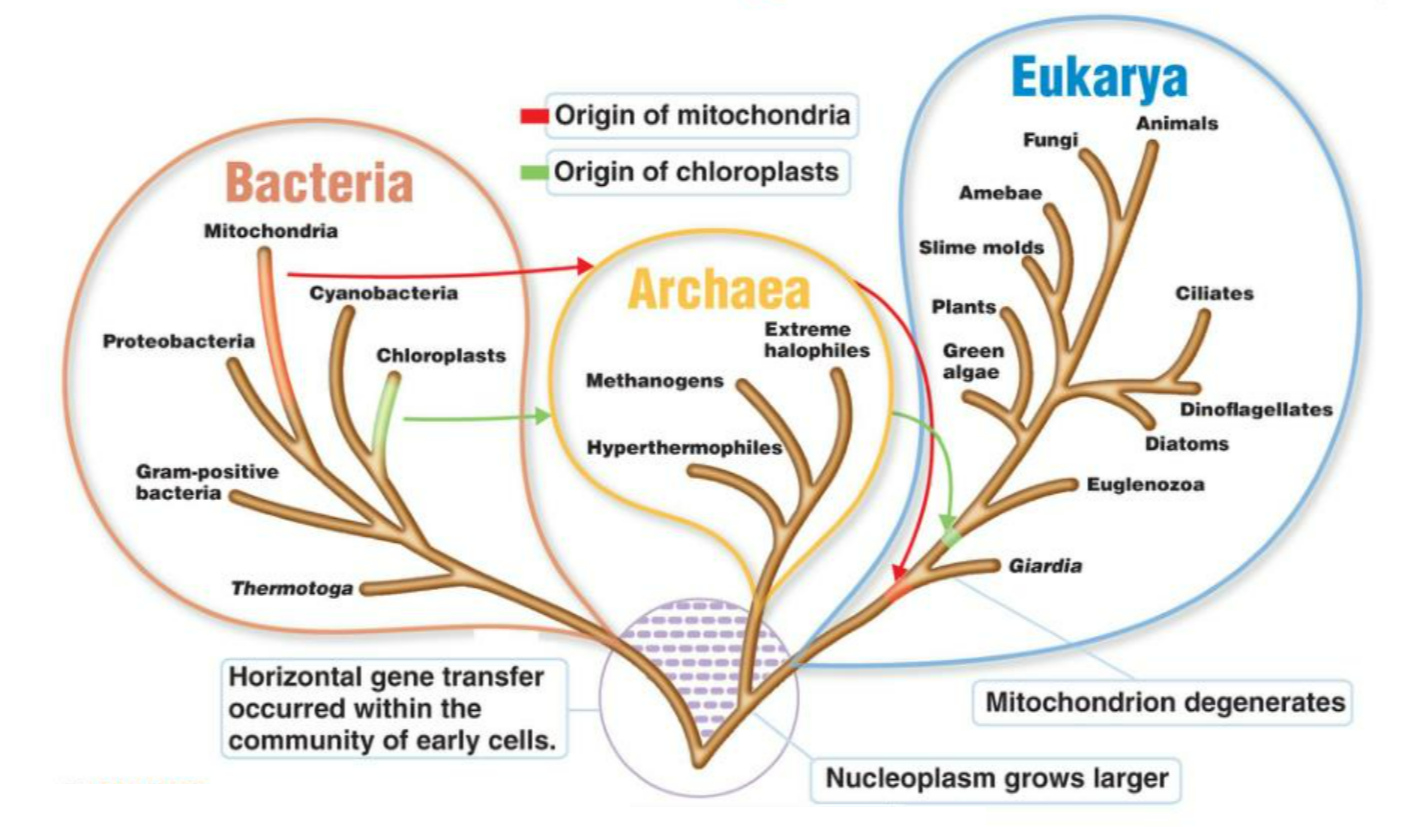
Evolution of Classification Systems
| System | Basis | Example / Note |
|---|---|---|
| Old system – 5 Kingdoms (Whittaker) | Based on cell structure & nutrition | Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia |
| Modern system – 3 Domains (Woese) | Based on molecular & genetic evidence (rRNA analysis) | Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya |
The Three-Domain System (Carl Woese, 1990)
| Domain | Cell Type | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic | Cell walls with peptidoglycan, circular DNA, no membrane-bound organelles | E. coli, Streptococcus |
| Archaea | Prokaryotic | No peptidoglycan, unique lipids, live in extreme environments, genes similar to eukaryotes | Thermophiles, Halophiles |
| Eukarya | Eukaryotic | Nucleus + membrane-bound organelles | Animals, plants, fungi, protists |
Key Point:
Molecular studies showed Archaea are more closely related to Eukarya than to Bacteria, even though both are prokaryotes – leading to this 3-domain revision.
🧠 Role of the Scientific Community
Critical Evaluation of New Data
- New discoveries are peer-reviewed by scientists before being accepted.
- DNA sequencing and molecular evidence have revolutionized taxonomy, causing reclassification of many organisms.
- Example: Some bacteria were reclassified as Archaea after rRNA analysis.
- Ongoing studies (like horizontal gene transfer) continue to refine classification.
📊 Summary Table
| Concept | Key Idea | Example / Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Grouping organisms by shared features | Simplifies study of biodiversity |
| Phenotype | Visible traits | Shape, structure, physiology |
| Genotype | DNA/protein sequence similarity | Genetic closeness between species |
| Species concept | Interbreeding group of fertile offspring | Basic classification unit |
| Critical evaluation | Peer review of new data | Ensures reliable taxonomy |
| 3-domain system | Based on molecular evidence | Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya |
⚡ Quick Recap
Classification helps understand diversity & evolution.
Based on phenotype + genotype similarities.
Species = interbreeding fertile group (basic unit).
Modern classification (Woese) uses rRNA & molecular data.
3 Domains:
• Bacteria – true prokaryotes
• Archaea – extremophiles, closer to eukaryotes
• Eukarya – all eukaryotic life
🧠 Scientific community continually updates systems with new molecular evidence.
