Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.5 The Vascular Structure of Plants- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.5 The Vascular Structure of Plants- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -4.5 The Vascular Structure of Plants- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 4.5 know the similarities and differences between the structures of, the position in the stem, and the function of sclerenchyma fibres (support), xylem vessels (support and transport of water and mineral ions) and phloem (translocation of organic solutes)
Comparison of Sclerenchyma Fibres, Xylem Vessels & Phloem
🌱 Introduction:
In vascular plants, sclerenchyma, xylem, and phloem work together to support the plant body and transport materials. Although they lie close in position inside the stem, they have different structures and roles.
🧩 1. Sclerenchyma Fibres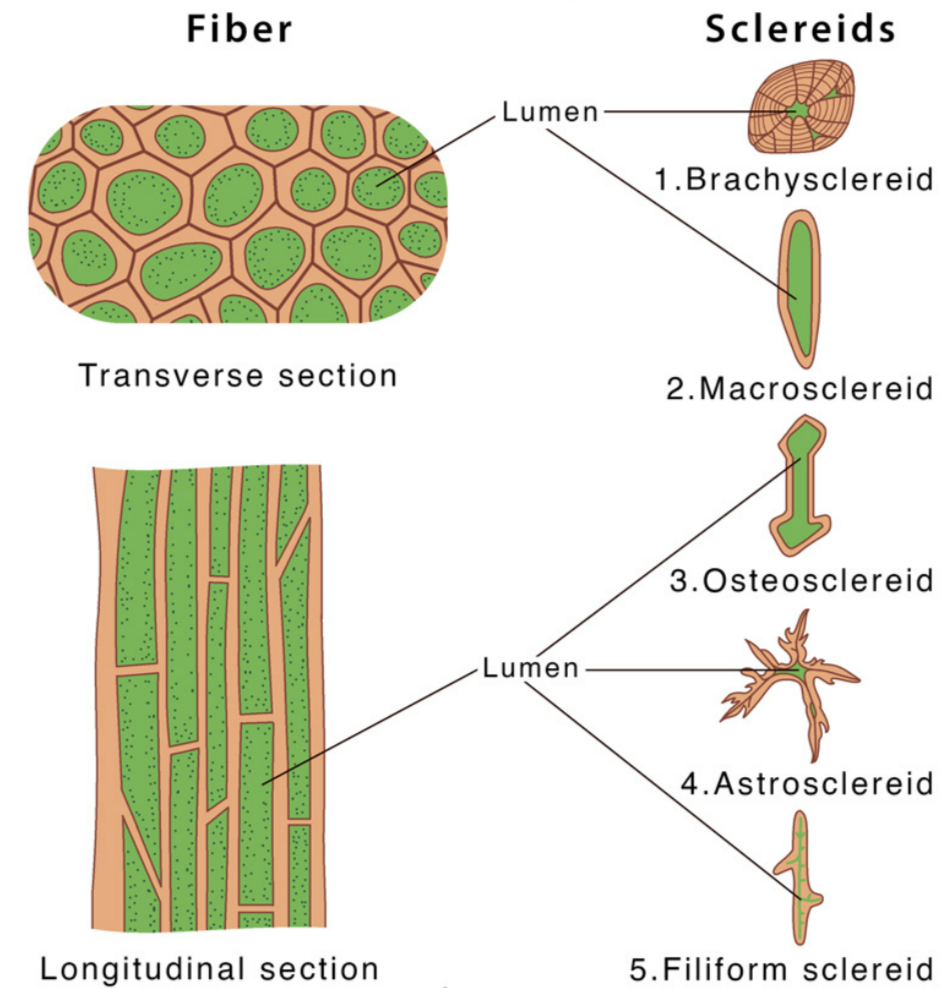
Structure:
- Long, narrow, dead cells with thick, lignified secondary walls.
- No cytoplasm or nucleus.
- Walls contain cellulose + lignin → rigid and strong.
- Found as bundles of fibres around vascular tissues.
Function:
- Provide mechanical strength and support.
- Allow stems and leaves to remain upright and flexible.
- Do not take part in transport.
Key Point: Purely supportive tissue – gives tensile strength, like natural rope fibres.
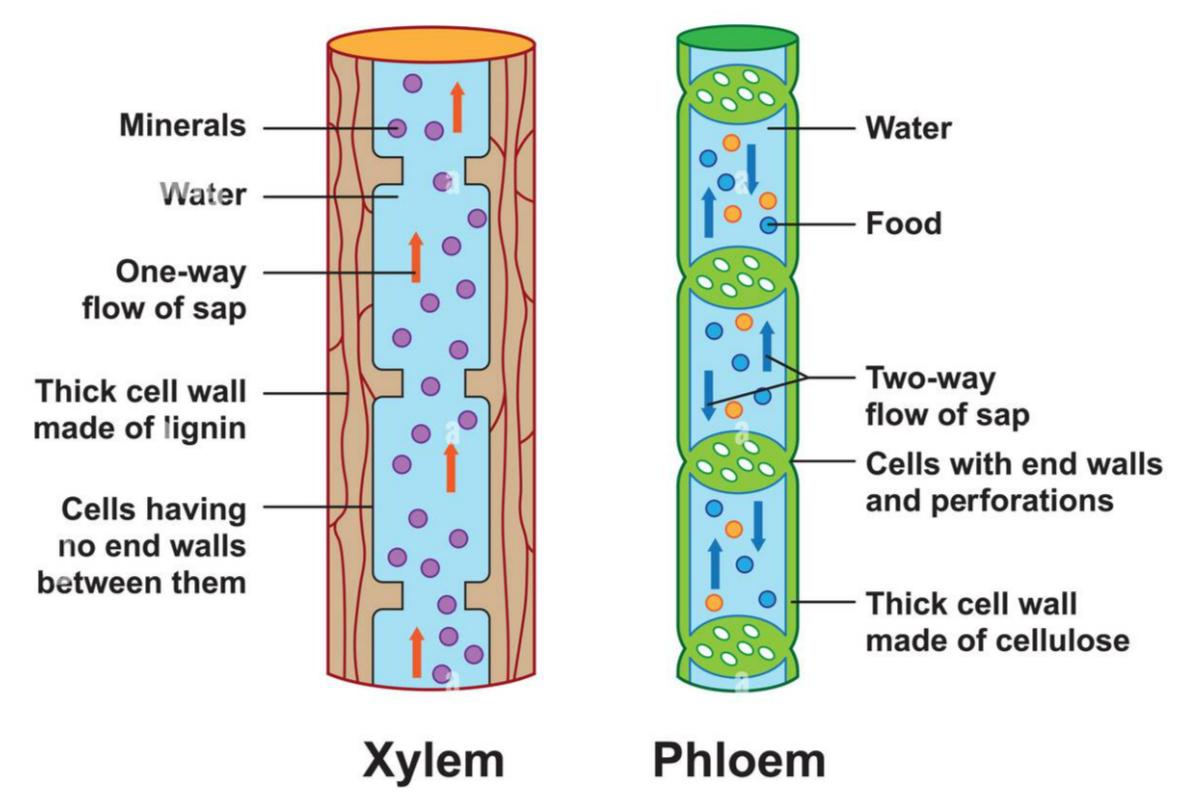
💧 2. Xylem Vessels
Structure:
- Made of dead, hollow cells joined end-to-end → form long tubes.
- Lignin deposited in spiral, annular, or reticulate patterns → gives strength & waterproofing.

- No cytoplasm or end walls → continuous hollow channels.
Function:
- Transports water & mineral ions from roots to leaves (unidirectional).
- Supports plant due to thick lignified walls.
Key Point: Dual role – transport + support. Lignin prevents collapse during water flow under tension.
🍬 3. Phloem
Structure:
- Made of living cells:
- Sieve tube elements (transport cells with perforated sieve plates).
- Companion cells (control metabolism).
- Phloem fibres & parenchyma (for support).
- No lignin, thin walls.
Function:
- Translocation of organic solutes (like sucrose, amino acids) in both directions – up & down the plant.
- Transport is active, requiring energy from companion cells.
Key Point: Living transport tissue – moves food made during photosynthesis.
🌿 4. Position in the Stem
| Tissue | Position in Stem (Cross Section) | Nature of Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Sclerenchyma | Found as a cap or sheath around vascular bundles (outermost) | Dead |
| Xylem | Located towards the center (inner part) of vascular bundle | Dead |
| Phloem | Located towards the outside of the xylem | Living |
🧠 Tip to Remember: From inside → out: Xylem → Phloem → Sclerenchyma Cap
📘 5. Summary Table
| Feature | Sclerenchyma | Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Cells | Dead | Dead | Living |
| Main Role | Mechanical support | Transport of water & minerals + support | Transport of organic solutes |
| Cell Wall | Thick, lignified | Thick, lignified | Thin, non-lignified |
| Cytoplasm | Absent | Absent | Present (in companion cells) |
| Transport Direction | None | Upward only | Upward & downward |
| Position in Stem | Outermost (around vascular bundle) | Innermost of vascular bundle | Between sclerenchyma & xylem |
| Special Feature | Long fibres | Continuous hollow tubes | Sieve tubes + companion cells |
🌸 6. Functions at a Glance
| Function | Sclerenchyma | Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | ✓ Main function | ✓ Secondary function | ✓ Weak support |
| Transport (Water/Minerals) | ✗ None | ✓ Yes | ✗ No |
| Transport (Organic Solutes) | ✗ None | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Living / Dead | Dead | Dead | Living |
| Mechanical Strength | High (due to lignin) | High | Low |
⚡ Quick Recap:
Sclerenchyma → Dead, lignified, support only.
Xylem → Dead, lignified, water transport + support.
Phloem → Living, transports food (sucrose), no lignin.
Arrangement in stem: Center → Xylem → Phloem → Sclerenchyma Cap (outermost).
🧠 Memory Trick: “SXP – Support, Xylem, Phloem” → from inside to outside in the stem.