Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.13 Niche- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.13 Niche- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.13 Niche- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.13 understand how the concept of niche accounts for the distribution and abundance of organisms in a habitat
Ecological Niche and How It Affects Distribution and Abundance
🌱 Introduction
Every organism has its own role in the habitat. This role decides where it can live and how many of them can survive. This special role is called its niche.
🧬 What is a Niche
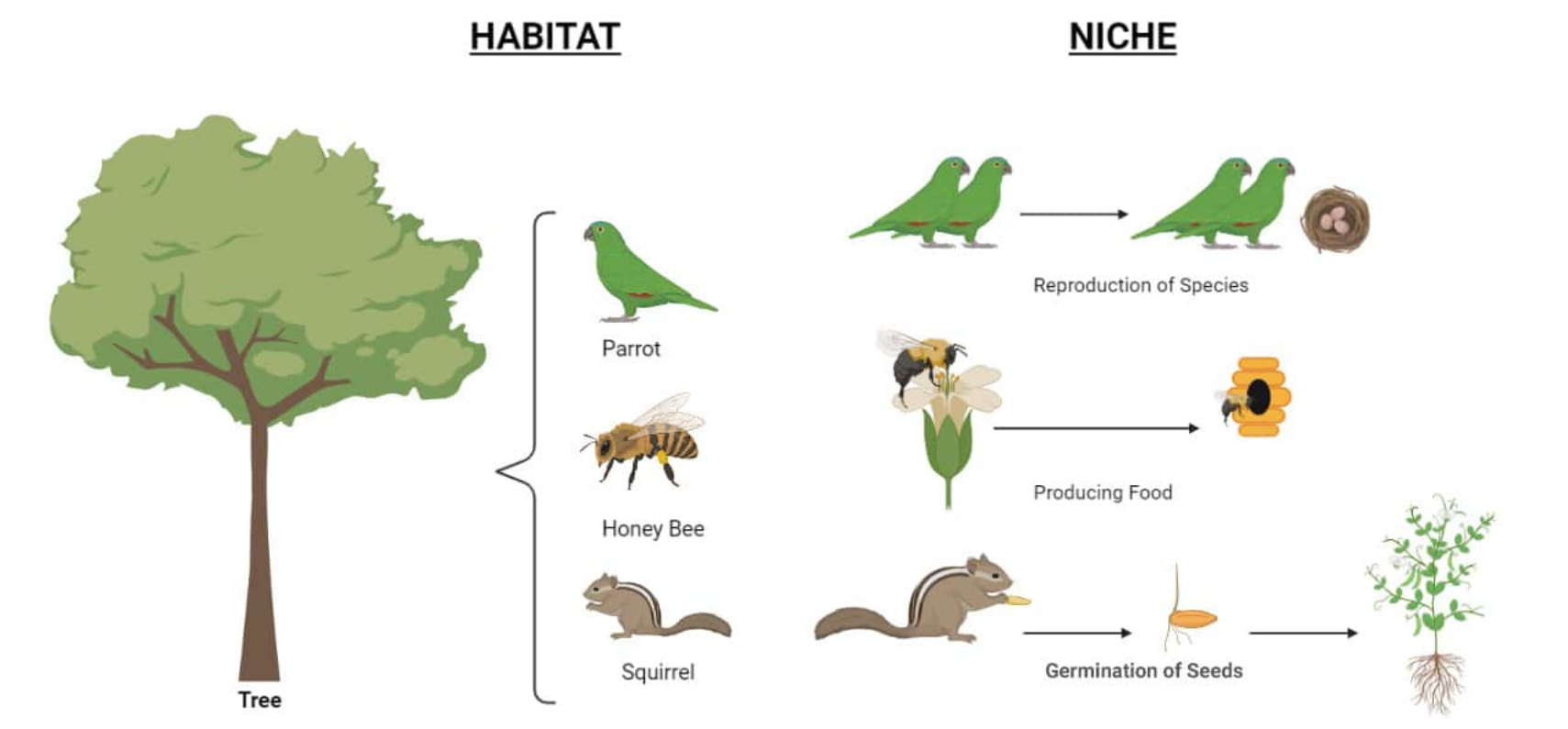
A niche is the way an organism lives in its habitat. It covers everything the organism needs to survive. Think of it as the organism’s personal job and lifestyle.
📌 A Niche includes:
- What it eats (food source)
- Where it feeds or lives (micro habitat)
- Its role (producer, predator, decomposer)
- Conditions it needs (light, temperature, moisture, pH)
- How it interacts with other species
Short example:
Two birds living on the same tree may feed at different heights. Different feeding spots = different niches.
🌍 How Niche Controls Distribution
A species can survive only in places that match its niche. If a habitat does not meet its needs, the organism won’t be found there. So niche acts like a filter deciding where the species lives.
Example: Cactus plants are found only in dry areas because their niche requires low water and high sunlight.
🌱 How Niche Controls Abundance
If niche conditions are perfect, individuals increase in number. Poor conditions lead to fewer individuals or none at all. When two species try to occupy the same niche, competition reduces their numbers.
- Generalists (wide niche) are usually abundant.
- Specialists (narrow niche) have smaller populations.
Tiny examples:
Raccoons (generalists) live in cities, forests and farmlands so they are common.
Koalas (specialists) need eucalyptus leaves only so they are less abundant.
📋 Summary Table
| Term | Meaning | Effect on Distribution | Effect on Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niche | Lifestyle and role of a species | Found only where needs are met | Best numbers in suitable habitats |
| Competition | Overlap of niches | Pushes one species out | Reduces population size |
| Generalist | Wide niche | Lives in many places | Usually abundant |
| Specialist | Narrow niche | Limited distribution | Small populations |
Niche = an organism’s lifestyle (food, place, role, conditions).
Species live only where their niche fits.
More suitable niche → more individuals.
Niche overlap causes competition.
Generalists spread widely; specialists don’t.
