Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.15 Ecological Succession- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.15 Ecological Succession- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.15 Ecological Succession- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.15 understand the stages of succession from colonisation to the formation of a climax community
Succession: From First Colonisers to Climax Community
🌱 Introduction
Succession describes how a community of organisms changes over time in a habitat. It starts with the arrival of pioneer species and ends with a stable climax community. It’s basically nature’s way of rebuilding an ecosystem step by step.
🌼 Key Idea: What is Succession
A gradual, ordered change in the structure and species composition of a community.
Happens when a new habitat forms (volcanic rock, sand dunes) or when a previous one is disturbed.
1. Pioneer Stage (Colonisation)
These are the first species to arrive in a bare habitat.
🌿Features of Pioneer Species
- Tough and resistant: can tolerate harsh conditions.
- Often small, fast-growing, short life cycle.
- Examples: algae, lichens, mosses on rocks.
🌱 What they do
- Break down rock into soil (weathering).
- Add organic matter as they die → improves soil fertility.
- Increase water retention in the habitat.
2. Intermediate Stages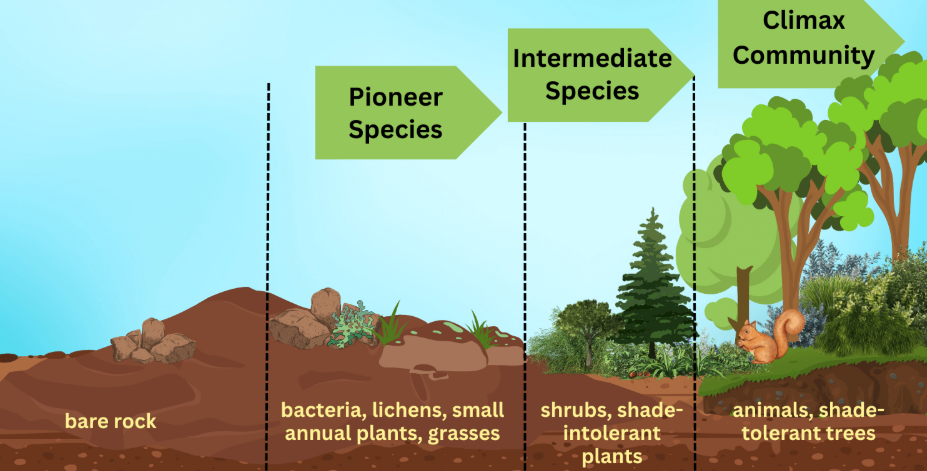
Once soil forms, more species can move in.
🌱 Early Intermediate
- Grasses and small herbs appear.
- Soil continues improving (more nutrients, better structure).
- More insects and small animals arrive.
🌳 Later Intermediate
- Shrubs and small trees begin to grow.
- Taller plants outcompete earlier ones for light.
- Biodiversity increases as niches increase.
3. Climax Community
The final, stable stage.
🌲 Features
- Dominated by large, long-lived plants (e.g., mature trees).
- Very stable structure with high biomass.
- Balanced interactions between organisms.
- Species composition stays fairly constant unless disturbed.
🌱 Examples
- Temperate forest
- Tropical rainforest
- Grassland (in areas with low rainfall)
📘 Summary Table
| Stage | Key Species | Soil Condition | Biodiversity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer | Lichens, mosses | Very poor | Low | First colonisers, start soil formation |
| Early Intermediate | Grasses, herbs | Improving | Rising | More life can establish |
| Late Intermediate | Shrubs, young trees | Quite fertile | High | Competition increases |
| Climax Community | Mature trees | Stable and rich | Very high | Long-term, stable community |
Succession: Gradual community change in a habitat.
Pioneer species: First arrivals, create basic soil.
Intermediate stages: Grasses → shrubs → young trees.
Climax community: Stable, mature ecosystem with high biodiversity.
Soil quality improves at each stage.
Competition increases as more species arrive.
