Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.16-5.17 Cause and Evidence for Climate Change- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.16-5.17 Cause and Evidence for Climate Change- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.16-5.17 Cause and Evidence for Climate Change- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.16 understand the different types of evidence for climate change and its causes, including records of carbon dioxide levels, temperature records, pollen in peat bogs and dendrochronology, recognising correlations and causal relationships
- 5.17 understand the causes of anthropogenic climate change, including the role of greenhouse gases in the greenhouse effect
Evidence for Climate Change and Its Causes
🌱 Introduction
Scientists use natural and historical records to understand how Earth’s climate has changed over thousands of years. These records help show correlations (patterns that match) and causal links (one factor causing another).
🧪 1. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Records
How CO₂ is Measured
- Ice cores trap tiny ancient air bubbles.
- These bubbles contain past CO₂ levels.
- Modern CO₂ is measured using atmospheric sensors.
What CO₂ Records Show
- CO₂ levels have risen sharply since the industrial revolution.
- Higher CO₂ usually matches warmer global temperatures.
Key Idea
High CO₂ → more heat trapped → global warming (a causal relationship).
🌡 2. Long-Term Temperature Records
Sources
- Direct thermometer readings (last ~150 years).
- Ice cores and tree rings for older temperature estimates.
What They Show
- A clear rise in global average temperature in the past century.
- The warming trend matches the rise in greenhouse gases.
🌾 3. Pollen Analysis from Peat Bogs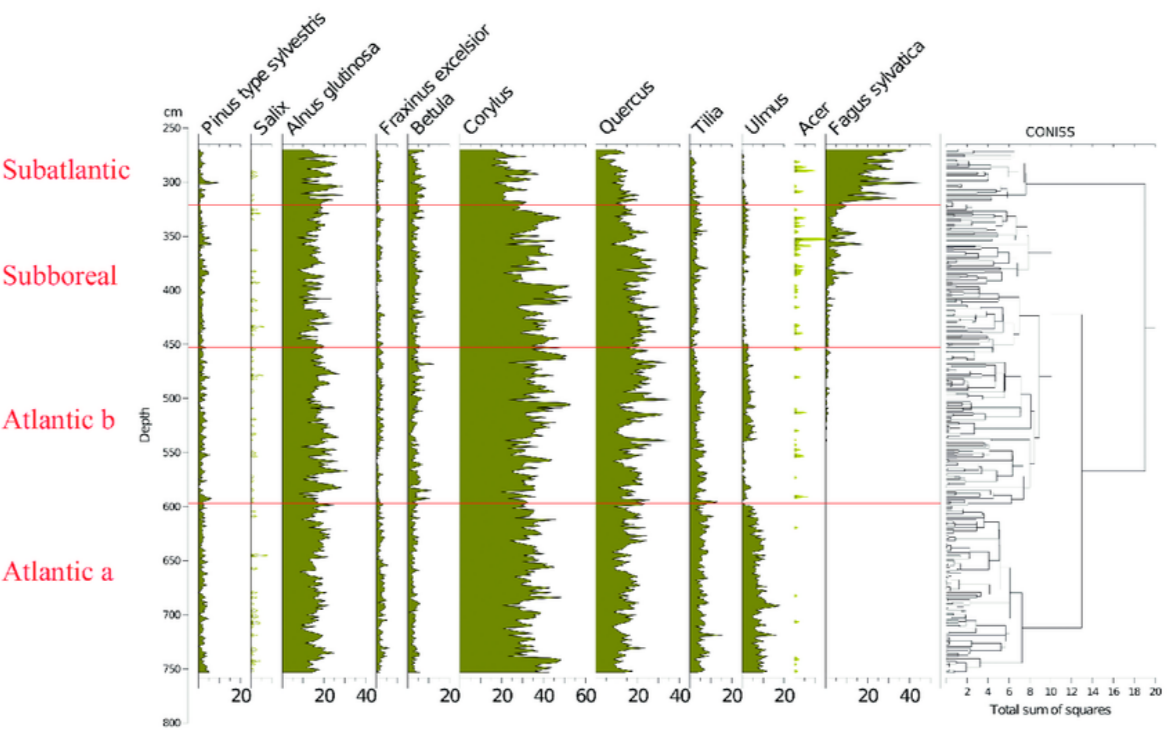
Why Pollen Is Useful
- Different plants grow in different climates.
- Pollen types reveal past vegetation and climate.
What Scientists Do
- Take peat cores.
- Identify pollen in each layer.
- Reconstruct past climate from plant types.
What Pollen Records Show
- Shifts between warm and cold periods.
- Vegetation changes linked to climate changes.
🌲 4. Dendrochronology (Tree-Ring Dating)
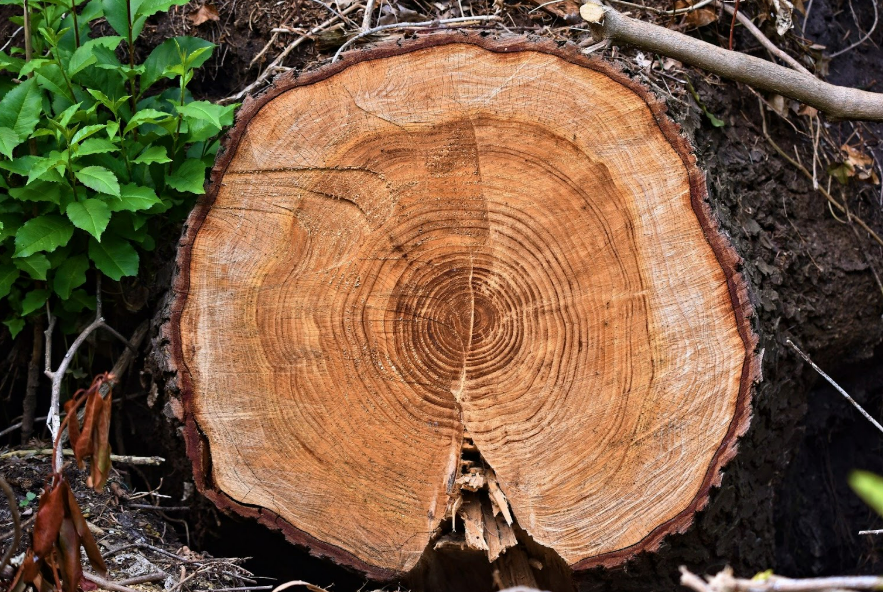

What Tree Rings Tell Us
- Wide rings = warm, wet years.
- Narrow rings = cold, dry years.
- Patterns can be traced back hundreds or thousands of years.
Why It Works
Trees respond directly to climate, so ring width reflects past conditions.
🔗 Correlation vs Causation
Correlation
Two things change together (e.g., CO₂ and temperature both rising).
Causation
One factor directly causes the other (e.g., increased CO₂ traps more heat).
In Climate Science
CO₂ and temperature show strong correlation, and greenhouse effect explains the causation.
📋 Summary Table
| Evidence Type | What It Measures | What It Shows | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO₂ Records (Ice Cores) | Past CO₂ levels | CO₂ rises with temperature | Strong causal link |
| Temperature Records | Long-term temperature change | Clear warming trend | Strong correlation |
| Pollen in Peat Bogs | Past vegetation | Climate shifts over time | Reliable indicator |
| Dendrochronology | Annual climate changes | Warm/wet and cold/dry years | High-detail record |
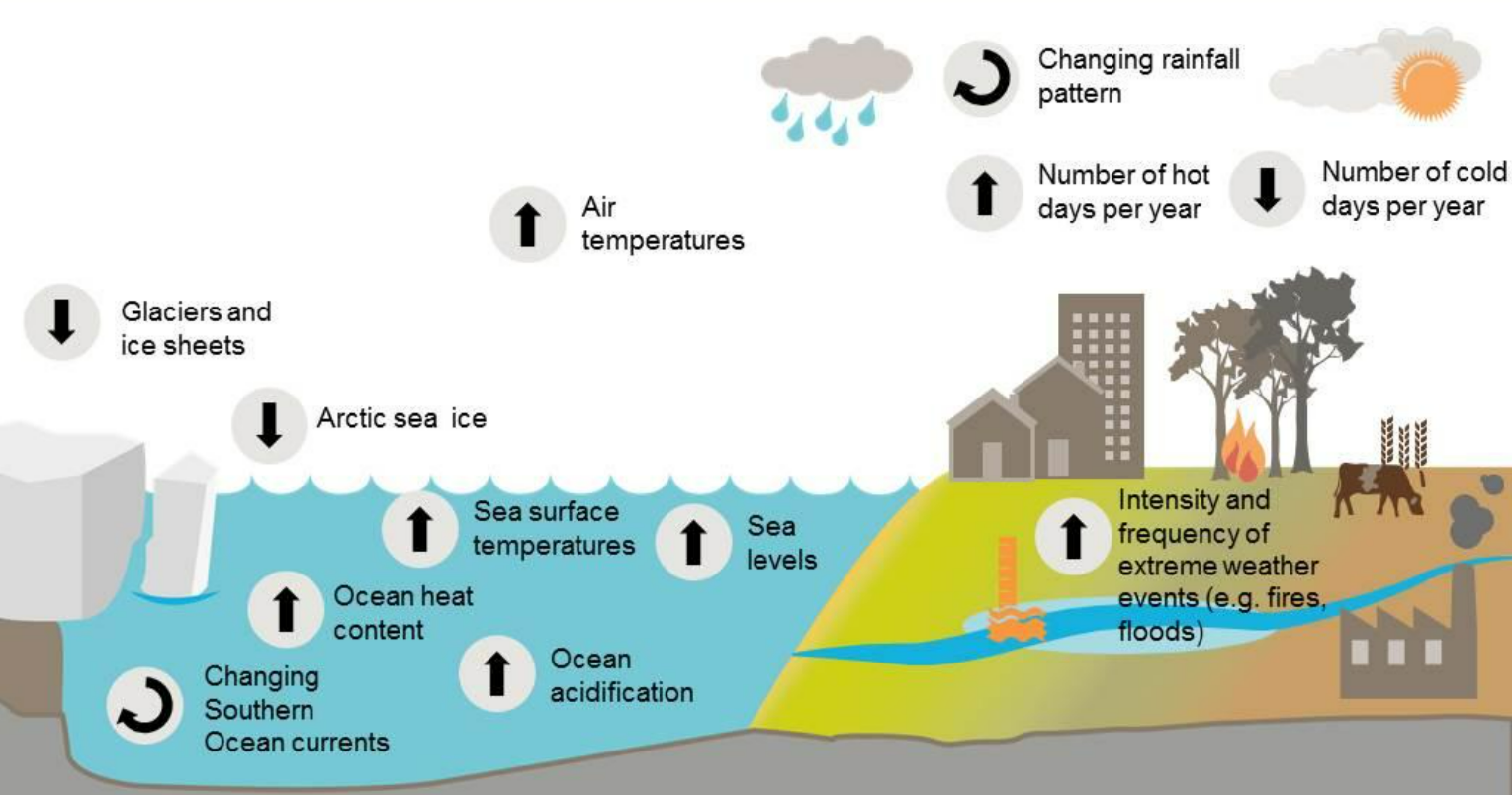
CO₂ levels and global temperature rise together.
Temperature records confirm long-term warming.
Pollen in peat bogs shows vegetation linked to climate.
Tree rings give yearly climate data.
Climate evidence shows both correlation and causation.
Anthropogenic Climate Change
🌱 Introduction
Climate change is speeding up mainly because of human activities. Humans have increased greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere, strengthening the greenhouse effect and warming the planet.
🔥 What Is Anthropogenic Climate Change
“Anthropogenic” means caused by humans. It refers to the rapid rise in global temperature due to actions like burning fossil fuels, deforestation and industrial activities.
☀️ The Greenhouse Effect
Natural Greenhouse Effect
- Sunlight enters the atmosphere.
- Earth absorbs some of it and warms up.
- Earth gives off heat as infrared radiation.
- Greenhouse gases trap a part of this heat, keeping the planet warm enough for life.
This natural process is essential.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect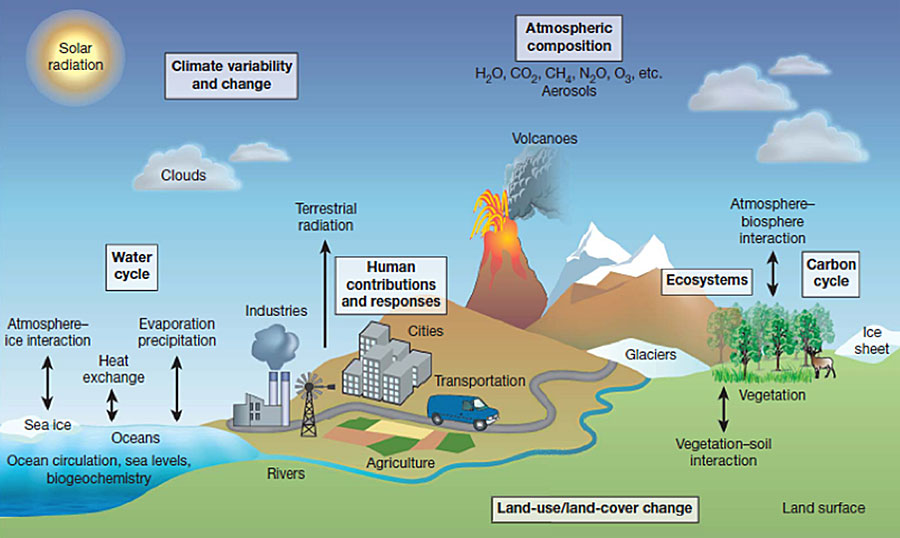
- Human activities increase greenhouse gas levels.
- More heat gets trapped.
- Average global temperature rises faster than normal.
🧪 Major Greenhouse Gases and Their Sources
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
- Main source: burning fossil fuels (coal, petrol, diesel, natural gas)
- Other sources: deforestation, cement production
- Biggest contributor to human-caused warming
2. Methane (CH₄)
- Released from rice fields, cattle farming, landfills and fossil fuel extraction
- Traps far more heat per molecule than CO₂
3. Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
- Comes from fertiliser use, car engines and industrial processes
- A very powerful heat-trapping gas
4. Water Vapour
- Not directly produced by humans
- But warming increases evaporation, which amplifies climate change
5. CFCs and Other Industrial Gases
- Released from old refrigerators, aerosol cans and industries
- Extremely strong greenhouse gases that also damage the ozone layer
🔥 Main Human Activities Causing Climate Change
1. Burning Fossil Fuels
- Electricity generation
- Transport
- Factories
- Produces massive amounts of CO₂
2. Deforestation
- Fewer trees means less CO₂ absorbed
- Burning forests releases more CO₂
3. Agriculture
- Cattle emit methane
- Rice fields release methane
- Fertilisers release nitrous oxide
4. Industry
- Cement production releases CO₂
- Chemical industries release strong greenhouse gases
5. Waste Management
- Landfills release methane as waste decomposes
🌡 How These Gases Cause Warming
- More greenhouse gases enter the atmosphere.
- More heat from Earth gets trapped.
- Less heat escapes into space.
- Global temperature rises.
- Climate patterns change (storms, melting ice, droughts).
This is a causal relationship, not just a correlation.
📋 Summary Table
| Greenhouse Gas | Major Human Source | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| CO₂ | Burning fuels, deforestation | Strong warming, long-lasting |
| CH₄ | Cattle, rice fields, landfills | Very strong heat trapping |
| N₂O | Fertilisers, engines | Potent greenhouse gas |
| CFCs | Refrigerants, aerosols | Extremely strong, also ozone damage |
Anthropogenic climate change means human-driven warming.
Greenhouse effect is natural but humans have strengthened it.
Fossil fuel burning is the biggest source of CO₂.
Agriculture releases methane and nitrous oxide.
More greenhouse gases → more heat trapped → rapid global warming.
