Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.18 Carbon Cycle & Environmental Management- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.18 Carbon Cycle & Environmental Management- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.18 Carbon Cycle & Environmental Management- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.18 understand how knowledge of the carbon cycle can be applied to methods to reduce atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide
Applying Carbon Cycle Knowledge to Reduce Atmospheric CO₂
🌱 Introduction
The carbon cycle explains how carbon moves between the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans and the ground. By understanding where carbon is stored and how it flows, we can design methods that remove CO₂ from the air or stop excess CO₂ from being released.
🌿 Key Points from the Carbon Cycle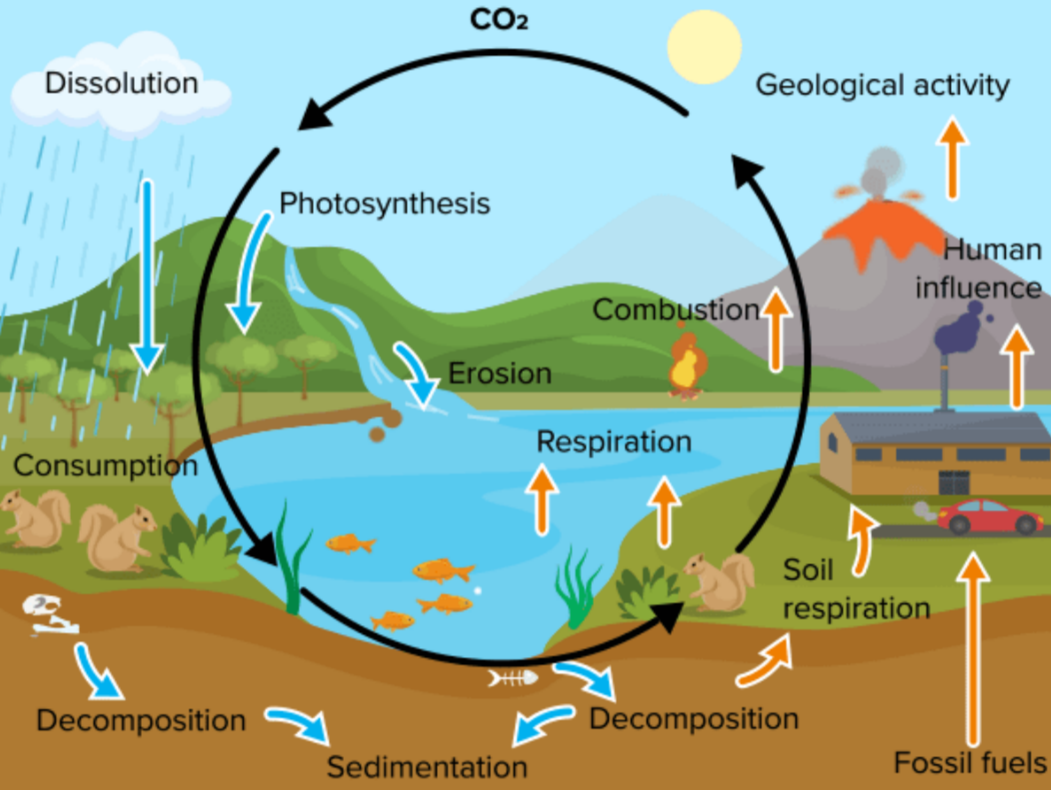
To reduce CO₂, we focus on:
- Increasing carbon sinks (places that absorb CO₂)
- Decreasing carbon sources (activities that release CO₂)
Major natural sinks: forests, oceans, soil, peat.
Major human sources: fossil fuel burning, deforestation.
🌳 1. Reforestation and Afforestation
Trees absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis. More trees = stronger carbon sink.
How it helps
- Removes CO₂ from the air and stores it as biomass.
- Restores natural carbon storage that was lost through deforestation.
Why it works (carbon cycle link)
Photosynthesis drives carbon from atmosphere → plants.
🌾 2. Protecting and Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems
Some ecosystems store large amounts of carbon for long periods.
Examples
- Peat bogs
- Mangroves
- Wetlands
- Seagrass meadows
How it helps
- Prevents stored carbon from being released.
- Maintains long-term carbon sinks in soil and plants.
Carbon cycle connection
Stops respiration and decay from releasing CO₂ by keeping these habitats intact.
🔥 3. Reducing Fossil Fuel Use
Burning coal, oil and gas converts long-term geological carbon into atmospheric CO₂.
Methods
- Switching to renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro)
- Improving energy efficiency
- Using electric transport
- Reducing industrial emissions
Carbon cycle connection
Prevents combustion from adding extra CO₂ to the atmosphere.
🧪 4. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
A technological approach.
How it works
- CO₂ from power plants and factories is captured before release.
- Compressed and stored underground in old oil/gas reservoirs.
Carbon cycle connection
Creates an artificial carbon sink, similar to long-term geological storage.
🌊 5. Ocean-Based Solutions
The ocean naturally absorbs large amounts of CO₂.
Methods
- Restoring marine vegetation (kelp forests, seagrass)
- Reducing pollution that harms these sinks
- Research into enhancing natural ocean uptake (still experimental)
Carbon cycle connection
Strengthens the ocean uptake pathway of CO₂.
🚜 6. Improving Agricultural and Soil Management
Healthy soil stores carbon in organic matter.
Methods
- No-till farming
- Cover crops
- Adding compost and organic material
- Reducing overgrazing
Carbon cycle connection
Carbon is held in soil instead of returning to the atmosphere through decay.
🧮 7. Reducing Waste and Increasing Recycling
Less waste means less decomposition and combustion.
How it helps
- Methane emissions from landfills decrease
- Lower energy demand reduces fossil fuel use
Carbon cycle connection
Prevents excess CO₂/CH₄ release from decomposition and combustion.
📋 Summary Table
| Method | How It Reduces CO₂ | Carbon Cycle Link |
|---|---|---|
| Reforestation | More CO₂ absorbed | Photosynthesis increases |
| Protecting peat/wetlands | Prevents stored carbon release | Stops decomposition releasing CO₂ |
| Reducing fossil fuels | Cuts major CO₂ sources | Less combustion |
| Carbon capture and storage | Stores CO₂ underground | Artificial long-term storage |
| Ocean ecosystem restoration | More CO₂ absorbed by oceans | Strengthens ocean sink |
| Soil carbon management | CO₂ stored in soil | Increases soil carbon pool |
| Waste reduction | Less decay and burning | Fewer emissions from biomass |
Knowledge of the carbon cycle helps identify where carbon comes from and where it can be stored.
Solutions focus on increasing sinks (forests, soil, oceans) and reducing sources (fossil fuels, waste, deforestation).
Reforestation and soil management remove CO₂ naturally.
Cutting fossil fuels and applying CCS prevent extra CO₂ from entering the air.
Protecting carbon-rich ecosystems stops huge releases from land and water.
