Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.19 Models for Predicting Climate Change- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.19 Models for Predicting Climate Change- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.19 Models for Predicting Climate Change- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.19 (i) understand that data can be extrapolated to make predictions and that these are used in models of future climate change
(ii) understand that models for climate change have limitations
Using Data to Predict Future Climate Change
🌱 Introduction
Scientists study climate patterns using data collected over years. From this data, they create predictions using a method called extrapolation and build climate models. These models help us understand future temperature rise, sea-level change and extreme weather but they are not perfect.
📊 1. Extrapolation for Climate Predictions
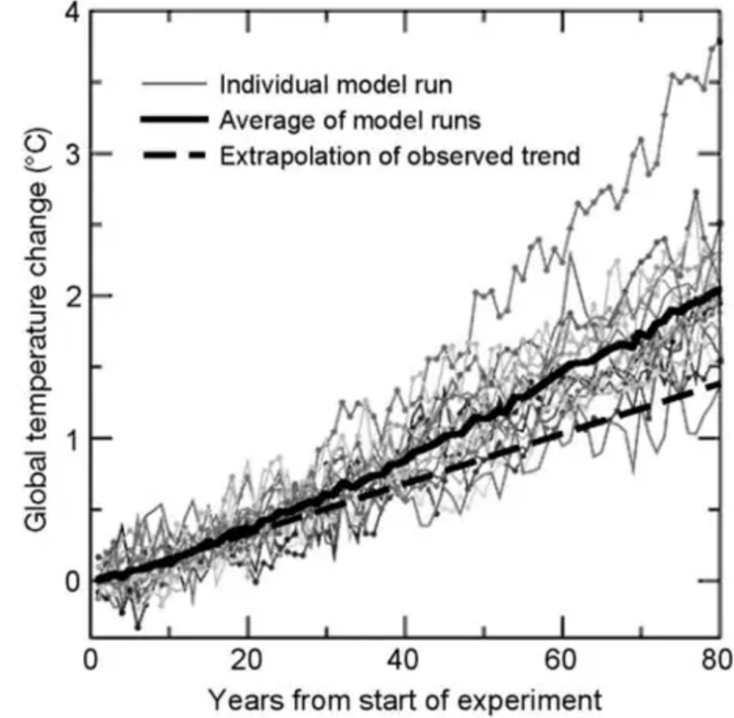
What is extrapolation?
- It means extending a trend into the future based on past data.
- If CO₂ levels or temperatures have been rising, scientists use that pattern to predict future values.
Why it works
- Many climate factors show steady trends over long periods.
- These trends help build mathematical predictions.
How it’s used in climate studies
- Predicting future global temperature rise.
- Forecasting sea-level changes.
- Estimating future CO₂ concentrations.
- Predicting changes in rainfall patterns, storms or drought risks.
Memory Trick
“Past pattern → future forecast”
🖥️ 2. Climate Models and Their Use
What are climate models?
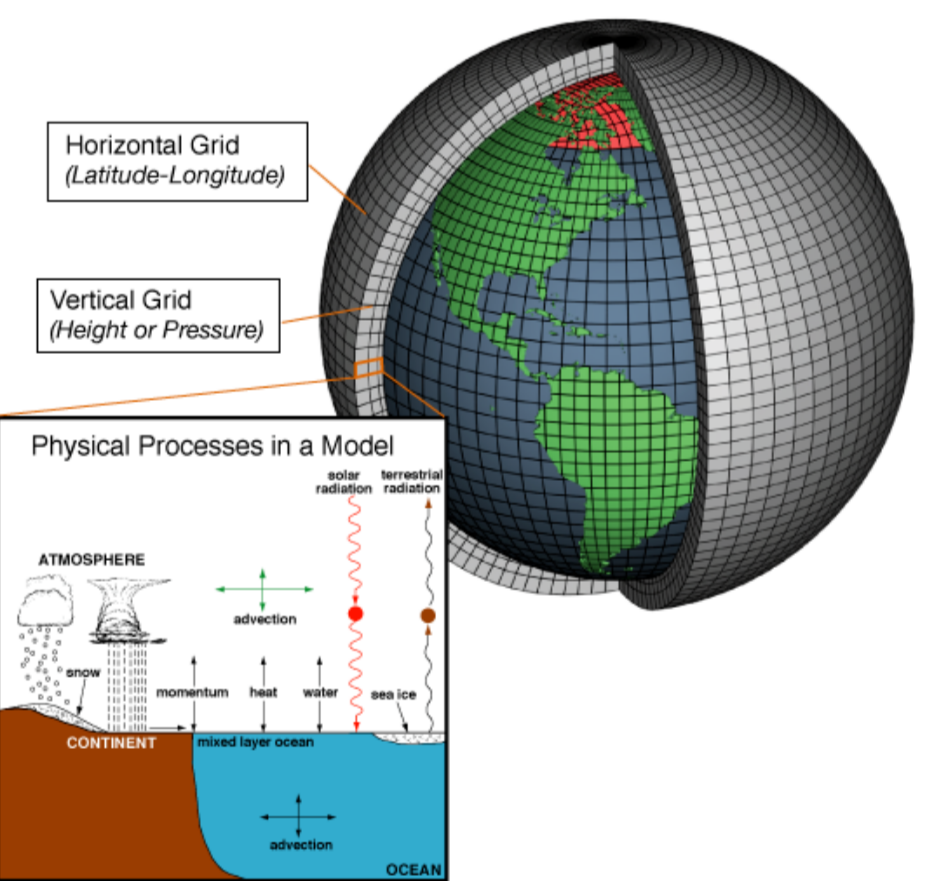
They are computer-based simulations that use real data (temperature, CO₂, ice cover, wind patterns etc.) to predict future climate conditions.
What they include
- Greenhouse gas levels
- Ocean currents
- Solar radiation
- Land and ice surface changes
- Atmosphere interactions
What they help us with
- Predicting warming rates
- Planning for extreme weather
- Understanding long-term climate consequences
- Helping governments make environmental policies
⚠️ 3. Limitations of Climate Models
Climate models are powerful, but not perfect. Here’s why:
1. Climate is extremely complex
- Too many interacting factors (oceans, atmosphere, clouds, ice).
- Even small errors can grow over time.
2. Incomplete or uncertain data
- Past climate records may be limited.
- Some regions have poor long-term data.
3. Future human behaviour is unpredictable
- Future emissions depend on future choices.
- Models must assume scenarios that may or may not happen.
4. Small-scale events are hard to model
- Local storms, cloud formation and volcanic eruptions are difficult to predict accurately.
Memory Trick
“Models guide, not guarantee”
📊 Summary Table
| Concept | Key Idea | Why Important |
|---|---|---|
| Extrapolation | Extending past trends into future predictions | Helps forecast temperature rise, CO₂ levels |
| Climate models | Computer simulations using climate data | Used for climate planning and risk analysis |
| Limitations | Incomplete data, complex systems, uncertain future emissions | Means predictions are estimates, not exact |
✔ Extrapolation uses past trends to predict future climate
✔ Climate models combine huge data sets to simulate future conditions
✔ Models help forecast warming, weather patterns and sea-level rise
✔ Limitations: complex climate, uncertain data, unpredictable human actions
✔ Remember: models suggest possibilities, not precise outcomes
