Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.20 How Climate Change Affects Species- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.20 How Climate Change Affects Species- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.20 How Climate Change Affects Species- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.20 understand the effects of climate change (changing rainfall patterns and changes in seasonal cycles) on plants and animals (distribution of species, development and lifecycles)
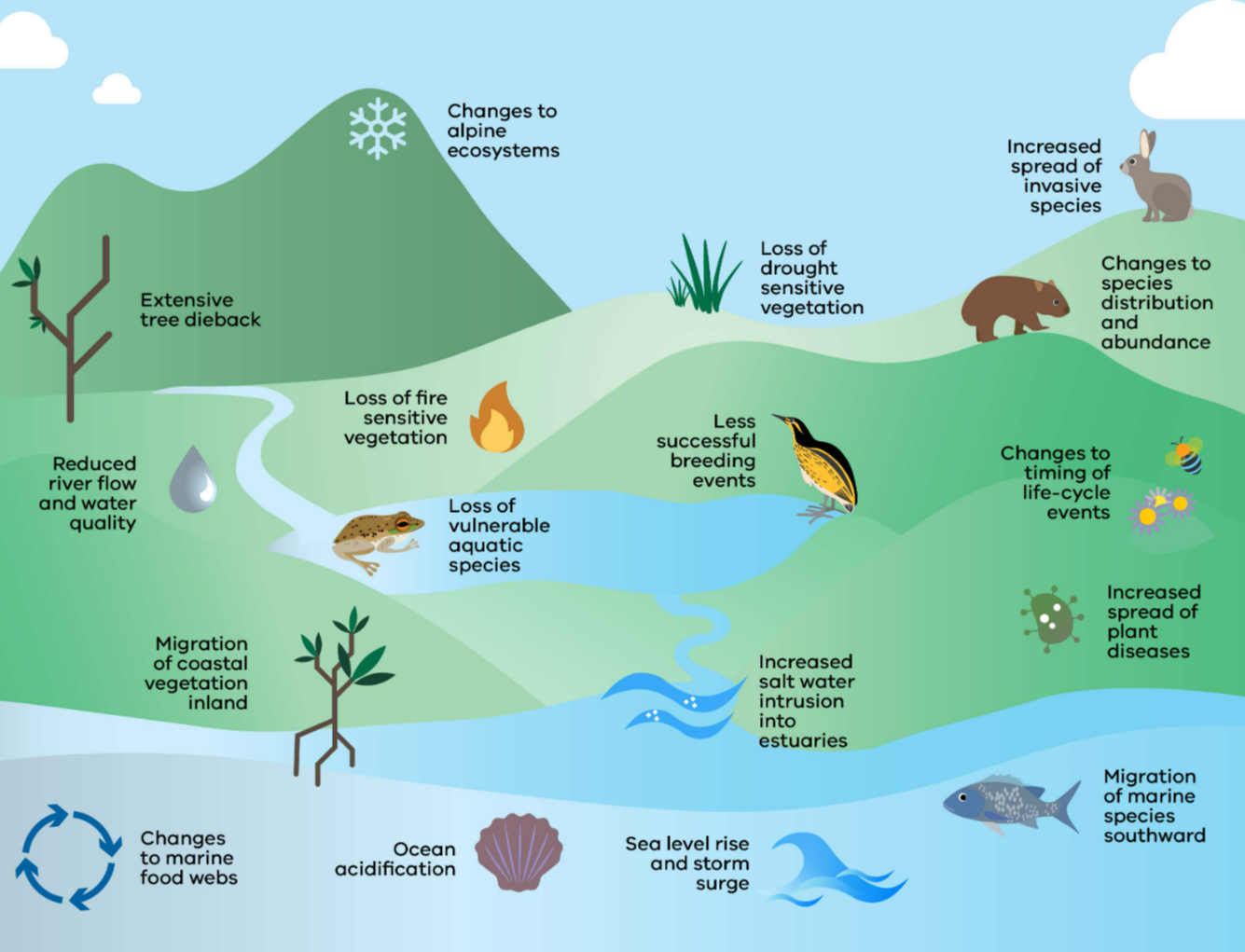
Effects of Climate Change on Plants and Animals
🌱 Introduction
Climate change is not just about rising temperatures. Two major changes that directly impact living organisms are:
- Altered rainfall patterns
- Shifted seasonal cycles
These changes affect where organisms can live, how they grow, when they reproduce, and how long their life cycles last.
🌦️ Changing Rainfall Patterns
What happens when rainfall becomes irregular?
- Some areas get too much rain, causing floods.
- Others face drought due to too little rain.
- Rainfall becomes unpredictable, disrupting ecosystems.
Effects on Plants
- Water shortage reduces growth, photosynthesis, and seed formation.
 Overwatering or waterlogging can damage roots.
Overwatering or waterlogging can damage roots.- Drought-tolerant species may outcompete others, changing plant distribution.
- Flowering and fruiting may shift or fail entirely.
Effects on Animals
- Herbivores migrate to find food if plants decline.
- Water-dependent animals struggle during droughts.
- Breeding success may drop due to lack of food or nesting areas.
- Moisture-loving species (frogs, insects) shrink in population.
🍁 Changes in Seasonal Cycles
(Also called phenological shifts – timing of seasons changes)
Effects on Plants
- Earlier springs cause early flowering and leafing.
- Delay or mismatch between flowering and pollinator availability harms reproduction.
- Some plants may start complete life cycles earlier, others may shorten theirs.
Effects on Animals
- Birds may migrate earlier or later than usual.
- Insects may hatch earlier, creating timing mismatches with predators or host plants.
- Breeding seasons shift, which may reduce survival of young ones.
- Hibernation/winter dormancy periods get disturbed.
🗺️ Impact on Distribution of Species
- Species move towards poles or higher altitudes where temperatures suit them.
- Local species decline if they cannot adapt quickly.
- New species may enter an ecosystem, altering food chains.
- Some sensitive species face local extinction due to unsuitable climate.
Impact on Development and Life Cycles
- Temperature and season changes alter growth speed.
- Some organisms complete life cycles faster (e.g., insects).
- Some delay reproduction due to stressful conditions.
- Food availability in early life stages may drop, reducing survival rates.
Memory Trick:
“Climate changes timing, timing changes survival” Helps remember that life cycles depend heavily on seasonal timing.
📊 Summary Table
| Factor | Effects on Plants | Effects on Animals |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular rainfall | Reduced growth, failed flowering, shift in distribution | Migration, lower breeding success, population decline |
| Shifted seasons | Early flowering, mismatch with pollinators | Early/late migration, altered breeding, hibernation disturbances |
| Overall species distribution | Plants shift to cooler areas | Animals move towards poles or higher altitudes |
| Life cycle changes | Altered germination and flowering periods | Faster/slower development, survival issues |
Rainfall changes: droughts or floods affect plant growth and animal food availability
Season shifts: early springs cause mismatches in flowering, migration, breeding
Species distribution: many shift to poles or hills to survive
Life cycles: timing of growth, reproduction, and development gets disrupted
