Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.22 Core Practical 12: Effect of Temperature on Development- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.22 Core Practical 12: Effect of Temperature on Development- Study Notes- New syllabus
Edexcel A Level (IAL) Biology -5.22 Core Practical 12: Effect of Temperature on Development- Study Notes -Edexcel A level Biology – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- 5.22 Investigate the effects of temperature on the development of organisms (such as seedling growth rate or brine shrimp hatch rates), taking into account the ethical use of organisms.
CORE PRACTICAL 12
Investigating the Effect of Temperature on Development of Organisms
🌱 Introduction
Temperature influences the speed of biological reactions because all development depends on enzyme activity. In this practical, we study how changing temperature affects growth or hatching, using simple organisms like seeds or brine shrimp.
🎯 Aim
To investigate how different temperatures affect the rate of development in organisms.
🧪 Organisms You Can Use
Option 1: Seedlings
Measure how fast seedlings grow at different temperatures.
Option 2: Brine Shrimp (Artemia)
Measure what percentage of eggs hatch at different temperatures.
📌 Key Ideas Before the Experiment
- Temperature affects enzyme activity, so development speeds up to an optimum.
- Too low → slow growth or hatching.
- Too high → enzymes denature, reducing survival.
- Many biological rates follow Q10 (rate change for every +10°C).
🔧 Variables
Independent variable: Temperature (e.g., 10°C, 20°C, 30°C).
Dependent variable:
- Seedlings → increase in length or % germination
- Brine shrimp → % hatch
Control variables: light, water/soil quality, seed/egg number, oxygen supply, container type.
🔬 Method (Seedlings)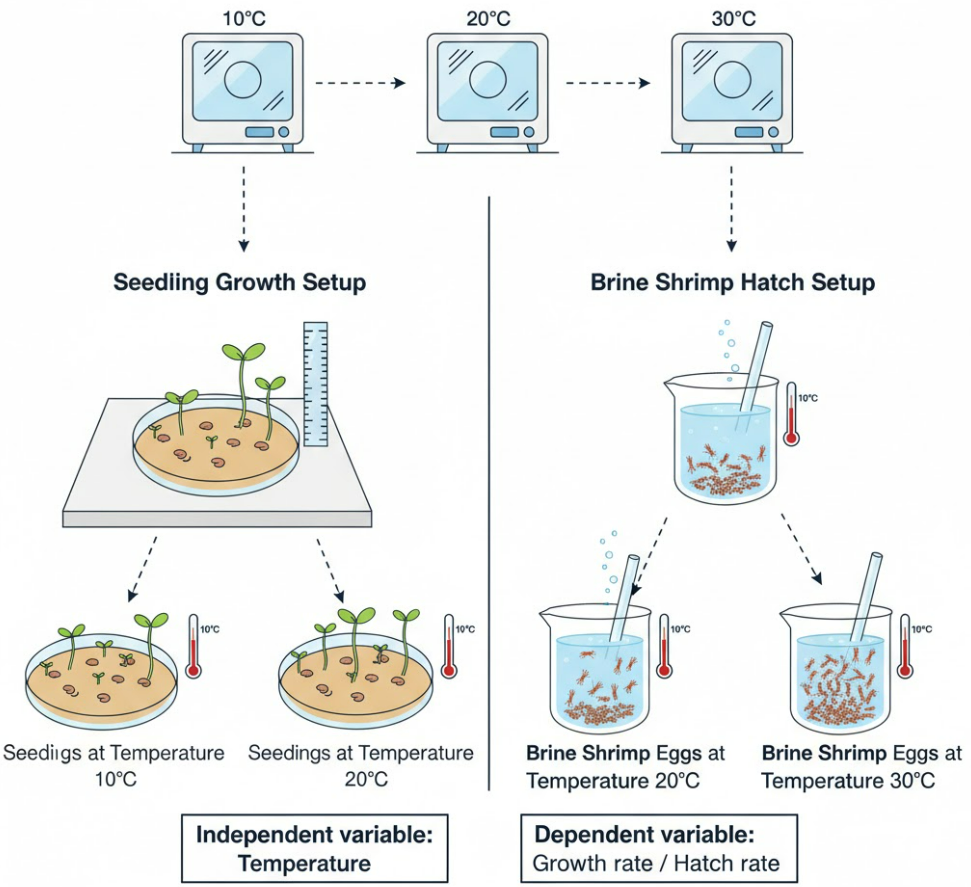
- Place equal numbers of seeds on moist filter paper in labelled dishes.
- Keep each dish at a different constant temperature.
- Measure stem length every 24 hours for several days.
- Calculate mean growth rate for each temperature.
🔬 Method (Brine Shrimp)
- Add equal numbers of brine shrimp eggs into identical tubes of seawater.
- Place tubes in different incubators.
- After a set time (e.g., 24 hours), count hatched vs unhatched eggs.
- Calculate % hatch rate for each temperature.
📊 Data Handling
- Repeat each temperature at least three times for reliability.
- Record mean, range, or standard deviation.
- Plot temperature on the x-axis and development rate or % hatch on the y-axis.
- Look for the optimum temperature.
🔢 Using Q10
Q10 helps describe how sensitive development is to temperature.
Formula:
\( Q_{10} = \frac{\text{Rate at }(T + 10^\circ\text{C})}{\text{Rate at }T} \)
Typical values around 2 show a doubling for every +10°C.
🌿 Expected Results
- Moderate temperatures → fastest growth or highest hatch.
- Low temperatures → slow metabolism, slow development.
- High temperatures → enzyme denaturation and reduced success.
🧭 Ethical Use of Organisms
- Use minimum numbers needed for reliable results.
- Keep conditions suitable (oxygen, water, temperature).
- Avoid unnecessary harm or stress.
- Handle and dispose of organisms responsibly (e.g., brine shrimp using mild bleach solution).
- Prefer simple organisms over complex ones.
📊 Summary Table
| Step | What You Measure | What It Shows |
|---|---|---|
| Set up organisms at different temperatures | Growth rate or % hatch | Effect of temperature |
| Record data daily | Length or hatch count | Development pattern |
| Calculate mean & plot graph | Trend line | Optimum temperature |
| Q10 calculation | Rate sensitivity | How strongly temperature affects development |
